filmov
tv
1 : 1 SQL Intermediate Interview Session | SQL Interview Q&A | SQL Training | Ivy Pro School

Показать описание
Most Common SQL Interview Questions are as follows:
1. What is Database?
A database is an organized collection of data, stored and retrieved digitally from a remote or local computer system. Databases can be vast and complex, and such databases are developed using fixed design and modeling approaches.
2. What is DBMS?
DBMS stands for Database Management System. DBMS is a system software responsible for the creation, retrieval, updation and management of the database. It ensures that our data is consistent, organized and is easily accessible by serving as an interface between the database and its end-users or application software.
3. What is RDBMS? How is it different from DBMS?
RDBMS stands for Relational Database Management System. The key difference here, compared to DBMS, is that RDBMS stores data in the form of a collection of tables and relations can be defined between the common fields of these tables. Most modern database management systems like MySQL, Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle, IBM DB2, and Amazon Redshift are based on RDBMS.
4. What is SQL?
SQL stands for Structured Query Language. It is the standard language for relational database management systems. It is especially useful in handling organized data comprised of entities (variables) and relations between different entities of the data.
5. What is the difference between SQL and MySQL?
SQL is a standard language for retrieving and manipulating structured databases. On the contrary, MySQL is a relational database management system, like SQL Server, Oracle, or IBM DB2, that is used to manage SQL databases.
6. What are Tables and Fields?
A table is an organized collection of data stored in the form of rows and columns. Columns can be categorized as vertical and rows as horizontal. The columns in a table are called fields while the rows can be referred to as records.
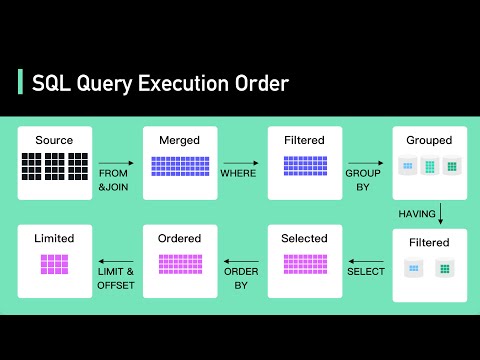
7. What are Constraints in SQL?
Constraints are used to specify the rules concerning data in the table. It can be applied for single or multiple fields in an SQL table during the creation of a table or after creating using the ALTER TABLE command. The constraints are:
- NOT NULL - Restricts NULL value from being inserted into a column.
- CHECK - Verifies that all values in a field satisfy a condition.
- DEFAULT - Automatically assigns a default value if no value has been specified for the field.
- UNIQUE - Ensures unique values to be inserted into the field.
- INDEX - Indexes a field providing faster retrieval of records.
- PRIMARY KEY - Uniquely identifies each record in a table.
- FOREIGN KEY - Ensures referential integrity for a record in another table.
8. What is a Primary Key?
The PRIMARY KEY constraint uniquely identifies each row in a table. It must contain UNIQUE values and has an implicit NOT NULL constraint.
A table in SQL is strictly restricted to have one and only one primary key, which is comprised of single or multiple fields (columns).
9. What is a UNIQUE constraint?
A UNIQUE constraint ensures that all values in a column are different. This provides uniqueness for the column(s) and helps identify each row uniquely. Unlike the primary key, there can be multiple unique constraints defined per table. The code syntax for UNIQUE is quite similar to that of PRIMARY KEY and can be used interchangeably.
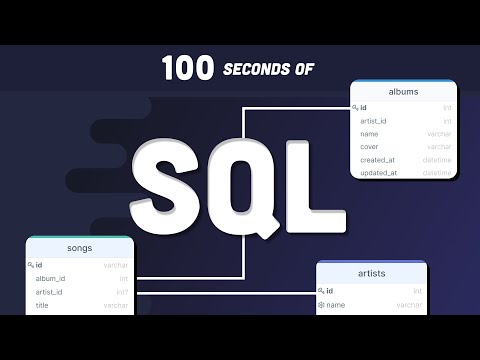
10. What is a Join? List its different types.
The SQL Join clause is used to combine records (rows) from two or more tables in a SQL database based on a related column between the two.
There are four different types of JOINs in SQL:
- (INNER) JOIN: Retrieves records that have matching values in both tables involved in the join. This is the widely used join for queries.
- LEFT (OUTER) JOIN: Retrieves all the records/rows from the left and the matched records/rows from the right table.
- RIGHT (OUTER) JOIN: Retrieves all the records/rows from the right and the matched records/rows from the left table.
- FULL (OUTER) JOIN: Retrieves all the records where there is a match in either the left or right table.
11. What is a Subquery? What are its types?
A subquery is a query within another query, also known as a nested query or inner query. It is used to restrict or enhance the data to be queried by the main query, thus restricting or enhancing the output of the main query respectively.
12. What are UNION, MINUS, and INTERSECT commands?
The UNION operator combines and returns the result-set retrieved by two or more SELECT statements.
The MINUS operator in SQL is used to remove duplicates from the result-set obtained by the second SELECT query from the result-set obtained by the first SELECT query and then return the filtered results from the first.
The INTERSECT clause in SQL combines the result-set fetched by the two SELECT statements where records from one match the other and then returns this intersection of result-sets.
1. What is Database?
A database is an organized collection of data, stored and retrieved digitally from a remote or local computer system. Databases can be vast and complex, and such databases are developed using fixed design and modeling approaches.
2. What is DBMS?
DBMS stands for Database Management System. DBMS is a system software responsible for the creation, retrieval, updation and management of the database. It ensures that our data is consistent, organized and is easily accessible by serving as an interface between the database and its end-users or application software.
3. What is RDBMS? How is it different from DBMS?
RDBMS stands for Relational Database Management System. The key difference here, compared to DBMS, is that RDBMS stores data in the form of a collection of tables and relations can be defined between the common fields of these tables. Most modern database management systems like MySQL, Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle, IBM DB2, and Amazon Redshift are based on RDBMS.
4. What is SQL?
SQL stands for Structured Query Language. It is the standard language for relational database management systems. It is especially useful in handling organized data comprised of entities (variables) and relations between different entities of the data.
5. What is the difference between SQL and MySQL?
SQL is a standard language for retrieving and manipulating structured databases. On the contrary, MySQL is a relational database management system, like SQL Server, Oracle, or IBM DB2, that is used to manage SQL databases.
6. What are Tables and Fields?
A table is an organized collection of data stored in the form of rows and columns. Columns can be categorized as vertical and rows as horizontal. The columns in a table are called fields while the rows can be referred to as records.
7. What are Constraints in SQL?
Constraints are used to specify the rules concerning data in the table. It can be applied for single or multiple fields in an SQL table during the creation of a table or after creating using the ALTER TABLE command. The constraints are:
- NOT NULL - Restricts NULL value from being inserted into a column.
- CHECK - Verifies that all values in a field satisfy a condition.
- DEFAULT - Automatically assigns a default value if no value has been specified for the field.
- UNIQUE - Ensures unique values to be inserted into the field.
- INDEX - Indexes a field providing faster retrieval of records.
- PRIMARY KEY - Uniquely identifies each record in a table.
- FOREIGN KEY - Ensures referential integrity for a record in another table.
8. What is a Primary Key?
The PRIMARY KEY constraint uniquely identifies each row in a table. It must contain UNIQUE values and has an implicit NOT NULL constraint.
A table in SQL is strictly restricted to have one and only one primary key, which is comprised of single or multiple fields (columns).
9. What is a UNIQUE constraint?
A UNIQUE constraint ensures that all values in a column are different. This provides uniqueness for the column(s) and helps identify each row uniquely. Unlike the primary key, there can be multiple unique constraints defined per table. The code syntax for UNIQUE is quite similar to that of PRIMARY KEY and can be used interchangeably.
10. What is a Join? List its different types.
The SQL Join clause is used to combine records (rows) from two or more tables in a SQL database based on a related column between the two.
There are four different types of JOINs in SQL:
- (INNER) JOIN: Retrieves records that have matching values in both tables involved in the join. This is the widely used join for queries.
- LEFT (OUTER) JOIN: Retrieves all the records/rows from the left and the matched records/rows from the right table.
- RIGHT (OUTER) JOIN: Retrieves all the records/rows from the right and the matched records/rows from the left table.
- FULL (OUTER) JOIN: Retrieves all the records where there is a match in either the left or right table.
11. What is a Subquery? What are its types?
A subquery is a query within another query, also known as a nested query or inner query. It is used to restrict or enhance the data to be queried by the main query, thus restricting or enhancing the output of the main query respectively.
12. What are UNION, MINUS, and INTERSECT commands?
The UNION operator combines and returns the result-set retrieved by two or more SELECT statements.
The MINUS operator in SQL is used to remove duplicates from the result-set obtained by the second SELECT query from the result-set obtained by the first SELECT query and then return the filtered results from the first.
The INTERSECT clause in SQL combines the result-set fetched by the two SELECT statements where records from one match the other and then returns this intersection of result-sets.
Комментарии
 1:08:49
1:08:49
 0:05:57
0:05:57
 0:08:53
0:08:53
 1:10:01
1:10:01
 0:26:21
0:26:21
 0:09:51
0:09:51
 0:06:00
0:06:00
 0:25:17
0:25:17
 0:04:38
0:04:38
 0:07:39
0:07:39
 0:05:02
0:05:02
 0:33:06
0:33:06
 0:17:40
0:17:40
 0:08:37
0:08:37
 4:20:39
4:20:39
 0:44:57
0:44:57
 0:56:24
0:56:24
 0:07:57
0:07:57
 1:00:08
1:00:08
 0:06:15
0:06:15
 0:49:56
0:49:56
 0:02:23
0:02:23
 0:27:20
0:27:20
 0:04:10
0:04:10