filmov
tv
Controller Area Network(CAN) programming Tutorial 17 : Coding for CAN data transmission

Показать описание
We have carefully crafted these courses by which you can learn STM32 internals, TIMERS, CAN, PWM, LOW POWER, RTC, PLL programming and debugging from ground level. Exploring various block diagrams and Technical reference manuals and step by step code exercises. Fully explained using Eclipse OpenSTM32 IDE
For all the future updates and coupons follow us on social media
Course Description :
====================================================
Mastering microcontroller : TIMERS,PWM,CAN,RTC,LOW POWER,STM32 Cube HAL APIs
This is course is highly recommended if you are seeking a career in the field of embedded systems and we have carefully crafted all these lectures with hands-on programming exercises, debugging tips and step by step guidance.
You will understand TIMERS, CAN, PWM, RTC, and LOW POWER working principles from ground level and code them using STM32 Device HAL APIs provided by ST.
Some of the highlights of the course are,
1. Understanding STM32 device HAL framework, ISRs, callbacks, and peripheral handle structures.
2. Internals of timers: basic and general purpose timers
3. Timers input capture and output compare unit and programming
4. PWM Programming
5. CAN fundamentals
6. CAN Frame formats, bus arbitration, bus signaling, transceiver and other important CAN details
7. STM32 bxCAN peripheral architecture and can filtering mechanism
8. Programming STM32 bxCAN peripheral
9. CAN protocol debugging and understanding CAN traffic.
10. Lower power modes of STM32: SLEEP/STOP/STANDBY and wake-up procedures and current measurements
11. Usage of WFI, WFE, SLEEPONEXIT feature of ARM Cortex Mx processor
12. RTC programming: calendar, Alarm, Wake-up timer unit, timestamp unit
13. RTC and low power modes
14. Eclipse based OpenSTM32 System workbench is used throughout the course to develop applications . The IDE supports windows/mac/Linux machines.
Комментарии
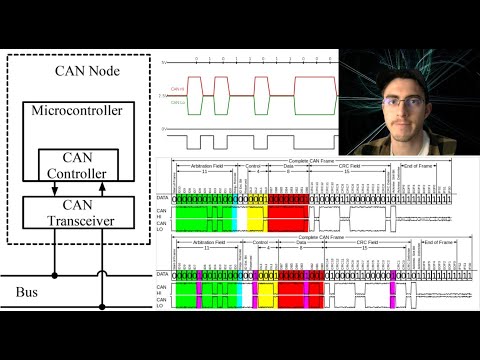 0:12:09
0:12:09
 0:03:49
0:03:49
 0:09:20
0:09:20
 0:11:25
0:11:25
 0:02:30
0:02:30
 0:06:00
0:06:00
 0:08:35
0:08:35
 0:03:12
0:03:12
 1:18:30
1:18:30
 0:08:42
0:08:42
 0:03:25
0:03:25
 0:02:59
0:02:59
 0:08:05
0:08:05
 0:37:36
0:37:36
 0:14:22
0:14:22
 0:33:54
0:33:54
 0:00:09
0:00:09
 0:14:18
0:14:18
 0:13:29
0:13:29
 0:12:20
0:12:20
 0:10:56
0:10:56
 0:02:54
0:02:54
 0:04:10
0:04:10
 0:14:44
0:14:44