filmov
tv
Definition of Homozygous, Heterozygous, Hemizygous

Показать описание
Homozygous, Heterozygous and Hemizygous – What is the Difference?
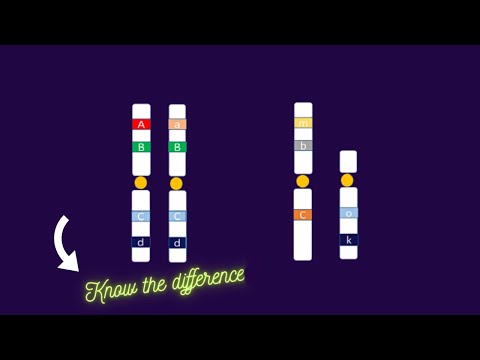
Homozygous, heterozygous and hemizygous describes the genotype for a single gene in a diploid organism. What does it mean? In humans, since we are diploid organisms we have two copies of every chromosome and they are called homologous chromosomes – one copy comes from mother and one copy comes from father. So that means we have two copies for every given gene because we have two copies of every chromosome. The locus of these genes is same for homologous chromosomes. For example, locus of gene X would be same on maternal as well as on paternal chromosome. So based on these two copies of every gene or alleles (alleles = different version of the same gene) we have different genotypes.
At this point it is important that we know the difference between gene and alleles to understand this concept. In case you want to know more about it visit our blog on Gene and Alleles.
Let’s understand homozygous and heterozygous first. Let’s say we are talking about eye pigment gene and let’s assume that we have two alleles for this gene – one allele codes for brown color eye (B) and the other allele codes for blue color (b). On the homologous pairs of chromosome we can either have same alleles (both either brown or blue) or different alleles (brown and blue). Only these possible combinations can be there. So based on whether we have got the same alleles or different alleles we describe the terms homozygous and heterozygous.
Homozygous, heterozygous and hemizygous describes the genotype for a single gene in a diploid organism. What does it mean? In humans, since we are diploid organisms we have two copies of every chromosome and they are called homologous chromosomes – one copy comes from mother and one copy comes from father. So that means we have two copies for every given gene because we have two copies of every chromosome. The locus of these genes is same for homologous chromosomes. For example, locus of gene X would be same on maternal as well as on paternal chromosome. So based on these two copies of every gene or alleles (alleles = different version of the same gene) we have different genotypes.
At this point it is important that we know the difference between gene and alleles to understand this concept. In case you want to know more about it visit our blog on Gene and Alleles.
Let’s understand homozygous and heterozygous first. Let’s say we are talking about eye pigment gene and let’s assume that we have two alleles for this gene – one allele codes for brown color eye (B) and the other allele codes for blue color (b). On the homologous pairs of chromosome we can either have same alleles (both either brown or blue) or different alleles (brown and blue). Only these possible combinations can be there. So based on whether we have got the same alleles or different alleles we describe the terms homozygous and heterozygous.
Комментарии
 0:11:06
0:11:06
 0:01:59
0:01:59
 0:01:41
0:01:41
 0:02:43
0:02:43
 0:05:52
0:05:52
 0:00:35
0:00:35
 0:01:47
0:01:47
 0:06:11
0:06:11
 0:00:29
0:00:29
 0:04:14
0:04:14
 0:00:27
0:00:27
 0:04:16
0:04:16
 0:00:26
0:00:26
 0:06:06
0:06:06
 0:05:45
0:05:45
 0:07:05
0:07:05
 0:01:24
0:01:24
 0:02:10
0:02:10
 0:00:48
0:00:48
 0:01:26
0:01:26
 0:06:29
0:06:29
 0:02:54
0:02:54
 0:07:12
0:07:12
 0:00:31
0:00:31