filmov
tv
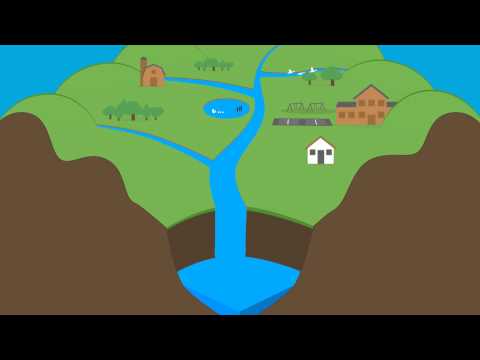
Drainage basin hydrological cycle
Показать описание
KEY TERMS:
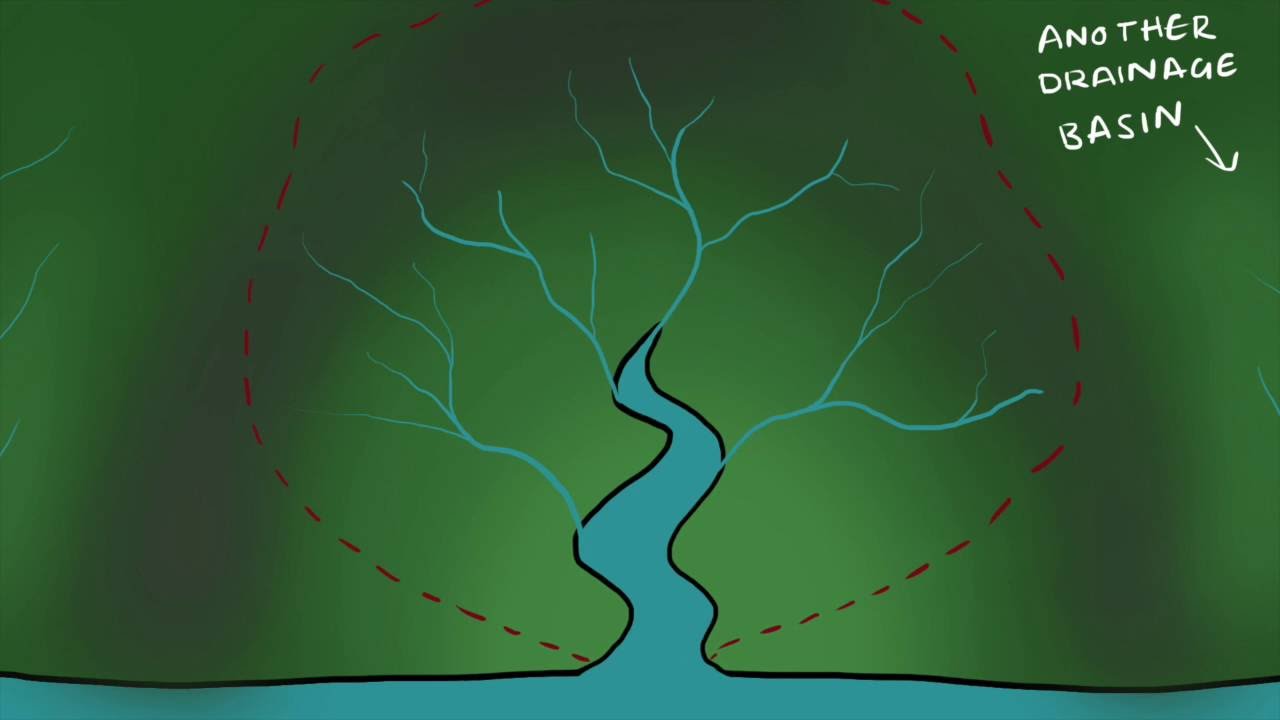
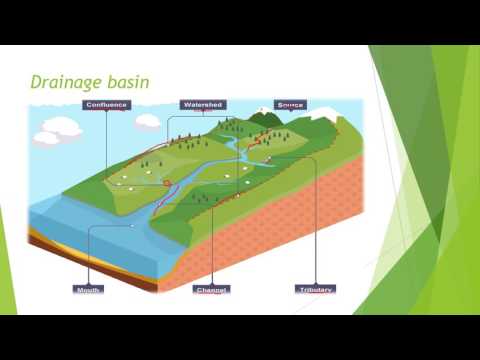
Drainage basin- The area that is drained by a river and its tributaries.
Watershed- The boundary between two separate basins.
Precipitation- All the ways moisture comes out of the atmosphere (usually rain).
Confluence- Where two tributaries meet.
Channel flow- The flow of water within the river channel.
Surface runoff- (overland flow) the flow of water over the land.
Infiltration- Water seeping from the surface into the soil.
Throughflow- A horizontal movement of water through the soil driven by gravity from soil moisture storage to the river channel storage.
Percolation- Water seeping deeper underground within the soil and rock to enter the groundwater storage.
Interflow- Water flowing downhill through permeable rock above the water table.
Groundwater flow- A very slow horizontal movement of water below the water table through permeable rock.
Baseflow- The groundwater flow that feeds into rivers through its banks and beds.
Throughfall- Precipitation falling through spaces in the vegetation canopy to the ground.
Stemflow- Precipitation flowing slowly down the branches and stems of vegetation to the ground.
Interception- Precipitation temporarily collected and stored by vegetation and or buildings in urban areas.
Vegetation storage- Water taken up and stored by plants.
Surface storage- Water stored on the surface of the land in puddles, lakes or man-made ditches and reservoirs.
Groundwater storage- Water stored, long-term, deep underground in rocks or the joints and cracks of rocks.
Channel storage- Water stored in the river channel as it moves through the drainage basin system.
Evaporation- Water changing from liquid to gas due to energy from the sun.
Transpiration- Water vapour leaving the stomata in the underside of plant leaves.
Evapotranspiration- A combination of evaporation and transpiration. Water is lost from the drainage basin system to the atmosphere as water vapour.
Drainage basin- The area that is drained by a river and its tributaries.
Watershed- The boundary between two separate basins.
Precipitation- All the ways moisture comes out of the atmosphere (usually rain).
Confluence- Where two tributaries meet.
Channel flow- The flow of water within the river channel.
Surface runoff- (overland flow) the flow of water over the land.
Infiltration- Water seeping from the surface into the soil.
Throughflow- A horizontal movement of water through the soil driven by gravity from soil moisture storage to the river channel storage.
Percolation- Water seeping deeper underground within the soil and rock to enter the groundwater storage.
Interflow- Water flowing downhill through permeable rock above the water table.
Groundwater flow- A very slow horizontal movement of water below the water table through permeable rock.
Baseflow- The groundwater flow that feeds into rivers through its banks and beds.
Throughfall- Precipitation falling through spaces in the vegetation canopy to the ground.
Stemflow- Precipitation flowing slowly down the branches and stems of vegetation to the ground.
Interception- Precipitation temporarily collected and stored by vegetation and or buildings in urban areas.
Vegetation storage- Water taken up and stored by plants.
Surface storage- Water stored on the surface of the land in puddles, lakes or man-made ditches and reservoirs.
Groundwater storage- Water stored, long-term, deep underground in rocks or the joints and cracks of rocks.
Channel storage- Water stored in the river channel as it moves through the drainage basin system.
Evaporation- Water changing from liquid to gas due to energy from the sun.
Transpiration- Water vapour leaving the stomata in the underside of plant leaves.
Evapotranspiration- A combination of evaporation and transpiration. Water is lost from the drainage basin system to the atmosphere as water vapour.
Комментарии
 0:03:11
0:03:11
 0:18:55
0:18:55
 0:21:51
0:21:51
 0:01:17
0:01:17
 0:04:33
0:04:33
 0:05:08
0:05:08
 0:17:53
0:17:53
 0:04:52
0:04:52
 0:00:40
0:00:40
 0:15:22
0:15:22
 0:01:18
0:01:18
 0:08:45
0:08:45
 0:20:16
0:20:16
 0:10:20
0:10:20
 0:07:52
0:07:52
 0:01:50
0:01:50
 0:10:42
0:10:42
 0:03:43
0:03:43
 0:06:32
0:06:32
 0:02:59
0:02:59
 0:06:55
0:06:55
 0:11:59
0:11:59
 0:02:38
0:02:38
 0:09:26
0:09:26