filmov
tv
UPPER CERVICAL SPINE STRUCTURE AND LIGAMENTS (BIOMECHANICS OF SPINE)Physiotherapy Tutorial

Показать описание
UPPER CERVICAL SPINE STRUCTURE AND LIGAMENTS (BIOMECHANIS OF SPINE)Physiotherapy Tutorial
summary of the video with the time for reference:
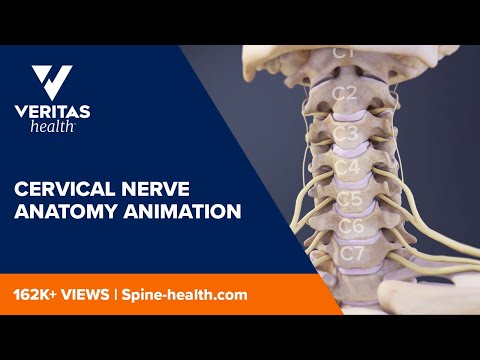
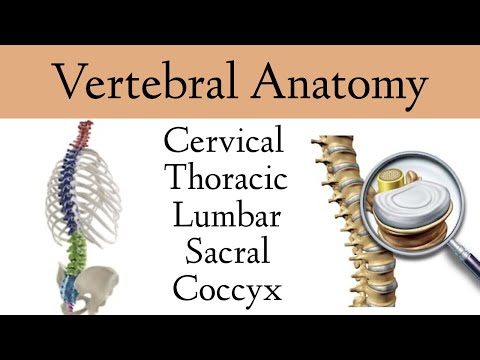
1.Cervical Spine
-Upper cervical region (c1, c2, occiput)
-Lower cervical region (c3 to c7)
-Typical and Atypical vertebra (c1, c2, c7)
2.Atlas
-Cradles occiput and transfers forces
-no body
-foramen at transverse process for vertebral artery
-Superior facet which are large and concave and kidney shaped which accommodates condyles of occiput
-Inferior facet articulates with axis and it is slightly convex
-Facet on the internal surface that articulates with the Dens of axis
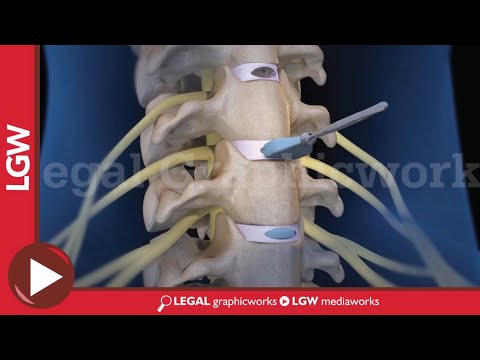
3.Articulation
-Atlanto-occipital articulation(2)
-Superior facet which are large and concave and kidney shaped which accommodates condyles of occiput
-Synovial type of articulation and has miniscoid and fibrocartilagenous structures
-Atlanto axial articulation (3)
-Median atlanto axial joint
-2 lateral joints between atlas and axis
-Axis provides rotation
3.Transverse Ligament
-Attached across the ring of atlas
-Dens present anteriorly
-Spinal cord present posteriorly
-Superiorly and inferiorly ligament is attached
-Together they form atlantal cruciform ligament
- C1 and C2 stability is provided by the transvers ligament assisted by superior and inferior ligament
-Transverse ligament is very strong and sometimes bone breaks before the ligamnet
-In downs syndrome and RA there can be laxity of this ligament which can cause C1-C2 instability
4.Alar ligament
-Attaches axis to Atlas through Dens
-Ligament is 1cm long and pencil width thickness
-Prevents C1 -C2 distraction
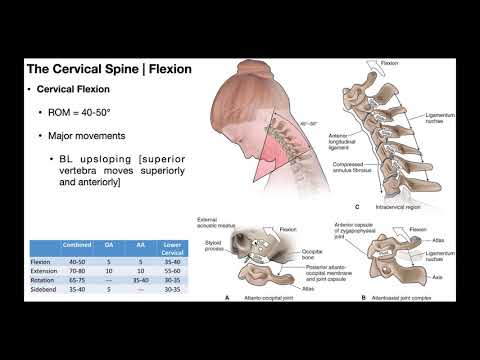
-It becomes taut in flexion and axial rotation
5.Ligamentum Neche
-Very thick
-Attached to external occipital protuberance and foramen magnum and C7 spinous process
-Dorsal raphe- narrow strips of collagenous tissue interlacing the tendons of upper traps and rhomboid minor
-Ventral midline septum and very close to inter spinous ligament and resists flexion at the spine
6.Longitudinal Ligament
-Ligamentum flavum-Posterior Atlanto occipital and Atlanto axial membrane-less elastic
-Anterior Atlanto occipital and Atlanto axial membrane -strong and thick and continuation of Anterior longitudinal ligament
-Tectorial membrane-Posterior longitudinal ligament
-Close relation with atlas, axis, dens and atlantal cruciform ligament
#biomechanicsofspine
#spinebiomechanics
#vertebralcolumnbiomechanics
summary of the video with the time for reference:
1.Cervical Spine
-Upper cervical region (c1, c2, occiput)
-Lower cervical region (c3 to c7)
-Typical and Atypical vertebra (c1, c2, c7)
2.Atlas
-Cradles occiput and transfers forces
-no body
-foramen at transverse process for vertebral artery
-Superior facet which are large and concave and kidney shaped which accommodates condyles of occiput
-Inferior facet articulates with axis and it is slightly convex
-Facet on the internal surface that articulates with the Dens of axis
3.Articulation
-Atlanto-occipital articulation(2)
-Superior facet which are large and concave and kidney shaped which accommodates condyles of occiput
-Synovial type of articulation and has miniscoid and fibrocartilagenous structures
-Atlanto axial articulation (3)
-Median atlanto axial joint
-2 lateral joints between atlas and axis
-Axis provides rotation
3.Transverse Ligament
-Attached across the ring of atlas
-Dens present anteriorly
-Spinal cord present posteriorly
-Superiorly and inferiorly ligament is attached
-Together they form atlantal cruciform ligament
- C1 and C2 stability is provided by the transvers ligament assisted by superior and inferior ligament
-Transverse ligament is very strong and sometimes bone breaks before the ligamnet
-In downs syndrome and RA there can be laxity of this ligament which can cause C1-C2 instability
4.Alar ligament
-Attaches axis to Atlas through Dens
-Ligament is 1cm long and pencil width thickness
-Prevents C1 -C2 distraction
-It becomes taut in flexion and axial rotation
5.Ligamentum Neche
-Very thick
-Attached to external occipital protuberance and foramen magnum and C7 spinous process
-Dorsal raphe- narrow strips of collagenous tissue interlacing the tendons of upper traps and rhomboid minor
-Ventral midline septum and very close to inter spinous ligament and resists flexion at the spine
6.Longitudinal Ligament
-Ligamentum flavum-Posterior Atlanto occipital and Atlanto axial membrane-less elastic
-Anterior Atlanto occipital and Atlanto axial membrane -strong and thick and continuation of Anterior longitudinal ligament
-Tectorial membrane-Posterior longitudinal ligament
-Close relation with atlas, axis, dens and atlantal cruciform ligament
#biomechanicsofspine
#spinebiomechanics
#vertebralcolumnbiomechanics
Комментарии
 0:21:53
0:21:53
 0:07:13
0:07:13
 0:02:03
0:02:03
 0:17:11
0:17:11
 0:04:42
0:04:42
 0:58:01
0:58:01
 0:15:27
0:15:27
 0:28:12
0:28:12
 1:02:53
1:02:53
 0:18:09
0:18:09
 0:01:43
0:01:43
 0:02:37
0:02:37
 0:06:56
0:06:56
 0:02:41
0:02:41
 0:02:59
0:02:59
 0:00:31
0:00:31
 0:56:42
0:56:42
 0:16:15
0:16:15
 0:03:18
0:03:18
 0:42:05
0:42:05
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:03:51
0:03:51
 0:07:06
0:07:06
 0:08:00
0:08:00