filmov
tv
Extending High-Level Synthesis for Task-Parallel Programs

Показать описание
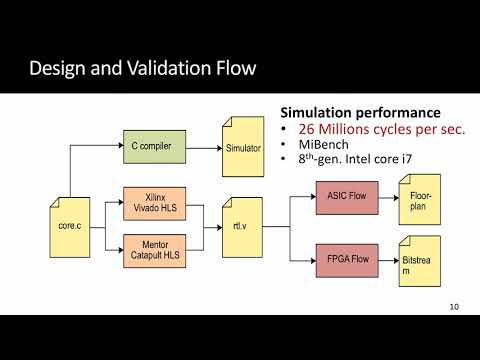
C/C++/OpenCL-based high-level synthesis (HLS) becomes more and more popular for field-programmable gate array (FPGA) accelerators in many application domains in recent years, thanks to its competitive quality of results (QoR) and short development cycles compared with the traditional register-transfer level design approach. Yet, limited by the sequential C semantics, it remains challenging to adopt the same highly productive high-level programming approach in many other application domains, where coarse-grained tasks run in parallel and communicate with each other at a fine-grained level. While current HLS tools do support task-parallel programs, the productivity is greatly limited ① in the code development cycle due to the poor programmability, ② in the correctness verification cycle due to restricted software simulation, and ③ in the QoR tuning cycle due to slow code generation. Such limited productivity often defeats the purpose of HLS and hinder programmers from adopting HLS for task-parallel FPGA accelerators.
--
The VAST lab at UCLA investigates cutting-edge research topics at the intersection of VLSI technologies, design automation, architecture, and compiler optimization at multiple scales, from micro-architecture building blocks to heterogeneous compute nodes and scalable data centers. Current focuses include architecture and design automation for emerging technologies, customizable domain-specific computing with applications to multiple domains, such as imaging processing, bioinformatics, data mining, and machine learning.
--
The VAST lab at UCLA investigates cutting-edge research topics at the intersection of VLSI technologies, design automation, architecture, and compiler optimization at multiple scales, from micro-architecture building blocks to heterogeneous compute nodes and scalable data centers. Current focuses include architecture and design automation for emerging technologies, customizable domain-specific computing with applications to multiple domains, such as imaging processing, bioinformatics, data mining, and machine learning.
 0:18:55
0:18:55
 0:30:31
0:30:31
 0:03:29
0:03:29
 0:50:40
0:50:40
 0:45:30
0:45:30
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:09:47
0:09:47
 0:11:06
0:11:06
 0:23:41
0:23:41
 0:11:04
0:11:04
 0:17:34
0:17:34
 0:16:55
0:16:55
 1:02:21
1:02:21
 0:12:38
0:12:38
 0:00:37
0:00:37
 0:08:32
0:08:32
 0:43:32
0:43:32
 0:00:36
0:00:36
 0:00:14
0:00:14
 0:58:02
0:58:02
 0:00:19
0:00:19
 0:00:11
0:00:11
 0:00:15
0:00:15
 0:00:15
0:00:15