filmov
tv
Explain instruction cycle, machine cycle and T-states | CSITAN

Показать описание
Explain instruction cycle, machine cycle and T-states. Draw the timing diagram of IN instructions
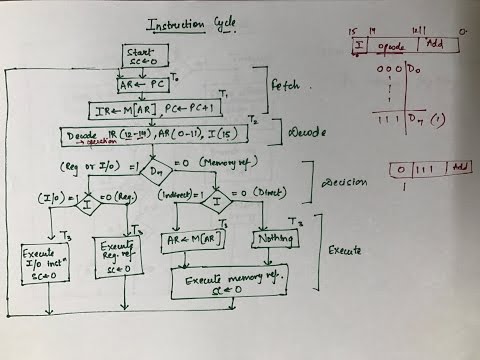
The instruction cycle (also known as the fetch-decode-execute cycle, or simply the fetch-execute cycle) is the cycle that the central processing unit (CPU) follows from boot-up until the computer has shut down in order to process instructions.
A program residing in the memory unit of a computer consists of a sequence of instructions. These instructions are executed by the processor by going through a cycle for each instruction. In a basic computer, each instruction cycle consists of the following phases:
1. Fetch instruction from memory.
2. Decode the instruction.
3. Read the effective address from memory.
4. Execute the instruction.
Fetch cycle: The next instruction is fetched by the address stored in program counter (PC) and then stored in the instruction register.
Decode instruction: Decoder interprets the encoded instruction from instruction register.
Reading effective address: The address given in instruction is read from main memory and required data is fetched. The effective address depends on direct addressing mode or indirect addressing mode.
Execution cycle: consists memory read (MR), memory write (MW), input output read (IOR) and input output write (IOW)
The instruction cycle (also known as the fetch-decode-execute cycle, or simply the fetch-execute cycle) is the cycle that the central processing unit (CPU) follows from boot-up until the computer has shut down in order to process instructions.
A program residing in the memory unit of a computer consists of a sequence of instructions. These instructions are executed by the processor by going through a cycle for each instruction. In a basic computer, each instruction cycle consists of the following phases:
1. Fetch instruction from memory.
2. Decode the instruction.
3. Read the effective address from memory.
4. Execute the instruction.
Fetch cycle: The next instruction is fetched by the address stored in program counter (PC) and then stored in the instruction register.
Decode instruction: Decoder interprets the encoded instruction from instruction register.
Reading effective address: The address given in instruction is read from main memory and required data is fetched. The effective address depends on direct addressing mode or indirect addressing mode.
Execution cycle: consists memory read (MR), memory write (MW), input output read (IOR) and input output write (IOW)
The Fetch-Execute Cycle: What's Your Computer Actually Doing?
What Is Machine Cycle ? | Difference Between Machine Cycle And Instruction Cycle | CPU Cycle
Explain instruction cycle, machine cycle and T-states | CSITAN
Instruction cycle | machine cycle | T state | microprocessor
What is Instruction Cycle in Computer Organization explained by Vikas Sir
computer architecture CPU instructions and addresses explained
understand very important CPU instruction cycle in short with diagram 🔥|| fetch-decode-execute cycle...
Instruction Cycle in Computer Organization & Architecture: Detailed Steps | COA
What Is Instruction Cycle ? | Fetch , Decode And Execute Cycle Explained Step By Step
What Is T State Machine Cycle and Instruction Cycle in 8051 Microcontroller
8085 Instruction Cycle | Malayaam
Machine Cycle and Instruction Cycle in 8051 Microcontroller - Microcontrollers and Its Applications
Computer Architecture - 006 : What is Instruction Cycle ? #os #tutorial
The Fetch Decode Execute Cycle
L-1.13: What is Instruction Format | Understand Computer Organisation with Simple Story
IB DP Computer Science - Topic 2: Computer Organization - 2.1.4: The Machine Instruction Cycle
Instruction cycle | COA
Instruction cycle ,machine cycle and T state
Machine Cycles in Microprocessor 8085 | Control Signals with Different Machine Cycles in 8085
The Fetch Decode Execute Cycle | GCSE Computer Science | BBC Bitesize | Too Tall Productions
Understanding Instruction Cycle Fetch and Decode Phase of Instruction Cycle || Lesson 19 ||
Instruction Cycle State Transition Diagram in Computer Organization & Architecture | COA
Instruction Cycle In Computer Organization || Architecture ||Flowchart|Register Transfer Fetch phase
Instruction Cycle
Комментарии
 0:09:04
0:09:04
 0:07:34
0:07:34
 0:00:05
0:00:05
 0:05:22
0:05:22
 0:05:50
0:05:50
 0:12:00
0:12:00
 0:00:09
0:00:09
 0:09:09
0:09:09
 0:20:01
0:20:01
 0:15:15
0:15:15
 0:14:38
0:14:38
 0:15:30
0:15:30
 0:00:59
0:00:59
 0:16:45
0:16:45
 0:10:40
0:10:40
 0:11:53
0:11:53
 0:00:09
0:00:09
 0:03:06
0:03:06
 0:10:32
0:10:32
 0:05:17
0:05:17
 0:23:23
0:23:23
 0:08:04
0:08:04
 0:21:29
0:21:29
 0:05:23
0:05:23