filmov
tv
Android Architecture Explained in Detail

Показать описание
In this video, we discuss all the layers of the Android Operating System including Stock Apps, Android Framework, Android Runtime, Native C, C++ Libraries, HAL(Hardware Abstraction Layer), Linux Kernal.
For structured courses on aosp, please use the below links. Good Luck.
Android Mobile OS Development
---------------------------------------------------
Android Automotive Development
-----------------------------------------------------
Android Deep Analysis - Startup and Window Management
-----------------------------------------------------------------
For structured courses on aosp, please use the below links. Good Luck.
Android Mobile OS Development
---------------------------------------------------
Android Automotive Development
-----------------------------------------------------
Android Deep Analysis - Startup and Window Management
-----------------------------------------------------------------
Android Architecture Explained in Detail
Android - Architecture
Android Architecture Full Information - [Hindi] - WsCube Tech#18
Android Architecture Easy Explanation in Hindi | 6 Marks Question in MSBTE Diploma Exam
App Excellence: Android Architecture
Android Automotive Architecture Explained in Detail 2023
ViewModel Explained - Android Architecture Component | Tutorial
Android Tutorial - Android Architecture Overview | Edureka
Android Audio Architecture Explained in 3 minutes
Do You Have to Learn Clean Architecture as a Beginner? - Android Development
Architecture of Android||MOBILE APPLICATION DEVELOPMENT IN TELUGU
Android Architecture | EMTERIA explains!
📱Android Architecture | Android Components💻 #android #androidarchitecture #androiddevelopment
Everything You NEED to Know About Client Architecture Patterns
Android Architecture in Tamil
Android Architecture in hindi #Android #architecture #application #computer
Learn Android - Module 2 II Android Architecture
Android Architecture Patterns - MVVM, MVP, MVC in Android | CheezyCode Hindi - #14
Android Graphics Architecture Explained
13 An Overview of the Android Architecture
Everything You NEED to Know About WEB APP Architecture
Top 6 Most Popular API Architecture Styles
What Is the Best Architecture for Android Apps?
Android app development tutorial in tamil - Android Architecture Explained
Комментарии
 0:11:18
0:11:18
 0:07:58
0:07:58
 0:13:20
0:13:20
 0:17:47
0:17:47
 0:01:34
0:01:34
 0:05:02
0:05:02
 0:08:27
0:08:27
 0:08:27
0:08:27
 0:03:07
0:03:07
 0:06:21
0:06:21
 0:11:20
0:11:20
 0:04:44
0:04:44
 0:05:42
0:05:42
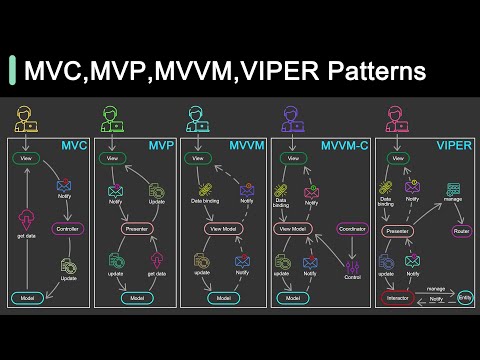 0:05:51
0:05:51
 0:22:26
0:22:26
 0:08:29
0:08:29
 0:03:43
0:03:43
 0:12:58
0:12:58
 0:06:19
0:06:19
 0:08:43
0:08:43
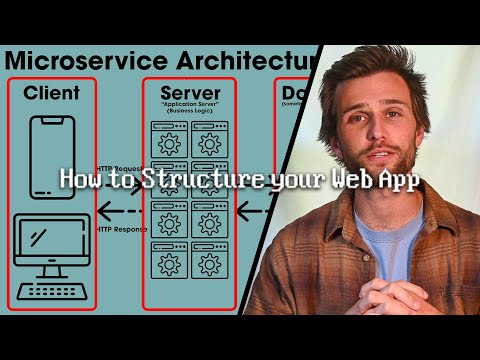 0:10:27
0:10:27
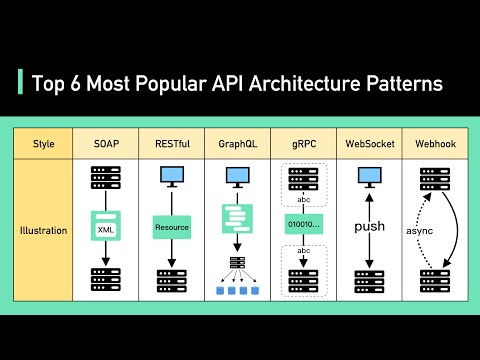 0:04:21
0:04:21
 0:17:57
0:17:57
 0:03:02
0:03:02