filmov
tv
Multivariable calculus, class #34: scalar surface integrals
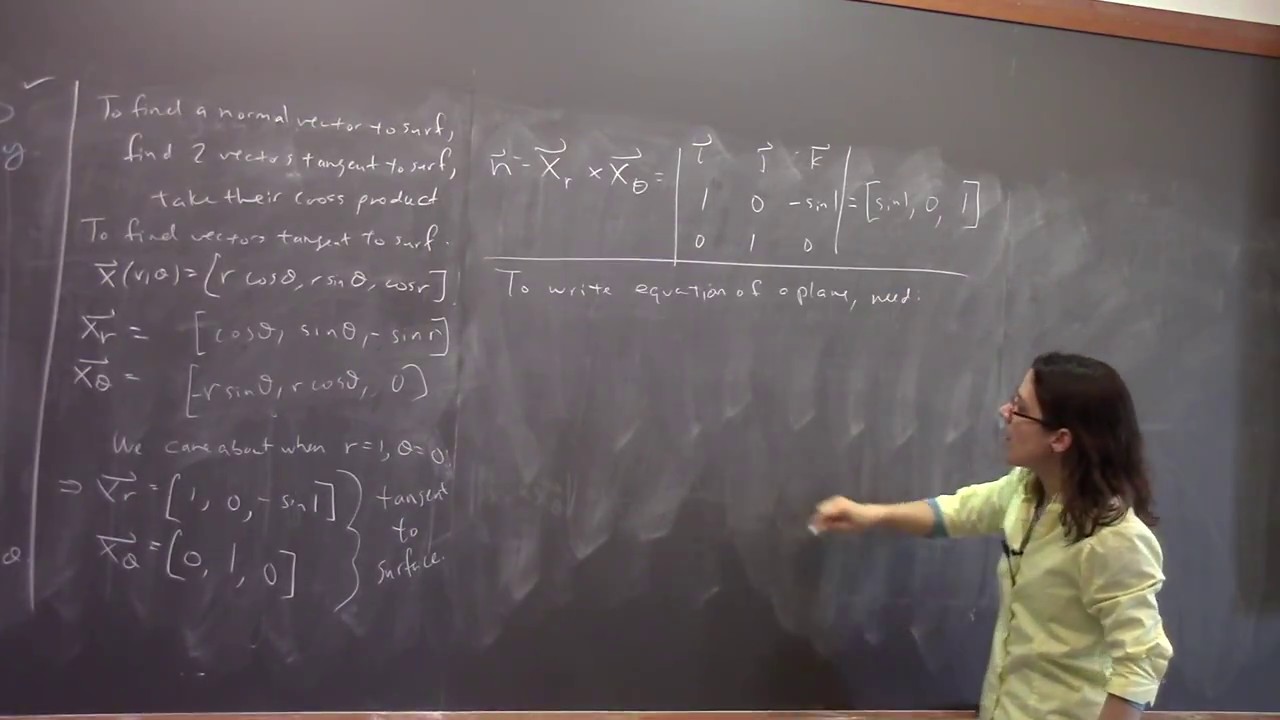
Показать описание
Mathematician spotlight: Henry Segerman
We briefly discuss 3D printing, and show a short clip about stereographic projection. We do an example using the parameterized "waterdrop surface" (DD's favorite surface), parameterized by r and theta. First we look at the r-curves and the theta-curves on the surface. We use the tangent vectors in the r- and theta-directions to find a normal vector to the surface, and we use it to find the equation for a tangent plane. Then we discuss how to find the surface area of a parameterized surface, using an infinitesimal parallelogram, and a method analogous to the Jacobian expansion factor. We find the surface area of a cone, first using basic geometry and then using the surface area method that we just derived. We give the equation for scalar surface integrals, and do an example where the "surface" is the xy-plane, and then compute it using a standard double integral in polar coordinates and then with parameterized surfaces, and see that everything comes out exactly the same.
We briefly discuss 3D printing, and show a short clip about stereographic projection. We do an example using the parameterized "waterdrop surface" (DD's favorite surface), parameterized by r and theta. First we look at the r-curves and the theta-curves on the surface. We use the tangent vectors in the r- and theta-directions to find a normal vector to the surface, and we use it to find the equation for a tangent plane. Then we discuss how to find the surface area of a parameterized surface, using an infinitesimal parallelogram, and a method analogous to the Jacobian expansion factor. We find the surface area of a cone, first using basic geometry and then using the surface area method that we just derived. We give the equation for scalar surface integrals, and do an example where the "surface" is the xy-plane, and then compute it using a standard double integral in polar coordinates and then with parameterized surfaces, and see that everything comes out exactly the same.
Multivariable calculus, class #34: scalar surface integrals
Multi Calc Class #34, Triple Integral Calculation (in Rect & Cylindrical Coords), Line Integrals
Vector Calculus Complete Animated Course for DUMMIES
Multivariable calculus, class #29: Scalar line integrals
Multivariable calculus 3.4 - Surface integrals
Multivariable Calculus full Course || Multivariate Calculus Mathematics
How much does B.TECH pay?
Line Integrals | Lecture 10 | Evaluation of Line Integral of a Scalar Field
How to Make it Through Calculus (Neil deGrasse Tyson)
Multivariable Calculus 34 Flux Integrals
How much does a PHYSICS RESEARCHER make?
How curvy is a curve? Intro to Curvature & Circles of Curvature | Multi-variable Calculus
MA 261 Calculus III Multivariate Calculus Lecture 34
Equations of Planes: Vector & Component Forms | Multivariable Calculus
Multivariable calculus, class #33: Parameterized surfaces
NEWYES Calculator VS Casio calculator
251 midterm 1 practice problems: #34-#36
EXAMPLE of COMPUTING a LINE INTEGRAL of SCALAR FIELD -- Vector Calculus, Calculus 3
Vector valued function derivative example | Multivariable Calculus | Khan Academy
Tamasha Dekho 😂 IITian Rocks Relatives Shock 😂😂😂 #JEEShorts #JEE #Shorts
Vector Calculus for BSc Physics | Scalar, Vector Field and Functions - with 3D Models | 1st year BSc
Fluid flow and vector fields | Multivariable calculus | Khan Academy
Ducky first meeting with his wife aroob jatoi#makhan
Scalar Line Integrals
Комментарии
 0:49:18
0:49:18
 0:47:52
0:47:52
 0:46:44
0:46:44
 0:45:31
0:45:31
 0:27:38
0:27:38
 3:36:30
3:36:30
 0:00:34
0:00:34
 0:06:34
0:06:34
 0:03:38
0:03:38
 0:48:07
0:48:07
 0:00:44
0:00:44
 0:07:48
0:07:48
 1:00:00
1:00:00
 0:04:28
0:04:28
 0:51:40
0:51:40
 0:00:14
0:00:14
 0:10:43
0:10:43
 0:04:01
0:04:01
 0:12:45
0:12:45
 0:00:13
0:00:13
 0:16:34
0:16:34
 0:03:35
0:03:35
 0:00:20
0:00:20
 0:34:02
0:34:02