filmov
tv
Lec-10: Floating Point Representation with examples | Number System

Показать описание
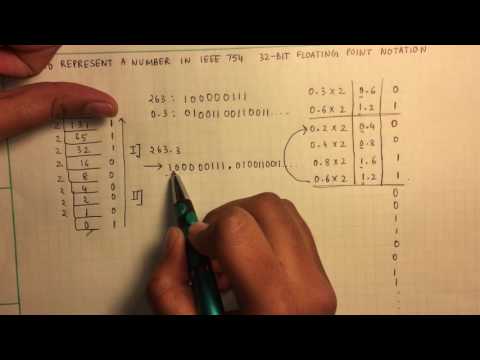
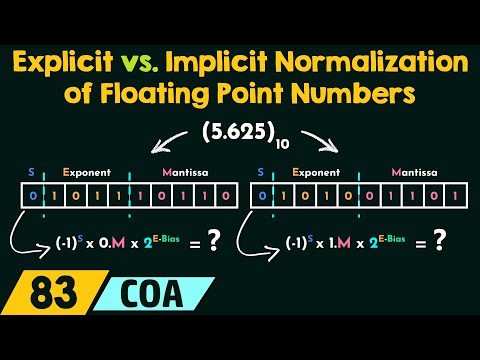
Floating point refers to the fact that a number's radix point(decimal point, or, more commonly in computers, binary point) can "float"; that is , it can be placed anywhere relative to the significant digits of the number.
►Number System (Complete Playlist):
Other subject-wise playlist Links:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
►Design and Analysis of algorithms (DAA):
►Database Management System:
► Software Engineering:
►Artificial Intelligence:
►Computer Networks:
►Operating System:
►Structured Query Language (SQL):
►Discrete Mathematics:
►Compiler Design:
►Theory of Computation :
►Cloud Computing & BIG Data:
►Programming in C :
►Data Structure:
►Computer Architecture :
►Graph Theory (Complete Playlist):
►Digital Logic:
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Our social media Links:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
►For Any Query, Suggestion or notes contribution:
Комментарии
 0:18:10
0:18:10
 0:08:13
0:08:13
 0:13:50
0:13:50
 0:09:37
0:09:37
 0:09:27
0:09:27
 0:09:16
0:09:16
 0:12:32
0:12:32
 0:05:31
0:05:31
 0:11:20
0:11:20
 0:13:12
0:13:12
 0:21:34
0:21:34
 0:14:03
0:14:03
 1:16:55
1:16:55
 0:42:29
0:42:29
 0:11:14
0:11:14
 1:36:22
1:36:22
 0:00:14
0:00:14
 0:09:24
0:09:24
 0:13:13
0:13:13
 0:07:54
0:07:54
 0:05:09
0:05:09
 0:16:20
0:16:20
 0:08:40
0:08:40
 0:17:03
0:17:03