filmov
tv
Blood-Brain Barrier

Показать описание
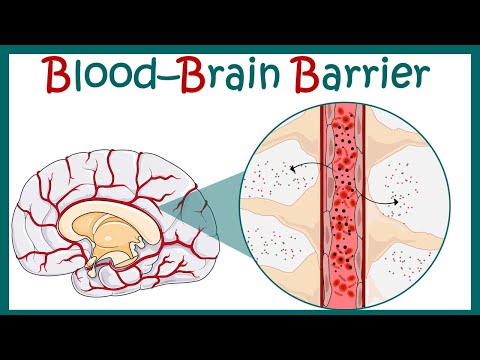
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a highly specialized and complex physiological structure that serves as a protective barrier between the blood circulation and the central nervous system (CNS), which includes the brain and spinal cord. Its primary function is to regulate the passage of substances from the bloodstream into the brain and spinal cord while maintaining a stable and controlled environment for proper neural function. The BBB plays a crucial role in safeguarding the sensitive neural tissue from potentially harmful substances while allowing essential nutrients to enter the CNS.
Key features and components of the blood-brain barrier include:
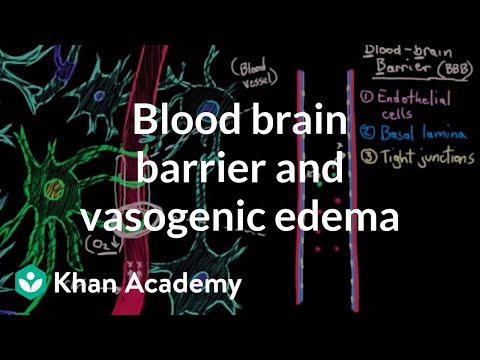
1. Endothelial Cells: The blood vessels in the brain are lined with endothelial cells that are tightly interconnected, forming a continuous layer. These cells are joined by specialized tight junctions that restrict the passage of most molecules, ions, and cells from the bloodstream into the brain tissue.
2. Tight Junctions: Tight junctions are specialized protein complexes that create a barrier between adjacent endothelial cells. These junctions prevent the free movement of molecules between cells, effectively blocking the paracellular route through which substances could leak between cells.
3. Astrocytes: Astrocytes are star-shaped cells that are closely associated with blood vessels in the brain. They contribute to the formation and maintenance of the BBB by releasing chemicals that help regulate the tightness of the junctions between endothelial cells.
4. Pericytes: Pericytes are another type of cell found in close proximity to blood vessels. They contribute to the stability of blood vessel walls and are thought to play a role in regulating the permeability of the BBB.
5. Basement Membrane: The basement membrane is a thin layer of extracellular matrix that surrounds blood vessels. It provides structural support to the blood vessels and contributes to the barrier function by restricting the movement of larger molecules.
The BBB selectively allows certain substances to cross into the brain while preventing others. Small molecules like oxygen, carbon dioxide, and some lipid-soluble substances can pass through the lipid bilayer of endothelial cells via passive diffusion. However, larger molecules, charged molecules, and many toxic substances are actively blocked by the tight junctions and active transport mechanisms present in the BBB.
While the BBB is vital for protecting the brain, it can also pose challenges for delivering therapeutic agents to the brain to treat neurological disorders. Researchers are actively studying ways to bypass or temporarily open the BBB to allow the delivery of drugs and therapies to the brain without compromising its integrity.
In summary, the blood-brain barrier is a sophisticated barrier system that protects the central nervous system from potentially harmful substances while maintaining the essential environment required for proper brain function.
Key features and components of the blood-brain barrier include:
1. Endothelial Cells: The blood vessels in the brain are lined with endothelial cells that are tightly interconnected, forming a continuous layer. These cells are joined by specialized tight junctions that restrict the passage of most molecules, ions, and cells from the bloodstream into the brain tissue.
2. Tight Junctions: Tight junctions are specialized protein complexes that create a barrier between adjacent endothelial cells. These junctions prevent the free movement of molecules between cells, effectively blocking the paracellular route through which substances could leak between cells.
3. Astrocytes: Astrocytes are star-shaped cells that are closely associated with blood vessels in the brain. They contribute to the formation and maintenance of the BBB by releasing chemicals that help regulate the tightness of the junctions between endothelial cells.
4. Pericytes: Pericytes are another type of cell found in close proximity to blood vessels. They contribute to the stability of blood vessel walls and are thought to play a role in regulating the permeability of the BBB.
5. Basement Membrane: The basement membrane is a thin layer of extracellular matrix that surrounds blood vessels. It provides structural support to the blood vessels and contributes to the barrier function by restricting the movement of larger molecules.
The BBB selectively allows certain substances to cross into the brain while preventing others. Small molecules like oxygen, carbon dioxide, and some lipid-soluble substances can pass through the lipid bilayer of endothelial cells via passive diffusion. However, larger molecules, charged molecules, and many toxic substances are actively blocked by the tight junctions and active transport mechanisms present in the BBB.
While the BBB is vital for protecting the brain, it can also pose challenges for delivering therapeutic agents to the brain to treat neurological disorders. Researchers are actively studying ways to bypass or temporarily open the BBB to allow the delivery of drugs and therapies to the brain without compromising its integrity.
In summary, the blood-brain barrier is a sophisticated barrier system that protects the central nervous system from potentially harmful substances while maintaining the essential environment required for proper brain function.
Комментарии
 0:08:31
0:08:31
 0:00:59
0:00:59
 0:06:02
0:06:02
 0:01:52
0:01:52
 0:04:56
0:04:56
 0:04:54
0:04:54
 0:01:09
0:01:09
 0:06:03
0:06:03
 0:05:13
0:05:13
 0:02:45
0:02:45
 0:48:44
0:48:44
 0:01:40
0:01:40
 0:00:53
0:00:53
 0:29:33
0:29:33
 0:07:02
0:07:02
 0:04:58
0:04:58
 0:03:26
0:03:26
 0:02:54
0:02:54
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:00:56
0:00:56
 0:03:21
0:03:21
 0:01:54
0:01:54
 0:02:43
0:02:43
 0:00:56
0:00:56