filmov
tv
Ideal Gas Law (PV=nRT) Example Problem

Показать описание
In this video we’ll work a practice problem for the Ideal Gas Law, PV=nRT. For this problem you can rearrange the equation to get V by itself to start with or just plug in values and solve for V.
Join this channel to get full access to Dr. B's chemistry guides:
We can determine the volume occupied by 2.34 grams of CO2 gas at 27.2°C and 2.2 atm using the ideal gas law:
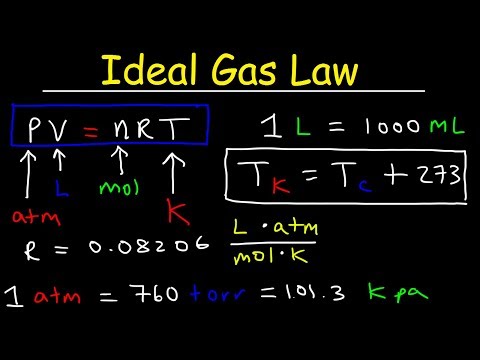
PV = nRT
where:
P is the pressure (in atm)
V is the volume (in L)
n is the number of moles of gas
R is the ideal gas constant (0.08206 L atm/mol K)
T is the temperature (in K)
Steps to solve:
Convert the temperature to Kelvin: T = 27.2°C + 273.15 K = 300.35 K
Calculate the number of moles of CO2: n = mass / molar mass = 2.34 g / 44.01 g/mol = 0.0532 mol
Apply the ideal gas law: V = nRT / P = (0.0532 mol)(0.08206 L atm/mol K)(300.35 K) / 2.2 atm ≈ 0.59 L
Therefore, the volume occupied by 2.34 grams of CO2 gas at 27.2°C and 2.2 atm is approximately 0.59 liters.
Other Videos about the Gas Laws:
Join this channel to get full access to Dr. B's chemistry guides:
We can determine the volume occupied by 2.34 grams of CO2 gas at 27.2°C and 2.2 atm using the ideal gas law:
PV = nRT
where:
P is the pressure (in atm)
V is the volume (in L)
n is the number of moles of gas
R is the ideal gas constant (0.08206 L atm/mol K)
T is the temperature (in K)
Steps to solve:
Convert the temperature to Kelvin: T = 27.2°C + 273.15 K = 300.35 K
Calculate the number of moles of CO2: n = mass / molar mass = 2.34 g / 44.01 g/mol = 0.0532 mol
Apply the ideal gas law: V = nRT / P = (0.0532 mol)(0.08206 L atm/mol K)(300.35 K) / 2.2 atm ≈ 0.59 L
Therefore, the volume occupied by 2.34 grams of CO2 gas at 27.2°C and 2.2 atm is approximately 0.59 liters.
Other Videos about the Gas Laws:
Ideal Gas Law Practice Problems
PV=nRT, the Ideal Gas Law, what is it and how to use it
General Chemistry | Ideal Gas Law (PV=nRT) [Example #1]
The ideal gas law (PV = nRT) | Intermolecular forces and properties | AP Chemistry | Khan Academy
Kinetic Molecular Theory and the Ideal Gas Laws
How to Use the Ideal Gas Law in Two Easy Steps
Ideal Gas Law (PV=nRT) Example Problem
The ideal gas law PV=nRT - simple example
Ideal Gas Law Explained with Examples | PV = nRT Chemistry Made Easy
General Chemistry | Ideal Gas Law (PV=nRT) [Example #2]
The Ideal Gas Law: pV = nRT - IB Physics
The Ideal Gas Law: Crash Course Chemistry #12
Ideal Gas Equation (PV=nRT) - Explanation and Examples
Ideal Gas Law PV=nRT - AP Chem Unit 3, Topic 4B
1.4.7 Solve problems using the ideal gas equation, PV = nRT
Ideal Gas Law Explained PV = nRT
Gas Law Formulas and Equations - College Chemistry Study Guide
Feeling the Pressure of the Ideal Gas Law
The Ideal Gas Law PV=nRT - AP Chemistry Complete Course - Lesson 24.2
Ideal Gas Law in Action: Can Crush Experiment
The Ideal Gas Law example - PV=nRT volume of CO2 produced
Ideal Gas Equation Explained with Balloons! PV = nRT
Ideal Gas Law (PV=nRT) Example Problem
Ideal Gas Law Explained | PV = nRT Made Easy with Examples | Chemistry for Beginners
Комментарии
 0:12:27
0:12:27
 0:03:40
0:03:40
 0:06:33
0:06:33
 0:06:19
0:06:19
 0:05:11
0:05:11
 0:02:44
0:02:44
 0:02:19
0:02:19
 0:03:36
0:03:36
 0:08:51
0:08:51
 0:04:36
0:04:36
 0:23:31
0:23:31
 0:09:03
0:09:03
 0:05:34
0:05:34
 0:11:14
0:11:14
 0:02:12
0:02:12
 0:02:11
0:02:11
 0:19:24
0:19:24
 0:00:18
0:00:18
 0:10:26
0:10:26
 0:00:50
0:00:50
 0:04:18
0:04:18
 0:08:19
0:08:19
 0:01:24
0:01:24
 0:12:28
0:12:28