filmov
tv
Reactsecurity attach a json web token in an axios request

Показать описание
okay, let's dive deep into react security, focusing on json web tokens (jwt) and how to securely attach them to axios requests within a react application. this will be a comprehensive guide, covering various aspects, best practices, and potential pitfalls.
**i. understanding the fundamentals**
* **what is a json web token (jwt)?**
* a jwt is a standard for securely transmitting information as a json object. it's commonly used for authentication and authorization. think of it like a digital passport or an id card.
* a jwt consists of three parts:
* **header:** contains metadata about the token, such as the algorithm used for signing (e.g., hs256, rs256) and the token type (`jwt`).
* **payload:** contains the claims (statements) about the user or entity. these claims can be registered claims (e.g., `iss`, `sub`, `aud`, `exp`), public claims (defined by the issuer), or private claims (custom claims specific to your application).
* **signature:** ensures the integrity of the token and verifies that it hasn't been tampered with. it's calculated by applying the specified algorithm to the encoded header, encoded payload, and a secret key (or a private key if using asymmetric encryption).
* **why use jwts?**
* **stateless authentication:** the server doesn't need to maintain session state for each user. the jwt contains all the information needed to authenticate the user on each request. this simplifies scaling.
* **scalability:** because authentication logic is stateless, it is easy to scale up the system to handle more concurrent users.
* **cross-domain authentication (cors):** jwts work well in scenarios where your api and client application are on different domains.
* **easy integration:** jwts can be generated and validated on different platforms.
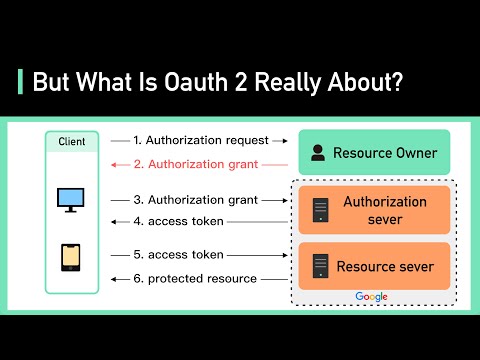
* **authentication vs. authorization**
* **authentication:** ver ...
#ReactSecurity #Axios #databaseerror
React
security
JSON Web Token
Axios
authentication
API requests
token handling
secure communication
frontend security
user authentication
state management
middleware
web application
REST API
client-side security
**i. understanding the fundamentals**
* **what is a json web token (jwt)?**
* a jwt is a standard for securely transmitting information as a json object. it's commonly used for authentication and authorization. think of it like a digital passport or an id card.
* a jwt consists of three parts:
* **header:** contains metadata about the token, such as the algorithm used for signing (e.g., hs256, rs256) and the token type (`jwt`).
* **payload:** contains the claims (statements) about the user or entity. these claims can be registered claims (e.g., `iss`, `sub`, `aud`, `exp`), public claims (defined by the issuer), or private claims (custom claims specific to your application).
* **signature:** ensures the integrity of the token and verifies that it hasn't been tampered with. it's calculated by applying the specified algorithm to the encoded header, encoded payload, and a secret key (or a private key if using asymmetric encryption).
* **why use jwts?**
* **stateless authentication:** the server doesn't need to maintain session state for each user. the jwt contains all the information needed to authenticate the user on each request. this simplifies scaling.
* **scalability:** because authentication logic is stateless, it is easy to scale up the system to handle more concurrent users.
* **cross-domain authentication (cors):** jwts work well in scenarios where your api and client application are on different domains.
* **easy integration:** jwts can be generated and validated on different platforms.
* **authentication vs. authorization**
* **authentication:** ver ...
#ReactSecurity #Axios #databaseerror
React
security
JSON Web Token
Axios
authentication
API requests
token handling
secure communication
frontend security
user authentication
state management
middleware
web application
REST API
client-side security
 0:05:40
0:05:40
 0:14:52
0:14:52
 0:10:07
0:10:07
 0:05:59
0:05:59
 0:10:50
0:10:50
 0:02:07
0:02:07
 0:05:07
0:05:07
 0:02:53
0:02:53
 0:04:32
0:04:32
 0:03:11
0:03:11
 0:03:14
0:03:14
 0:30:50
0:30:50
 0:04:39
0:04:39
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:00:48
0:00:48
 0:07:04
0:07:04
 0:00:55
0:00:55
 0:20:36
0:20:36
 0:39:33
0:39:33
 0:03:19
0:03:19
 0:52:03
0:52:03
 0:23:45
0:23:45
 0:07:42
0:07:42
 0:03:20
0:03:20