filmov
tv
Homeostatic Control Systems - Homeostatic Control Mechanisms and Feedback Control Loops
Показать описание
In this video we discuss what are homeostatic control systems and how they work. We cover feedback loops and how they work to help maintain homeostasis.
Homeostatic control mechanisms or systems
In order to maintain homeostasis cells must be in an environment that allows them to function properly with changing external conditions. Almost all of the organs and systems in the body must work to maintain homeostasis. If the body needs to change the internal environment it does so through what is called homeostatic control mechanisms.
For instance, when you go for a run, your body needs more oxygen, and your body produces more carbon dioxide. So, the internal environment must adapt to the changing needs. During your run, your breathing will increase, bringing more oxygen in and eliminating the increased production of carbon dioxide, your heart beat and stroke volume will increase, thus increasing the amount of nutrient rich blood being sent throughout your body.
This process of the body adjusting to a change is called a feedback control loop or feedback control system. These control loops transmit information in mainly 2 ways, through nervous impulses or by chemical messengers called hormones. Weather the nervous impulses or hormones are transmitting the information, the feedback control loops work in the same way and have the same basic components.
The feedback control loops consist of 4 main components. A sensor mechanism, an integrator or control center, an effector mechanism and feedback.
Hormone producing glands and sensory nerve cells can act as homeostatic sensors. If something changes outside of the normal set point range for homeostasis, a sensor transmits a signal to the next component of the feedback loop, the integrator.
The integrator is the control center of the feedback loop and many times it is in an area of the brain. It gets this signal or variable and analyzes it and checks it with other signals or variables it has received from other sensors. It checks the value of the variables it has received against the normal set point range for those variables. If the integrator determines these variables are outside of the normal set point range, then, some type of action is needed.
If action is necessary, the integrator sends a signal to the third component of the feedback control loop, the effector mechanism.
Effectors are organs, like glands or muscles, which provide the response that the integrator, or control center desires. The goal of the effectors is to influence or change the values of the variables. This can be positive or negative changes to the variables, such as increasing or decreasing heart rate, or altering the concentration of glucose in the blood stream. Glucose being the main source of fuel for cells.
As these effectors make changes, the variables attain new values, and this is sent back through the feedback control loop. For instance, if you are walking, then you start jogging, effectors will increase your heart rate, based on the mechanisms of the feedback control loop.
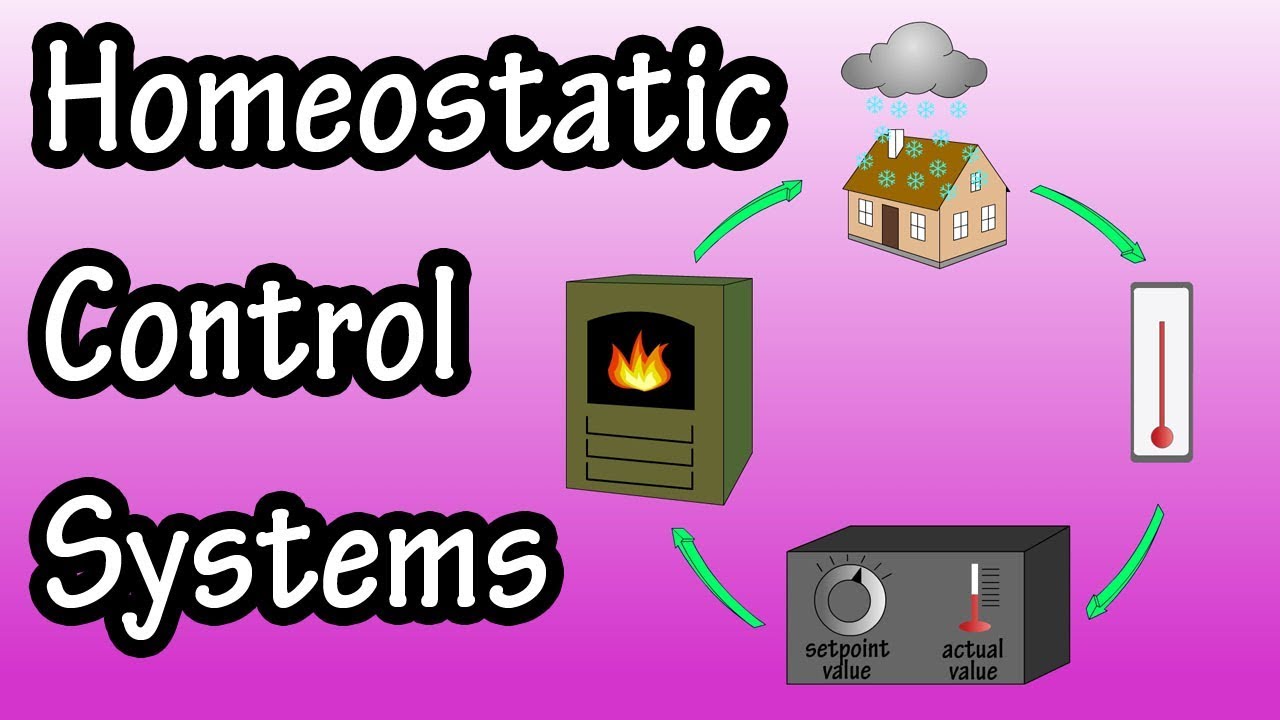
Many sources use a diagram of a furnace controlled by a thermostat to explain this process more clearly.
Here we have a house, and here we have a person. Let’s say that in both situations a stimulus happens, that being a cold front blows in, causing a decrease in temperature. The house has a thermometer, which is its sensor, and the person has temperature receptors in the skin, which are the sensor mechanism for the body. The thermometer sends the information that the temperature or variable has decreased, through wires to its integrator, the thermostat. The temperature receptors in the skin send the variable change through nerve fibers to the brain, or the integrator for the body in this situation. The integrators, or control centers for both the body and house, check the value of the newly received variables against the set point range that each of them has allowed for this type of variable.
Since this temperature variable change does not lie in the set point range, the integrators send a signal to effectors to do something to get these variables within this set point range. In the case of the house the thermostat sends a message through wires to the furnace to crank the heat up. In the body, the brain sends a message through nerve fibers to the muscles to start shivering to generate some heat.
Timestamps
0:00 Maintaining homeostasis
0:17 Homeostatic control mechanisms
0:49 What are feedback control loops
1:15 The 4 main components of feedback control loops
1:26 Sensor mechanism
1:37 Integrator/control center
2:10 Effector mechanism
3:06 Feedback control loop example
Homeostatic control mechanisms or systems
In order to maintain homeostasis cells must be in an environment that allows them to function properly with changing external conditions. Almost all of the organs and systems in the body must work to maintain homeostasis. If the body needs to change the internal environment it does so through what is called homeostatic control mechanisms.
For instance, when you go for a run, your body needs more oxygen, and your body produces more carbon dioxide. So, the internal environment must adapt to the changing needs. During your run, your breathing will increase, bringing more oxygen in and eliminating the increased production of carbon dioxide, your heart beat and stroke volume will increase, thus increasing the amount of nutrient rich blood being sent throughout your body.
This process of the body adjusting to a change is called a feedback control loop or feedback control system. These control loops transmit information in mainly 2 ways, through nervous impulses or by chemical messengers called hormones. Weather the nervous impulses or hormones are transmitting the information, the feedback control loops work in the same way and have the same basic components.
The feedback control loops consist of 4 main components. A sensor mechanism, an integrator or control center, an effector mechanism and feedback.
Hormone producing glands and sensory nerve cells can act as homeostatic sensors. If something changes outside of the normal set point range for homeostasis, a sensor transmits a signal to the next component of the feedback loop, the integrator.
The integrator is the control center of the feedback loop and many times it is in an area of the brain. It gets this signal or variable and analyzes it and checks it with other signals or variables it has received from other sensors. It checks the value of the variables it has received against the normal set point range for those variables. If the integrator determines these variables are outside of the normal set point range, then, some type of action is needed.
If action is necessary, the integrator sends a signal to the third component of the feedback control loop, the effector mechanism.
Effectors are organs, like glands or muscles, which provide the response that the integrator, or control center desires. The goal of the effectors is to influence or change the values of the variables. This can be positive or negative changes to the variables, such as increasing or decreasing heart rate, or altering the concentration of glucose in the blood stream. Glucose being the main source of fuel for cells.
As these effectors make changes, the variables attain new values, and this is sent back through the feedback control loop. For instance, if you are walking, then you start jogging, effectors will increase your heart rate, based on the mechanisms of the feedback control loop.
Many sources use a diagram of a furnace controlled by a thermostat to explain this process more clearly.
Here we have a house, and here we have a person. Let’s say that in both situations a stimulus happens, that being a cold front blows in, causing a decrease in temperature. The house has a thermometer, which is its sensor, and the person has temperature receptors in the skin, which are the sensor mechanism for the body. The thermometer sends the information that the temperature or variable has decreased, through wires to its integrator, the thermostat. The temperature receptors in the skin send the variable change through nerve fibers to the brain, or the integrator for the body in this situation. The integrators, or control centers for both the body and house, check the value of the newly received variables against the set point range that each of them has allowed for this type of variable.
Since this temperature variable change does not lie in the set point range, the integrators send a signal to effectors to do something to get these variables within this set point range. In the case of the house the thermostat sends a message through wires to the furnace to crank the heat up. In the body, the brain sends a message through nerve fibers to the muscles to start shivering to generate some heat.
Timestamps
0:00 Maintaining homeostasis
0:17 Homeostatic control mechanisms
0:49 What are feedback control loops
1:15 The 4 main components of feedback control loops
1:26 Sensor mechanism
1:37 Integrator/control center
2:10 Effector mechanism
3:06 Feedback control loop example
Комментарии
 0:04:57
0:04:57
 0:06:24
0:06:24
 0:21:59
0:21:59
 0:05:50
0:05:50
 0:15:20
0:15:20
 0:06:07
0:06:07
 0:03:47
0:03:47
 0:08:10
0:08:10
 0:14:32
0:14:32
 0:03:09
0:03:09
 0:06:56
0:06:56
 0:02:26
0:02:26
 0:07:16
0:07:16
 0:00:44
0:00:44
 0:12:49
0:12:49
 0:44:28
0:44:28
 0:07:55
0:07:55
 0:10:18
0:10:18
 0:05:17
0:05:17
 0:28:27
0:28:27
 0:14:46
0:14:46
 0:12:47
0:12:47
 0:09:28
0:09:28
 0:04:40
0:04:40