filmov
tv
Probabilities involving Equally Likely Outcomes | Probability Theory
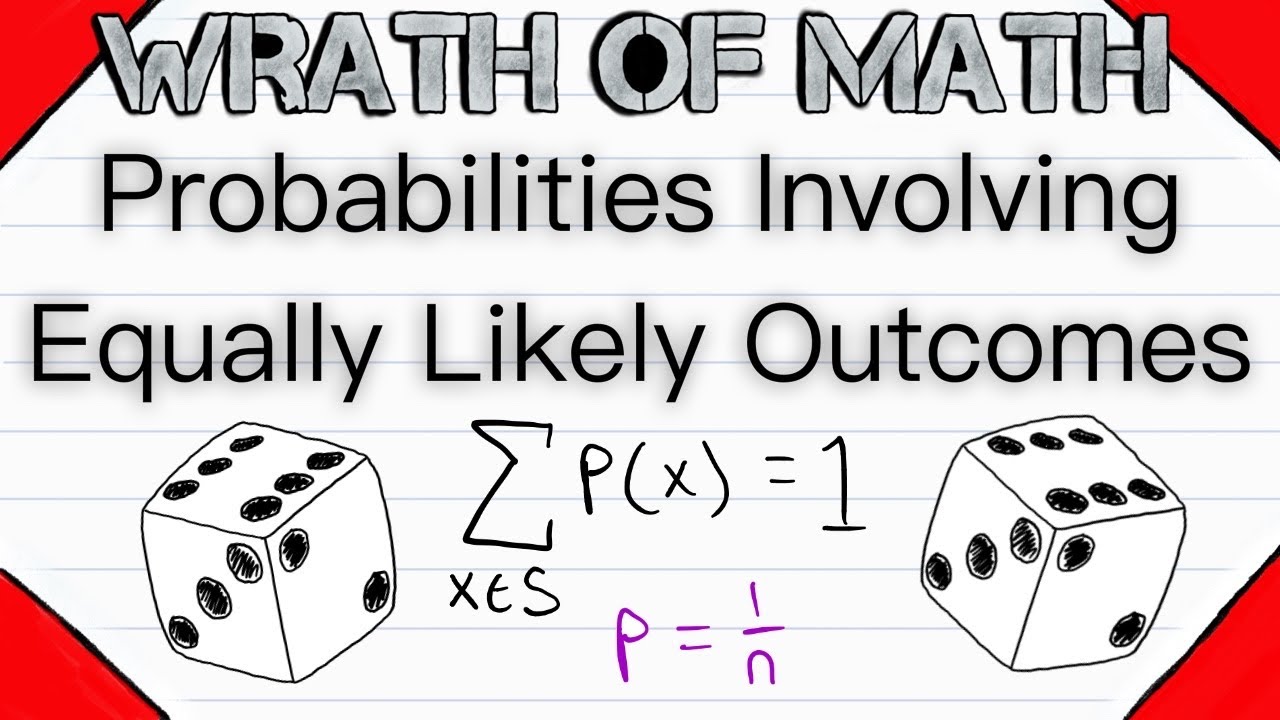
Показать описание
How do we assess probabilities of events in sample spaces that have equal outcomes? Like tossing a coin or a die? We'll be going over some of these basic probability concepts in today's probability theory lesson! We'll also touch on an example of the inclusion exclusion principle for probability.
The basic idea, when evaluating the probability of an event in a sample space of equally likely outcomes is that the probability of an event is the number of ways the event can occur divided by the total number of outcomes in the sample space.
SOLUTION TO PRACTICE PROBLEM:
We assume all numbers are equally likely to be chosen, so each number has a 1/100 chance of being chosen (since there are 100 possibilities: 1, 2, 3, ..., 100). Which numbers have two digits? That would be all numbers from 10 to 99. This is a total of 90 numbers. Thus, the probability that the chosen number has two digits is 90/100 = 90% = 0.9 = 9/10; however you choose to write it.
I hope you find this video helpful, and be sure to ask any questions down in the comments!
********************************************************************
The outro music is by a favorite musician of mine named Vallow, who, upon my request, kindly gave me permission to use his music in my outros. I usually put my own music in the outros, but I love Vallow's music, and wanted to share it with those of you watching. Please check out all of his wonderful work.
********************************************************************
+WRATH OF MATH+
Follow Wrath of Math on...
The basic idea, when evaluating the probability of an event in a sample space of equally likely outcomes is that the probability of an event is the number of ways the event can occur divided by the total number of outcomes in the sample space.
SOLUTION TO PRACTICE PROBLEM:
We assume all numbers are equally likely to be chosen, so each number has a 1/100 chance of being chosen (since there are 100 possibilities: 1, 2, 3, ..., 100). Which numbers have two digits? That would be all numbers from 10 to 99. This is a total of 90 numbers. Thus, the probability that the chosen number has two digits is 90/100 = 90% = 0.9 = 9/10; however you choose to write it.
I hope you find this video helpful, and be sure to ask any questions down in the comments!
********************************************************************
The outro music is by a favorite musician of mine named Vallow, who, upon my request, kindly gave me permission to use his music in my outros. I usually put my own music in the outros, but I love Vallow's music, and wanted to share it with those of you watching. Please check out all of his wonderful work.
********************************************************************
+WRATH OF MATH+
Follow Wrath of Math on...
Комментарии
 0:09:50
0:09:50
 0:04:40
0:04:40
 0:01:52
0:01:52
 0:02:57
0:02:57
 0:05:48
0:05:48
 0:08:57
0:08:57
 0:06:33
0:06:33
 0:05:07
0:05:07
 0:04:02
0:04:02
 0:02:06
0:02:06
 0:17:44
0:17:44
 0:04:51
0:04:51
 0:03:59
0:03:59
![[Chapter 2] #7](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/tvsdkep803M/hqdefault.jpg) 0:11:13
0:11:13
 0:03:12
0:03:12
 0:24:45
0:24:45
 0:10:25
0:10:25
 0:11:28
0:11:28
 0:09:43
0:09:43
 0:40:17
0:40:17
 0:08:10
0:08:10
 0:01:36
0:01:36
![[Chapter 2] #4](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/5Sf0rCkKC5Y/hqdefault.jpg) 0:03:53
0:03:53
 0:16:35
0:16:35