filmov
tv
What is an RTD | Working Principles
Показать описание
============================
▶ You can read the full post here:
⌚Timestamps:
00:00 - Intro
00:56 - Electrical Resistance
03:17 - How does an RTD work?
04:31 - RTD components
06:22 - Summary
=============================
Temperature measurement in machines and other industrial processes is one of the key control variables used to guarantee the quality of products manufactured in different segments of the industry.
In this video, we will cover what are Resistive Temperature Detectors, commonly known as RTDs, how they work, and how their signal is transmitted.
A Resistive Temperature Detector is an instrument that detects temperature based on resistivity.
Electrical resistance is defined as the ability of a body to oppose the flow of electric current. The standard international unit of resistance is the Ohm (Ω) and represents the volt/ampere ratio.
When a conductor is subjected to a potential difference, an electric current passes through it, which is constituted by the movement of free electrons inside the conductor.
When these free electrons get into motion, they begin to collide with each other and with the atoms in the conductor.
The greater the number of collisions, the greater the difficulty encountered by the electric current in crossing the conductor. This difficulty in moving charges is what characterizes electrical resistance.
Electrical resistance varies depending on the length, width, and nature of the conductor material, as well as the temperature to which it is subjected.
Resistance is directly proportional to the length of the conductor. It is also inversely proportional to the area of the conductor.
Electrical resistance can also vary according to the variation of voltage and electric current in a conductor.
The potential difference between the ends of a conductor is proportional to the current flowing through it.
When the conductor is heated, its atoms absorb this heat energy, resulting in an increase in vibration.
As heat rises, the ability of a metal to oppose the flow of electric current also increases, therefore less current can flow. As heat decreases the ability of a metal to oppose the flow of electric current is reduced, hence more current can flow.
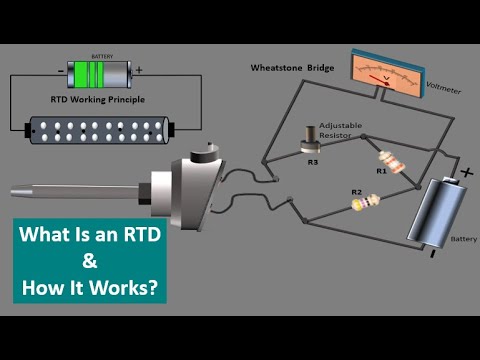
RTD sensors use this variation in electrical resistance to measure the change in temperature.
The most popular RTD sensors are platinum ones, such as the PT100 and the PT1000, and nickel ones, such as the Ni500.
Let’s take a look at the different components of an RTD:
- The Resistance or sensing element is the literal temperature-detecting portion of the RTD. It is a metal wire either on an etched grid on a substrate, or a wire wound in a coil. They can be made from numeral materials such as platinum, copper, and nickel, among others.
- The Protecting Tubing is mostly made out of stainless steel, which can be used for assemblies up to 500° F.
- The Process Connection is a standard fitting.
There are several wire configurations of RTDs available: 2, 3, and 4 wire. The 3-wire RTD is the most commonly used in industrial applications,
The unit given by our RTD is in Ohms. We need to convert this delta in resistance to a delta in voltage or current to use this signal. This is done by connecting the wires from our RTD to a transmitter, a PLC, DCS, or even a PID controller.
A bridge circuit known as the Wheatstone bridge is used for that purpose: The Wheatstone bridge is composed of three resistors, a power source, a voltmeter, or a voltage transducer.
=============================
=============================
=============================
Did you miss out on the latest and greatest? Catch up now by watching our videos right here:
=============================
Ready to stay on the cutting edge of our newest video content? Be sure to hit subscribe and join us on this exciting YouTube channel!
=============================
=============================
#rtd #sensor #realpars
Комментарии
 0:01:41
0:01:41
 0:08:10
0:08:10
 0:02:55
0:02:55
 0:05:17
0:05:17
 0:11:34
0:11:34
 0:02:16
0:02:16
 0:09:05
0:09:05
 0:02:10
0:02:10
 0:00:51
0:00:51
 0:03:17
0:03:17
 0:05:56
0:05:56
 0:11:02
0:11:02
 0:02:36
0:02:36
 0:08:59
0:08:59
 0:04:59
0:04:59
 0:08:30
0:08:30
 0:08:52
0:08:52
 0:03:04
0:03:04
 0:02:53
0:02:53
 0:05:25
0:05:25
 0:08:54
0:08:54
 0:08:41
0:08:41
 0:07:26
0:07:26
 0:01:41
0:01:41