filmov
tv
Extensor digitorum brevis and extensor hallucis brevis | Sports massage for foot pain, part 1

Показать описание
In this series of videos, we're looking at massage techniques for foot pain. To kick things off, we're covering the extensor digitorum brevis and extensor hallucis brevis.
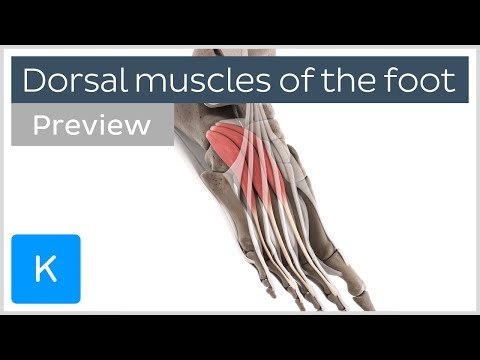
These two tissues are part of the small extensor muscles of the toes. They are found at the front of the forefoot and attach proximally to our calcaneus bone. The extensor digitorum brevis interdigitates with the second, third, and fourth phalanx of the toes (and very occasionally the fifth), while the extensor hallicus brevis attaches to the phalanx of the big toe.
Because of their role as extensors of the toes, dysfunction in them can impact a variety of everyday activities like walking, running, and even balance. A dead giveaway is ankle sprain injuries: if your client has sprained their ankle, but complains of foot pain as opposed to ankle pain then I would highlight these muscles.
There are three trigger points to be aware of with these muscles: the extensor hallucis brevis has a single trigger point and the extensor digitorum longus has two. These trigger points are local to the muscles and can refer to the distal dorsum.
The small size of these tissues means you can use your fingers and thumbs, but you should always take a slow, purposeful approach. Work these muscles with care and watch your pressure as the bones are superficial so feedback can be strong.
*BE AWESOME AT WHAT YOU DO!*
Want to learn more? Join our membership for CPE-accredited masterclasses, in-person and remote workshops, and a dedicated community of therapists like you. Check it all out and join today with a free seven-day trial!
#StuartHindsAcademy #massage #sportsmassage #foot #footpain #footmassage
* * *
These videos are intended to be used for information purposes only and are not intended to be used for medical diagnosis or treatment or to substitute for medical diagnosis and/or treatment rendered or prescribed by a physician or trained healthcare professional. This information is designed as educational material and should not be taken as a recommendation for the treatment of any particular person or patient. Always consult your physician if you think you need treatment or if you feel unwell.
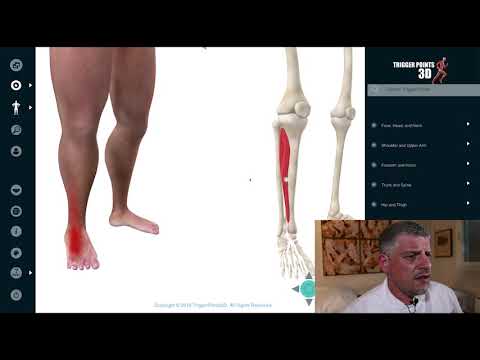
These two tissues are part of the small extensor muscles of the toes. They are found at the front of the forefoot and attach proximally to our calcaneus bone. The extensor digitorum brevis interdigitates with the second, third, and fourth phalanx of the toes (and very occasionally the fifth), while the extensor hallicus brevis attaches to the phalanx of the big toe.
Because of their role as extensors of the toes, dysfunction in them can impact a variety of everyday activities like walking, running, and even balance. A dead giveaway is ankle sprain injuries: if your client has sprained their ankle, but complains of foot pain as opposed to ankle pain then I would highlight these muscles.
There are three trigger points to be aware of with these muscles: the extensor hallucis brevis has a single trigger point and the extensor digitorum longus has two. These trigger points are local to the muscles and can refer to the distal dorsum.
The small size of these tissues means you can use your fingers and thumbs, but you should always take a slow, purposeful approach. Work these muscles with care and watch your pressure as the bones are superficial so feedback can be strong.
*BE AWESOME AT WHAT YOU DO!*
Want to learn more? Join our membership for CPE-accredited masterclasses, in-person and remote workshops, and a dedicated community of therapists like you. Check it all out and join today with a free seven-day trial!
#StuartHindsAcademy #massage #sportsmassage #foot #footpain #footmassage
* * *
These videos are intended to be used for information purposes only and are not intended to be used for medical diagnosis or treatment or to substitute for medical diagnosis and/or treatment rendered or prescribed by a physician or trained healthcare professional. This information is designed as educational material and should not be taken as a recommendation for the treatment of any particular person or patient. Always consult your physician if you think you need treatment or if you feel unwell.
Комментарии
 0:02:59
0:02:59
 0:08:13
0:08:13
 0:06:51
0:06:51
 0:01:50
0:01:50
 0:03:28
0:03:28
 0:02:12
0:02:12
 0:01:24
0:01:24
 0:01:43
0:01:43
 0:00:41
0:00:41
 0:01:05
0:01:05
 0:02:53
0:02:53
 0:01:30
0:01:30
 0:01:12
0:01:12
 0:00:38
0:00:38
 0:03:48
0:03:48
 0:01:39
0:01:39
 0:01:43
0:01:43
 0:00:36
0:00:36
 0:01:34
0:01:34
 0:00:30
0:00:30
 0:02:18
0:02:18
 0:03:36
0:03:36
 0:01:25
0:01:25
 0:00:47
0:00:47