filmov
tv
HOW TO STOP LIVER PAIN?

Показать описание
.
Chapters
0:00 Introduction
0:05 What is Liver Pain?
0:12 What causes liver Pain
0:19 Infection
0:44 medication Abuse
1:02 Alcohol Abuse
1:20 Autoimmune Diseases
1:37 Fatty Liver
1:56 Cancer
2:06 How to stop Liver pain
2:12 Healthy Diet
2:32 Stay Hydrated
2:56 Infection
Liver disease, or hepatic disease, is any of many diseases of the liver.[1] If long-lasting it is termed chronic liver disease.[3] Although the diseases differ in detail, liver diseases often have features in common. Some of the signs and symptoms of a liver disease are the following:
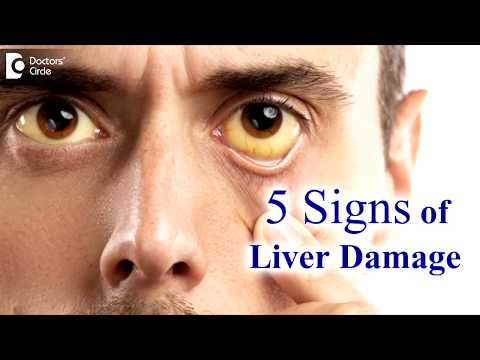
Jaundice[4]
Confusion and altered consciousness caused by hepatic encephalopathy.[5]
Thrombocytopenia and coagulopathy.[6]
Risk of bleeding symptoms particularly taking place in gastrointestinal tract[There are more than a hundred different liver diseases. Some of the most common are:[8]
Fascioliasis, a parasitic infection of liver caused by a liver fluke of the genus Fasciola, mostly Fasciola hepatica.[9]
Hepatitis, inflammation of the liver, is caused by various viruses (viral hepatitis) also by some liver toxins (e.g. alcoholic hepatitis), autoimmunity (autoimmune hepatitis) or hereditary conditions.[10]
Alcoholic liver disease is a hepatic manifestation of alcohol overconsumption, including fatty liver disease, alcoholic hepatitis, and cirrhosis. Analogous terms such as "drug-induced" or "toxic" liver disease are also used to refer to disorders caused by various drugs.[11]
Fatty liver disease (hepatic steatosis) is a reversible condition where large vacuoles of triglyceride fat accumulate in liver cells.[12] Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is a spectrum of disease associated with obesity and metabolic syndrome.[13]
Hereditary diseases that cause damage to the liver include hemochromatosis,[14] involving accumulation of iron in the body, and Wilson's disease. Liver damage is also a clinical feature of alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency[15] and glycogen storage disease type II.[16]
In transthyretin-related hereditary amyloidosis, the liver produces a mutated transthyretin protein which has severe neurodegenerative or cardiopathic effects. Liver transplantation can be curative.[17]
Chapters
0:00 Introduction
0:05 What is Liver Pain?
0:12 What causes liver Pain
0:19 Infection
0:44 medication Abuse
1:02 Alcohol Abuse
1:20 Autoimmune Diseases
1:37 Fatty Liver
1:56 Cancer
2:06 How to stop Liver pain
2:12 Healthy Diet
2:32 Stay Hydrated
2:56 Infection
Liver disease, or hepatic disease, is any of many diseases of the liver.[1] If long-lasting it is termed chronic liver disease.[3] Although the diseases differ in detail, liver diseases often have features in common. Some of the signs and symptoms of a liver disease are the following:
Jaundice[4]
Confusion and altered consciousness caused by hepatic encephalopathy.[5]
Thrombocytopenia and coagulopathy.[6]
Risk of bleeding symptoms particularly taking place in gastrointestinal tract[There are more than a hundred different liver diseases. Some of the most common are:[8]
Fascioliasis, a parasitic infection of liver caused by a liver fluke of the genus Fasciola, mostly Fasciola hepatica.[9]
Hepatitis, inflammation of the liver, is caused by various viruses (viral hepatitis) also by some liver toxins (e.g. alcoholic hepatitis), autoimmunity (autoimmune hepatitis) or hereditary conditions.[10]
Alcoholic liver disease is a hepatic manifestation of alcohol overconsumption, including fatty liver disease, alcoholic hepatitis, and cirrhosis. Analogous terms such as "drug-induced" or "toxic" liver disease are also used to refer to disorders caused by various drugs.[11]
Fatty liver disease (hepatic steatosis) is a reversible condition where large vacuoles of triglyceride fat accumulate in liver cells.[12] Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is a spectrum of disease associated with obesity and metabolic syndrome.[13]
Hereditary diseases that cause damage to the liver include hemochromatosis,[14] involving accumulation of iron in the body, and Wilson's disease. Liver damage is also a clinical feature of alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency[15] and glycogen storage disease type II.[16]
In transthyretin-related hereditary amyloidosis, the liver produces a mutated transthyretin protein which has severe neurodegenerative or cardiopathic effects. Liver transplantation can be curative.[17]
Комментарии
 0:04:11
0:04:11
 0:04:05
0:04:05
 0:01:27
0:01:27
 0:07:29
0:07:29
 0:05:58
0:05:58
 0:01:20
0:01:20
 0:01:10
0:01:10
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:32:07
0:32:07
 0:01:19
0:01:19
 0:09:28
0:09:28
 0:03:35
0:03:35
 0:12:30
0:12:30
 0:07:10
0:07:10
 0:01:52
0:01:52
 0:04:11
0:04:11
 0:02:40
0:02:40
 0:00:53
0:00:53
 0:06:21
0:06:21
 0:07:16
0:07:16
 0:01:18
0:01:18
 0:13:23
0:13:23
 0:03:18
0:03:18
 0:05:26
0:05:26