filmov
tv
Types of Rainfall in Kannada |Class 11 NCERT Geography | Kannada Geography class #geographyclass11

Показать описание
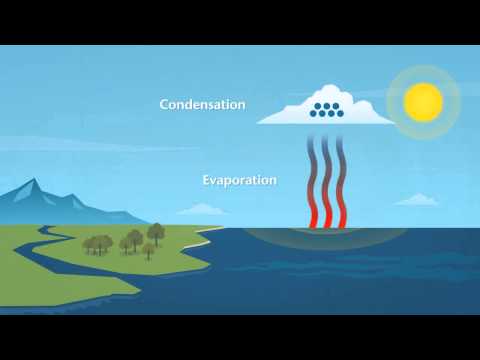
Rainfall can be classified into three main types based on the mechanisms that cause the air to rise, cool, and condense into precipitation:
1. Orographic Rainfall (Relief Rainfall):
Mechanism: Occurs when moist air is forced to rise over a mountain or hill.
Process: As the air ascends, it cools and condenses to form clouds, resulting in rainfall on the windward side of the mountain. The leeward side, often called the "rain shadow," receives much less rainfall.
Example: Western Ghats in India receive heavy rainfall due to this type.
2.Convectional Rainfall:
Mechanism: Occurs due to the intense heating of the earth's surface, usually in tropical regions.
Process: The hot ground heats the air above it, causing it to rise rapidly. As it rises, it cools, condenses, and falls as rain, often accompanied by thunderstorms.
Example: Common in equatorial regions, such as the Amazon Basin.
3. Cyclonic (Frontal) Rainfall:
Mechanism: Occurs when warm and cold air masses meet, creating a front.
Process: The warm air is forced to rise over the cold air, leading to cooling and condensation, resulting in rainfall. This is common in temperate regions where cyclones or fronts frequently form.
Example: Rainfall associated with tropical cyclones or depressions.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1. ಓರೋಗ್ರಾಫಿಕ್ ಮಳೆ (ಪರಿಹಾರ ಮಳೆ):
ಯಾಂತ್ರಿಕತೆ: ತೇವಾಂಶವುಳ್ಳ ಗಾಳಿಯು ಪರ್ವತ ಅಥವಾ ಬೆಟ್ಟದ ಮೇಲೆ ಬಲವಂತವಾಗಿ ಏರಿದಾಗ ಸಂಭವಿಸುತ್ತದೆ.
ಪ್ರಕ್ರಿಯೆ: ಗಾಳಿಯು ಏರುತ್ತಿದ್ದಂತೆ, ಅದು ತಂಪಾಗುತ್ತದೆ ಮತ್ತು ಮೋಡಗಳನ್ನು ರೂಪಿಸಲು ಘನೀಕರಣಗೊಳ್ಳುತ್ತದೆ, ಇದರ ಪರಿಣಾಮವಾಗಿ ಪರ್ವತದ ಗಾಳಿಯ ಭಾಗದಲ್ಲಿ ಮಳೆಯಾಗುತ್ತದೆ. ಸಾಮಾನ್ಯವಾಗಿ "ಮಳೆ ನೆರಳು" ಎಂದು ಕರೆಯಲ್ಪಡುವ ಲೆವಾರ್ಡ್ ಭಾಗವು ಕಡಿಮೆ ಮಳೆಯನ್ನು ಪಡೆಯುತ್ತದೆ.
ಉದಾಹರಣೆ: ಭಾರತದಲ್ಲಿನ ಪಶ್ಚಿಮ ಘಟ್ಟಗಳು ಈ ಪ್ರಕಾರದ ಕಾರಣದಿಂದಾಗಿ ಭಾರೀ ಮಳೆಯನ್ನು ಪಡೆಯುತ್ತವೆ.
2. ಸಂವಹನ ಮಳೆ:
ಯಾಂತ್ರಿಕ ವ್ಯವಸ್ಥೆ: ಸಾಮಾನ್ಯವಾಗಿ ಉಷ್ಣವಲಯದ ಪ್ರದೇಶಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಭೂಮಿಯ ಮೇಲ್ಮೈಯ ತೀವ್ರ ತಾಪದಿಂದಾಗಿ ಸಂಭವಿಸುತ್ತದೆ.
ಪ್ರಕ್ರಿಯೆ: ಬಿಸಿ ನೆಲವು ಅದರ ಮೇಲಿರುವ ಗಾಳಿಯನ್ನು ಬಿಸಿಮಾಡುತ್ತದೆ, ಇದರಿಂದಾಗಿ ಅದು ವೇಗವಾಗಿ ಏರುತ್ತದೆ. ಅದು ಏರುತ್ತಿದ್ದಂತೆ, ಅದು ತಣ್ಣಗಾಗುತ್ತದೆ, ಘನೀಕರಿಸುತ್ತದೆ ಮತ್ತು ಮಳೆಯಾಗಿ ಬೀಳುತ್ತದೆ, ಆಗಾಗ್ಗೆ ಗುಡುಗು ಸಹಿತ ಮಳೆಯಾಗುತ್ತದೆ.
ಉದಾಹರಣೆ: ಅಮೆಜಾನ್ ಜಲಾನಯನ ಪ್ರದೇಶದಂತಹ ಸಮಭಾಜಕ ಪ್ರದೇಶಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಸಾಮಾನ್ಯವಾಗಿದೆ.
3. ಸೈಕ್ಲೋನಿಕ್ (ಮುಂಭಾಗ) ಮಳೆ:
ಯಾಂತ್ರಿಕತೆ: ಬೆಚ್ಚಗಿನ ಮತ್ತು ತಣ್ಣನೆಯ ಗಾಳಿಯ ದ್ರವ್ಯರಾಶಿಗಳು ಭೇಟಿಯಾದಾಗ ಸಂಭವಿಸುತ್ತದೆ, ಮುಂಭಾಗವನ್ನು ರಚಿಸುತ್ತದೆ.
ಪ್ರಕ್ರಿಯೆ: ತಂಪಾದ ಗಾಳಿಯ ಮೇಲೆ ಬೆಚ್ಚಗಿನ ಗಾಳಿಯು ಬಲವಂತವಾಗಿ ಏರುತ್ತದೆ, ಇದು ತಂಪಾಗುವಿಕೆ ಮತ್ತು ಘನೀಕರಣಕ್ಕೆ ಕಾರಣವಾಗುತ್ತದೆ, ಇದರಿಂದಾಗಿ ಮಳೆಯಾಗುತ್ತದೆ. ಚಂಡಮಾರುತಗಳು ಅಥವಾ ಮುಂಭಾಗಗಳು ಆಗಾಗ್ಗೆ ರೂಪುಗೊಳ್ಳುವ ಸಮಶೀತೋಷ್ಣ ಪ್ರದೇಶಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಇದು ಸಾಮಾನ್ಯವಾಗಿದೆ.
ಉದಾಹರಣೆ: ಉಷ್ಣವಲಯದ ಚಂಡಮಾರುತಗಳು
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
upsc kannada classes
geography kannada class
geography class in kannada
geography in kannada
00:00 Introduction
00:31 Convection Rainfall
05:00 Orographic Rainfall
10:04 Cyclonic Rainfall
1. Orographic Rainfall (Relief Rainfall):
Mechanism: Occurs when moist air is forced to rise over a mountain or hill.
Process: As the air ascends, it cools and condenses to form clouds, resulting in rainfall on the windward side of the mountain. The leeward side, often called the "rain shadow," receives much less rainfall.
Example: Western Ghats in India receive heavy rainfall due to this type.
2.Convectional Rainfall:
Mechanism: Occurs due to the intense heating of the earth's surface, usually in tropical regions.
Process: The hot ground heats the air above it, causing it to rise rapidly. As it rises, it cools, condenses, and falls as rain, often accompanied by thunderstorms.
Example: Common in equatorial regions, such as the Amazon Basin.
3. Cyclonic (Frontal) Rainfall:
Mechanism: Occurs when warm and cold air masses meet, creating a front.
Process: The warm air is forced to rise over the cold air, leading to cooling and condensation, resulting in rainfall. This is common in temperate regions where cyclones or fronts frequently form.
Example: Rainfall associated with tropical cyclones or depressions.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1. ಓರೋಗ್ರಾಫಿಕ್ ಮಳೆ (ಪರಿಹಾರ ಮಳೆ):
ಯಾಂತ್ರಿಕತೆ: ತೇವಾಂಶವುಳ್ಳ ಗಾಳಿಯು ಪರ್ವತ ಅಥವಾ ಬೆಟ್ಟದ ಮೇಲೆ ಬಲವಂತವಾಗಿ ಏರಿದಾಗ ಸಂಭವಿಸುತ್ತದೆ.
ಪ್ರಕ್ರಿಯೆ: ಗಾಳಿಯು ಏರುತ್ತಿದ್ದಂತೆ, ಅದು ತಂಪಾಗುತ್ತದೆ ಮತ್ತು ಮೋಡಗಳನ್ನು ರೂಪಿಸಲು ಘನೀಕರಣಗೊಳ್ಳುತ್ತದೆ, ಇದರ ಪರಿಣಾಮವಾಗಿ ಪರ್ವತದ ಗಾಳಿಯ ಭಾಗದಲ್ಲಿ ಮಳೆಯಾಗುತ್ತದೆ. ಸಾಮಾನ್ಯವಾಗಿ "ಮಳೆ ನೆರಳು" ಎಂದು ಕರೆಯಲ್ಪಡುವ ಲೆವಾರ್ಡ್ ಭಾಗವು ಕಡಿಮೆ ಮಳೆಯನ್ನು ಪಡೆಯುತ್ತದೆ.
ಉದಾಹರಣೆ: ಭಾರತದಲ್ಲಿನ ಪಶ್ಚಿಮ ಘಟ್ಟಗಳು ಈ ಪ್ರಕಾರದ ಕಾರಣದಿಂದಾಗಿ ಭಾರೀ ಮಳೆಯನ್ನು ಪಡೆಯುತ್ತವೆ.
2. ಸಂವಹನ ಮಳೆ:
ಯಾಂತ್ರಿಕ ವ್ಯವಸ್ಥೆ: ಸಾಮಾನ್ಯವಾಗಿ ಉಷ್ಣವಲಯದ ಪ್ರದೇಶಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಭೂಮಿಯ ಮೇಲ್ಮೈಯ ತೀವ್ರ ತಾಪದಿಂದಾಗಿ ಸಂಭವಿಸುತ್ತದೆ.
ಪ್ರಕ್ರಿಯೆ: ಬಿಸಿ ನೆಲವು ಅದರ ಮೇಲಿರುವ ಗಾಳಿಯನ್ನು ಬಿಸಿಮಾಡುತ್ತದೆ, ಇದರಿಂದಾಗಿ ಅದು ವೇಗವಾಗಿ ಏರುತ್ತದೆ. ಅದು ಏರುತ್ತಿದ್ದಂತೆ, ಅದು ತಣ್ಣಗಾಗುತ್ತದೆ, ಘನೀಕರಿಸುತ್ತದೆ ಮತ್ತು ಮಳೆಯಾಗಿ ಬೀಳುತ್ತದೆ, ಆಗಾಗ್ಗೆ ಗುಡುಗು ಸಹಿತ ಮಳೆಯಾಗುತ್ತದೆ.
ಉದಾಹರಣೆ: ಅಮೆಜಾನ್ ಜಲಾನಯನ ಪ್ರದೇಶದಂತಹ ಸಮಭಾಜಕ ಪ್ರದೇಶಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಸಾಮಾನ್ಯವಾಗಿದೆ.
3. ಸೈಕ್ಲೋನಿಕ್ (ಮುಂಭಾಗ) ಮಳೆ:
ಯಾಂತ್ರಿಕತೆ: ಬೆಚ್ಚಗಿನ ಮತ್ತು ತಣ್ಣನೆಯ ಗಾಳಿಯ ದ್ರವ್ಯರಾಶಿಗಳು ಭೇಟಿಯಾದಾಗ ಸಂಭವಿಸುತ್ತದೆ, ಮುಂಭಾಗವನ್ನು ರಚಿಸುತ್ತದೆ.
ಪ್ರಕ್ರಿಯೆ: ತಂಪಾದ ಗಾಳಿಯ ಮೇಲೆ ಬೆಚ್ಚಗಿನ ಗಾಳಿಯು ಬಲವಂತವಾಗಿ ಏರುತ್ತದೆ, ಇದು ತಂಪಾಗುವಿಕೆ ಮತ್ತು ಘನೀಕರಣಕ್ಕೆ ಕಾರಣವಾಗುತ್ತದೆ, ಇದರಿಂದಾಗಿ ಮಳೆಯಾಗುತ್ತದೆ. ಚಂಡಮಾರುತಗಳು ಅಥವಾ ಮುಂಭಾಗಗಳು ಆಗಾಗ್ಗೆ ರೂಪುಗೊಳ್ಳುವ ಸಮಶೀತೋಷ್ಣ ಪ್ರದೇಶಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಇದು ಸಾಮಾನ್ಯವಾಗಿದೆ.
ಉದಾಹರಣೆ: ಉಷ್ಣವಲಯದ ಚಂಡಮಾರುತಗಳು
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
upsc kannada classes
geography kannada class
geography class in kannada
geography in kannada
00:00 Introduction
00:31 Convection Rainfall
05:00 Orographic Rainfall
10:04 Cyclonic Rainfall
 0:11:51
0:11:51
 0:42:47
0:42:47
 0:50:22
0:50:22
 0:06:49
0:06:49
 0:06:13
0:06:13
 0:11:13
0:11:13
 0:08:17
0:08:17
 0:11:26
0:11:26
 0:10:39
0:10:39
 0:01:48
0:01:48
 0:04:00
0:04:00
 0:07:22
0:07:22
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:04:10
0:04:10
 0:02:11
0:02:11
 0:05:45
0:05:45
 0:04:26
0:04:26
 0:00:10
0:00:10
 0:01:40
0:01:40
 0:00:43
0:00:43
 0:00:48
0:00:48
 0:00:26
0:00:26
 0:01:27
0:01:27
 0:01:43
0:01:43