filmov
tv
Measures of Forecasting Errors

Показать описание
Measures of Forecasting Errors
Forecasting: Moving Averages, MAD, MSE, MAPE
Forecasting Techniques : Moving Average, MAD, MSE,MAPE
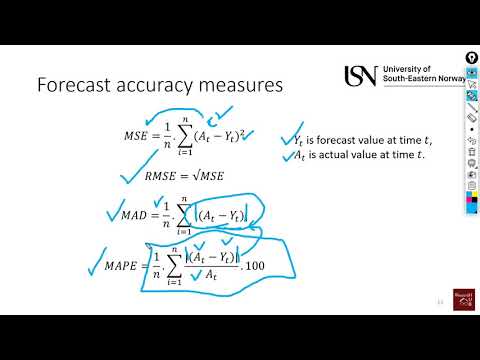
Forecasting (7): Forecast accuracy measures (MSE, RMSE, MAD & MAPE)
Measuring Forecast Error in Time Series Forecasting using MSE, MAD, and MAPE techniques
Forecasting - Measurement of Forecasting error - Part 2
03_01_P1 Introduction to Demand Forecasting, Measures of Forecast Error
Forecasting - Measurement of Forecasting error - Part 3
Ch04. Forecasting (5) Forecasting Accuracy Measures
Error Measures in Forecasting
Measures of Forecasting Error
Forecasting Error Measures
Forecasting Metrics | How To Evaluate Your Time Series Forecast
Basic Excel Business Analytics #54: Basic Forecasting Methods & Measures of Forecast Error
Forecasting - Measurement of Forecasting error - Part 1
Forecasting Common measure of error
Forecast Accuracy & Time Series Regression | SCMT 3623
DEMAND PLANNING: PART 2-FORECASTING, TIME SERIES ANALYSIS, CALCULATING ERRORS IN FORECASTING
Forecasting Accuracy
Forecasting: Exponential Smoothing, MSE
Forecasting Part 2 (Accuracy Measures)
7. Forecasting errors in operations management | Business forecasting #demand #forecast
Forecasting Errors
Lec 14- Forecasting Errors
Комментарии
 0:30:19
0:30:19
 0:04:52
0:04:52
 0:10:45
0:10:45
 0:04:35
0:04:35
 0:25:27
0:25:27
 0:17:33
0:17:33
 0:19:16
0:19:16
 0:10:06
0:10:06
 0:09:20
0:09:20
 0:02:40
0:02:40
 0:00:34
0:00:34
 0:16:18
0:16:18
 0:05:31
0:05:31
 0:32:13
0:32:13
 0:15:59
0:15:59
 0:16:23
0:16:23
 0:05:24
0:05:24
 0:56:24
0:56:24
 0:17:18
0:17:18
 0:04:59
0:04:59
 0:20:14
0:20:14
 0:28:18
0:28:18
 0:16:24
0:16:24
 0:32:28
0:32:28