filmov
tv
Integral using angle sum identity
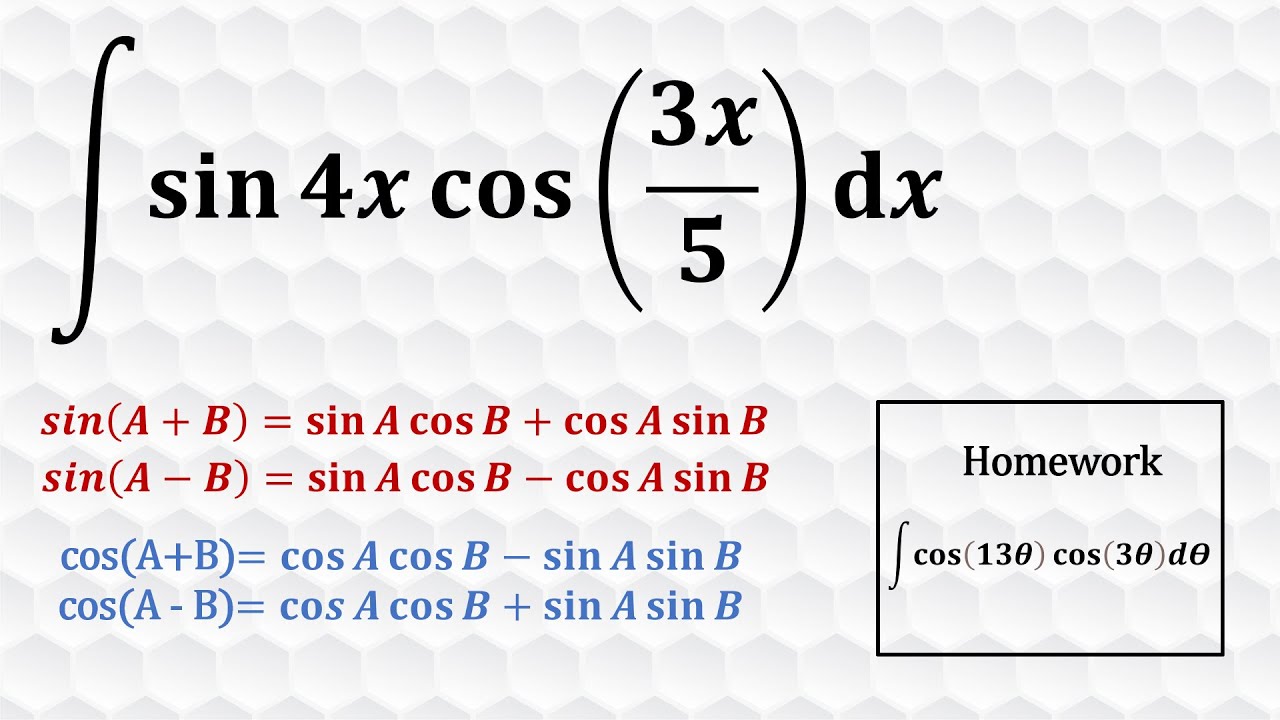
Показать описание
In this video, I showed how to modify and evaluate an integral using angle sum identities
Integral using angle sum identity
Using angle sum identities for Integration
How REAL Men Integrate Functions
Never forget your angle sum identities again
Integrating by Double Angle Substitution
Integration Using the Double Angle Formulae for Sine and Cosine
Product To Sum Identities and Sum To Product Formulas - Trigonometry
Determine Indefinite Integrals of Trig Functions with Double Angle Substitutions
Finding the sine angle sum formula using Euler's identity
Trigonometric Integrals 3: The Square to Double-Angle Formulas
Integration Using the Double Angle Formula
Double Angle Formula
What Integration Technique Should I Use? (trig sub, u sub, DI method, partial fractions) calculus 2
Easy Way to Remember Derivatives of Trigonometry Ratios #shorts | How to Remember Derivatives Easily
Topic 5 Integrals By Double Angle Identities
7.2.5 Trigonometric Integrals involving the half angle formulas
Integrating using Half/Double Angle Identities
YOU CAN'T USE EULER'S IDENTITY TO PROVE THE ANGLE SUM IDENTITIES! | Tricky Parts of Calcul...
Using double angle identities to solve integrals (Part 1)
OCR MEI Core 4 1.19 Using a Double Angle Formula to Integrate
100 integrals (world record?)
Trigonometry double angle formulae #shorts #shortsvideo #trending #viral #ncertsolutions
Angle Sum formula, proof by complex number
Calculus 2 Lecture 7.3: Integrals By Trigonometric Substitution
Комментарии
 0:08:23
0:08:23
 0:08:12
0:08:12
 0:00:35
0:00:35
 0:03:12
0:03:12
 0:05:57
0:05:57
 0:14:08
0:14:08
 0:13:25
0:13:25
 0:04:14
0:04:14
 0:05:54
0:05:54
 0:06:03
0:06:03
 0:06:26
0:06:26
 0:00:54
0:00:54
 0:22:40
0:22:40
 0:00:50
0:00:50
 0:12:19
0:12:19
 0:06:49
0:06:49
 0:07:42
0:07:42
 0:15:20
0:15:20
 0:12:33
0:12:33
 0:03:25
0:03:25
 5:50:23
5:50:23
 0:00:05
0:00:05
 0:05:02
0:05:02
 2:09:24
2:09:24