filmov
tv
What are Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) certificates?

Показать описание
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) certificates are a crucial component of online security. They enable secure communication between a client and a server, protecting sensitive data such as credit card numbers, login credentials, and personal information. In this essay, we will discuss what SSL certificates are, how they work, and why they are essential for online security.
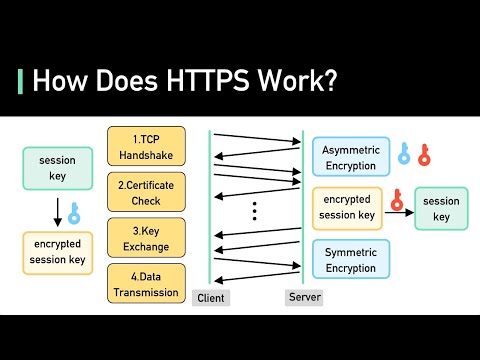
SSL certificates are digital certificates that authenticate the identity of a website and encrypt the data transmitted between the website and the user's browser. They are issued by trusted third-party Certificate Authorities (CAs) that verify the website owner's identity and the website's domain name. When a user visits a website with an SSL certificate, their browser initiates a secure connection to the website's server, which encrypts all data transmitted between the user's browser and the server.
SSL certificates use two keys to encrypt the data transmitted between the server and the user's browser: a public key and a private key. The public key is freely available to anyone who wants to communicate with the server, while the private key is kept secret by the server. When a user's browser initiates a secure connection to a website, it requests the website's public key, which the server sends back to the browser. The browser then encrypts all data transmitted to the server using the public key. The server, which holds the corresponding private key, can then decrypt the data.
SSL certificates are essential for online security for several reasons. First, they authenticate the identity of a website, ensuring that the user is communicating with the website they intended to visit and not an impostor. Second, they encrypt all data transmitted between the user's browser and the server, protecting sensitive information from eavesdropping and tampering. Third, they provide assurance that the website is trustworthy and has been vetted by a trusted third-party CA.
SSL certificates come in different types, with varying levels of validation and encryption strength. Domain Validated (DV) certificates are the most basic type and only validate that the website owner has control over the domain name. Organization Validated (OV) certificates provide additional validation of the website owner's identity and are suitable for businesses that require a higher level of trust. Extended Validation (EV) certificates are the most stringent type and provide the highest level of validation, requiring the website owner to undergo a rigorous vetting process.
In conclusion, SSL certificates are a crucial component of online security. They authenticate the identity of a website, encrypt all data transmitted between the user's browser and the server, and provide assurance that the website is trustworthy. SSL certificates come in different types, with varying levels of validation and encryption strength, and are issued by trusted third-party CAs. Without SSL certificates, online communication would be vulnerable to eavesdropping and tampering, compromising the security of sensitive information.
SSL certificates are digital certificates that authenticate the identity of a website and encrypt the data transmitted between the website and the user's browser. They are issued by trusted third-party Certificate Authorities (CAs) that verify the website owner's identity and the website's domain name. When a user visits a website with an SSL certificate, their browser initiates a secure connection to the website's server, which encrypts all data transmitted between the user's browser and the server.
SSL certificates use two keys to encrypt the data transmitted between the server and the user's browser: a public key and a private key. The public key is freely available to anyone who wants to communicate with the server, while the private key is kept secret by the server. When a user's browser initiates a secure connection to a website, it requests the website's public key, which the server sends back to the browser. The browser then encrypts all data transmitted to the server using the public key. The server, which holds the corresponding private key, can then decrypt the data.
SSL certificates are essential for online security for several reasons. First, they authenticate the identity of a website, ensuring that the user is communicating with the website they intended to visit and not an impostor. Second, they encrypt all data transmitted between the user's browser and the server, protecting sensitive information from eavesdropping and tampering. Third, they provide assurance that the website is trustworthy and has been vetted by a trusted third-party CA.
SSL certificates come in different types, with varying levels of validation and encryption strength. Domain Validated (DV) certificates are the most basic type and only validate that the website owner has control over the domain name. Organization Validated (OV) certificates provide additional validation of the website owner's identity and are suitable for businesses that require a higher level of trust. Extended Validation (EV) certificates are the most stringent type and provide the highest level of validation, requiring the website owner to undergo a rigorous vetting process.
In conclusion, SSL certificates are a crucial component of online security. They authenticate the identity of a website, encrypt all data transmitted between the user's browser and the server, and provide assurance that the website is trustworthy. SSL certificates come in different types, with varying levels of validation and encryption strength, and are issued by trusted third-party CAs. Without SSL certificates, online communication would be vulnerable to eavesdropping and tampering, compromising the security of sensitive information.
 0:03:28
0:03:28
 0:06:31
0:06:31
 0:01:47
0:01:47
 0:07:38
0:07:38
 0:05:54
0:05:54
 0:02:57
0:02:57
 0:08:44
0:08:44
 0:01:07
0:01:07
 0:01:30
0:01:30
 0:09:56
0:09:56
 0:15:33
0:15:33
 0:04:46
0:04:46
 0:05:04
0:05:04
 0:03:16
0:03:16
 0:19:03
0:19:03
 0:00:36
0:00:36
 0:02:48
0:02:48
 0:01:40
0:01:40
 0:02:54
0:02:54
 0:14:34
0:14:34
 0:02:32
0:02:32
 0:02:45
0:02:45
 0:11:14
0:11:14
 0:00:39
0:00:39