filmov
tv
Atomic Structure | A-level Chemistry | OCR, AQA, Edexcel
Показать описание
Atomic Structure in a Snap!
SnapRevise is the UK’s leading A-level and GCSE revision & exam preparation resource offering comprehensive video courses created by A* tutors. Our courses are designed around the OCR, AQA, SNAB, Edexcel B, WJEC, CIE and IAL exam boards, concisely covering all the important concepts required by each specification. In addition to all the content videos, our courses include hundreds of exam question videos, where we show you how to tackle questions and walk you through step by step how to score full marks.
Sign up today and together, let’s make A-level Chemistry a walk in the park!
The key points covered in this video include:
1. What is an Atom?
2. Atomic Structure
3. Sub-Atomic Particles
4. Mass Number and Atomic Mass
5. Example: Element
What is an Atom?
Fundamental piece of matter. Everything is made of atoms! (Apart from energy). Basic Unit - The smallest particle of a chemical element. Many models of the atom have been proposed.
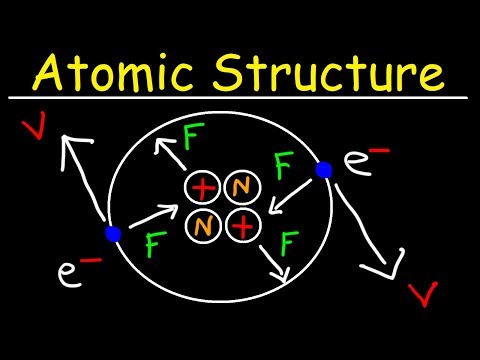
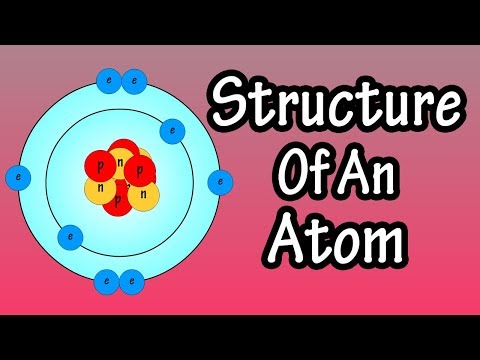
The Structure of the Atom
Nucleus: Centre of the atom, Tiny! Dense. Electrons: Orbit the nucleus in shells, Do not contribute much to the mass of the atom.
Sub-Atomic Particles
Neutral Atoms: Protons = Electrons, + ve = - ve
Mass and Atomic Number
A: Mass Number, Number of Nucleons, Protons + Neutrons. Z: Atomic Number, Number of Protons. X: Element
Example: Aluminum
Atomic Number: Protons. Mass Number: Protons + Neutrons. Mass number will be the bigger number.
Summary
Atoms are the smallest particle of an element
Atoms consist of a central nucleus orbited by shells of electrons
The atom is composed of sub-atomic particles
a. Protons (P)
b. Neutrons (N)
c. Electrons (E)
The nucleus is composed of:
a. Protons
b. Neutrons
Each sub-atomic particle has its own identity
a. Different relative mass and charge
In neutral atoms: Protons = Electrons
Mass Number (A) = P + N
Atomic Number (Z) = P
SnapRevise is the UK’s leading A-level and GCSE revision & exam preparation resource offering comprehensive video courses created by A* tutors. Our courses are designed around the OCR, AQA, SNAB, Edexcel B, WJEC, CIE and IAL exam boards, concisely covering all the important concepts required by each specification. In addition to all the content videos, our courses include hundreds of exam question videos, where we show you how to tackle questions and walk you through step by step how to score full marks.
Sign up today and together, let’s make A-level Chemistry a walk in the park!
The key points covered in this video include:
1. What is an Atom?
2. Atomic Structure
3. Sub-Atomic Particles
4. Mass Number and Atomic Mass
5. Example: Element
What is an Atom?
Fundamental piece of matter. Everything is made of atoms! (Apart from energy). Basic Unit - The smallest particle of a chemical element. Many models of the atom have been proposed.
The Structure of the Atom
Nucleus: Centre of the atom, Tiny! Dense. Electrons: Orbit the nucleus in shells, Do not contribute much to the mass of the atom.
Sub-Atomic Particles
Neutral Atoms: Protons = Electrons, + ve = - ve
Mass and Atomic Number
A: Mass Number, Number of Nucleons, Protons + Neutrons. Z: Atomic Number, Number of Protons. X: Element
Example: Aluminum
Atomic Number: Protons. Mass Number: Protons + Neutrons. Mass number will be the bigger number.
Summary
Atoms are the smallest particle of an element
Atoms consist of a central nucleus orbited by shells of electrons
The atom is composed of sub-atomic particles
a. Protons (P)
b. Neutrons (N)
c. Electrons (E)
The nucleus is composed of:
a. Protons
b. Neutrons
Each sub-atomic particle has its own identity
a. Different relative mass and charge
In neutral atoms: Protons = Electrons
Mass Number (A) = P + N
Atomic Number (Z) = P
Комментарии
 1:14:48
1:14:48
 0:39:59
0:39:59
 0:09:16
0:09:16
 0:11:45
0:11:45
 0:33:00
0:33:00
 0:27:47
0:27:47
 0:49:10
0:49:10
 0:05:22
0:05:22
 0:08:08
0:08:08
 0:27:22
0:27:22
 0:11:19
0:11:19
 0:08:42
0:08:42
 0:05:30
0:05:30
 0:16:56
0:16:56
 0:05:07
0:05:07
 0:21:15
0:21:15
 0:02:20
0:02:20
 1:20:36
1:20:36
 0:10:52
0:10:52
 0:13:58
0:13:58
 0:13:31
0:13:31
 0:21:44
0:21:44
 0:05:26
0:05:26
 0:45:42
0:45:42