filmov
tv
Burkitt lymphoma overview

Показать описание
Burkitt lymphoma (BL) is a highly aggressive B cell neoplasm that can present in one of three distinct clinical forms: endemic, sporadic, and immunodeficiency-associated.
Starry sky: The benign histiocytes ("the stars") are large with abundant, clear cytoplasm and are dispersed relatively evenly throughout a background of basophilic tumor cells ("the sky").
There is an extremely high rate of proliferation, as well as a high rate of apoptotic cell death as evidenced by a Ki-67+ (MIB-1+) cells fraction approaching 100 percent and a "starry-sky" pattern.
BL cells express surface IgM and B cell-associated antigens (CD19, CD20, CD22, CD79a), as well as CD10, HLA-DR, and CD43. They lack CD5, BCL-2, TdT, and typically lack CD23.
BL tumor cells are monomorphic, medium-sized cells with round nuclei, multiple nucleoli, and basophilic cytoplasm. Prominent cytoplasmic lipid vacuoles are usually evident on imprints or smears.
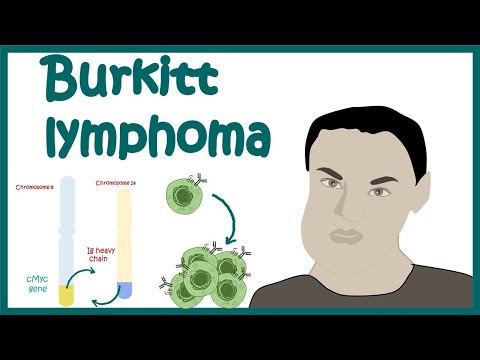
BL is strongly (but not uniformly) associated with a translocation between the long arm of chromosome 8, the site of the MYC oncogene (8q24), and one of three locations on Ig genes: t(8;14), t(2;8), or t(8;22).
Starry sky: The benign histiocytes ("the stars") are large with abundant, clear cytoplasm and are dispersed relatively evenly throughout a background of basophilic tumor cells ("the sky").
There is an extremely high rate of proliferation, as well as a high rate of apoptotic cell death as evidenced by a Ki-67+ (MIB-1+) cells fraction approaching 100 percent and a "starry-sky" pattern.
BL cells express surface IgM and B cell-associated antigens (CD19, CD20, CD22, CD79a), as well as CD10, HLA-DR, and CD43. They lack CD5, BCL-2, TdT, and typically lack CD23.
BL tumor cells are monomorphic, medium-sized cells with round nuclei, multiple nucleoli, and basophilic cytoplasm. Prominent cytoplasmic lipid vacuoles are usually evident on imprints or smears.
BL is strongly (but not uniformly) associated with a translocation between the long arm of chromosome 8, the site of the MYC oncogene (8q24), and one of three locations on Ig genes: t(8;14), t(2;8), or t(8;22).
 0:07:50
0:07:50
 0:07:24
0:07:24
 0:34:43
0:34:43
 0:12:21
0:12:21
 0:06:40
0:06:40
 0:04:47
0:04:47
 0:05:20
0:05:20
 0:56:47
0:56:47
 0:05:10
0:05:10
 0:09:18
0:09:18
 0:02:27
0:02:27
 0:16:08
0:16:08
 0:01:25
0:01:25
 0:04:50
0:04:50
 0:03:16
0:03:16
 0:01:22
0:01:22
 0:01:20
0:01:20
 0:32:15
0:32:15
 0:06:17
0:06:17
 0:04:00
0:04:00
 0:01:04
0:01:04
 0:02:09
0:02:09
 0:03:10
0:03:10
 0:03:46
0:03:46