filmov
tv
Dicot leaf anatomy | 11th biology practical | Monocot leaf anatomy | 'Exploring Leaf Anatomy biolab

Показать описание
Title for YouTube: "Exploring Leaf Anatomy: A Comparative Study of Dicot and Monocot Leaves in 11th Biology Practical"
Aim: The aim of this biology practical experiment is to analyze and compare the anatomical characteristics of dicot and monocot leaves under a microscope, highlighting their structural differences and adaptations.
Requirements:
1. Dicot and monocot leaf specimens (e.g., rose and grass leaves)
2. Microscope
3. Microscope slides
4. Cover slips
5. Razor blade or scalpel
6. Forceps
7. Iodine solution (for starch detection)
8. Safranin stain (for cell structures)
9. Dropper
10. Water
11. Paper towels
Procedure:
1. Carefully collect fresh dicot and monocot leaf specimens.
2. Using a razor blade or scalpel, gently cut thin sections of the leaves.
3. Place these thin sections onto separate microscope slides.
4. Add a small drop of iodine solution onto each slide to test for the presence of starch.
5. Stain the leaf sections with safranin to enhance the visibility of cell structures.
6. Gently lower a cover slip onto each slide to prevent air bubbles.
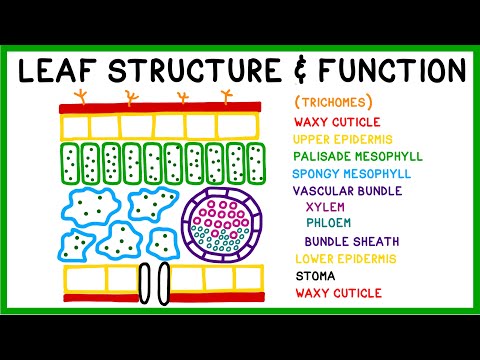
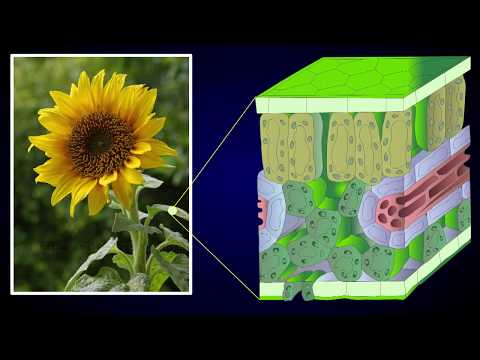
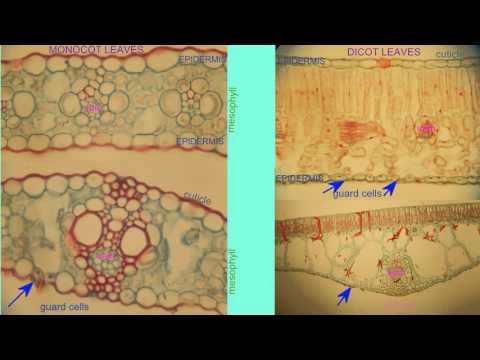
7. Under the microscope, begin your observation by focusing on the epidermal layers.
8. Compare and contrast the differences in epidermal cells, stomata, and their distribution on both types of leaves.
9. Move on to studying the arrangement of vascular bundles, noting any variations between dicot and monocot leaves.
10. Examine the palisade and spongy mesophyll layers, and observe the presence and distribution of chloroplasts.
11. Record your observations, noting any distinctive features, cell shapes, and sizes.
Result:
After a thorough microscopic analysis, document the structural differences between dicot and monocot leaves. Highlight the adaptations that each leaf type has developed based on their environment and functions.
Tags: Biology practical, Leaf anatomy, Dicot leaves, Monocot leaves, Microscopic observation, Plant adaptations.
Aim: The aim of this biology practical experiment is to analyze and compare the anatomical characteristics of dicot and monocot leaves under a microscope, highlighting their structural differences and adaptations.
Requirements:
1. Dicot and monocot leaf specimens (e.g., rose and grass leaves)
2. Microscope
3. Microscope slides
4. Cover slips
5. Razor blade or scalpel
6. Forceps
7. Iodine solution (for starch detection)
8. Safranin stain (for cell structures)
9. Dropper
10. Water
11. Paper towels
Procedure:
1. Carefully collect fresh dicot and monocot leaf specimens.
2. Using a razor blade or scalpel, gently cut thin sections of the leaves.
3. Place these thin sections onto separate microscope slides.
4. Add a small drop of iodine solution onto each slide to test for the presence of starch.
5. Stain the leaf sections with safranin to enhance the visibility of cell structures.
6. Gently lower a cover slip onto each slide to prevent air bubbles.
7. Under the microscope, begin your observation by focusing on the epidermal layers.
8. Compare and contrast the differences in epidermal cells, stomata, and their distribution on both types of leaves.
9. Move on to studying the arrangement of vascular bundles, noting any variations between dicot and monocot leaves.
10. Examine the palisade and spongy mesophyll layers, and observe the presence and distribution of chloroplasts.
11. Record your observations, noting any distinctive features, cell shapes, and sizes.
Result:
After a thorough microscopic analysis, document the structural differences between dicot and monocot leaves. Highlight the adaptations that each leaf type has developed based on their environment and functions.
Tags: Biology practical, Leaf anatomy, Dicot leaves, Monocot leaves, Microscopic observation, Plant adaptations.
Комментарии
 0:05:53
0:05:53
 0:05:53
0:05:53
 0:09:36
0:09:36
 0:00:11
0:00:11
 0:04:33
0:04:33
 0:04:32
0:04:32
 0:08:27
0:08:27
 0:00:30
0:00:30
 0:36:07
0:36:07
 0:02:41
0:02:41
 0:10:18
0:10:18
 0:04:29
0:04:29
 0:21:21
0:21:21
 0:36:18
0:36:18
 0:03:10
0:03:10
 0:04:31
0:04:31
 0:00:07
0:00:07
 0:17:04
0:17:04
 0:07:20
0:07:20
 0:46:40
0:46:40
 0:46:07
0:46:07
 0:08:16
0:08:16
 0:00:59
0:00:59
 0:01:49
0:01:49