filmov
tv
Calculus 2: Ch. 1.5 Differentials in Integration (1 of 10) Why Do We Need Differentials in Integrals

Показать описание
We will learn why we need differentials in certain integrations.
Next video in the series can be seen at:
Calculus 2: Ch. 1.5 Differentials in Integration (5 of 10) Example 4
Calculus 2: Ch. 1.5 Differentials in Integration (6 of 10) Example 5
Calculus 2: Ch. 1.5 Differentials in Integration (2 of 10) Example 1
How to Make it Through Calculus (Neil deGrasse Tyson)
Calculus 2: Ch. 1.5 Differentials in Integration (1 of 10) Why Do We Need Differentials in Integrals
Calculus 2: Ch. 1.5 Differentials in Integration (3 of 10) Example 2
Calculus 2: Ch. 1.5 Differentials in Integration (4 of 10) Example 3
Calculus 2: Ch. 1.5 Differentials in Integration (10 of 10) Example 9
Continuous Function | NCERT Class 12th Maths | Chapter 5th By GP Sir
Why People FAIL Calculus (Fix These 3 Things to Pass)
We Need To Talk About Calculus 2
Understand Calculus in 35 Minutes
ALL OF Calculus 2 in 5 minutes
Calculus 2: Modeling with Differential Equations (Video #11) | Math with Professor V
Memorization Trick for Graphing Functions Part 1 | Algebra Math Hack #shorts #math #school
Mixing Problems and Separable Differential Equations - Calculus 2
Differential equations, a tourist's guide | DE1
Differential equation introduction | First order differential equations | Khan Academy
Isaac Newton's INSANE Sleep Habits 😬
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Part 1
🔥 POV: Integration - Look at me! 👀 💪 | JEE 2024 | Math | Bhoomika Ma'am
Calculus 2 Lecture 9.1: Convergence and Divergence of Sequences
Calculus 1 - Integration & Antiderivatives
Integrals: degree of top GREATER than bottom. #calculus #integrals #mathchallenge #mathtricks
Комментарии
 0:02:40
0:02:40
 0:02:02
0:02:02
 0:03:30
0:03:30
 0:03:38
0:03:38
 0:06:34
0:06:34
 0:03:06
0:03:06
 0:02:22
0:02:22
 0:03:13
0:03:13
 0:24:22
0:24:22
 0:03:15
0:03:15
 0:08:55
0:08:55
 0:36:22
0:36:22
 0:06:09
0:06:09
 0:16:00
0:16:00
 0:00:15
0:00:15
 0:24:45
0:24:45
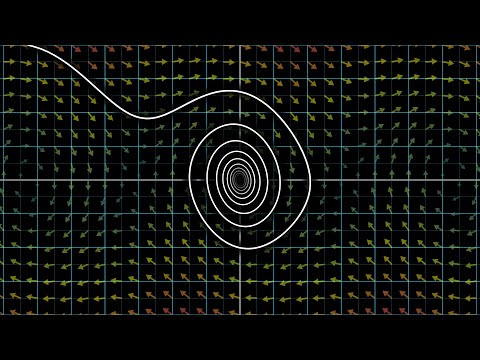 0:27:16
0:27:16
 0:07:49
0:07:49
 0:00:24
0:00:24
 0:11:30
0:11:30
 0:00:48
0:00:48
 2:27:29
2:27:29
 0:40:04
0:40:04
 0:00:48
0:00:48