filmov
tv
Parts of the Brain and Their Functions | Brain Functions | Traumatic Brain Injuries | Brain Anatomy

Показать описание
In this video, personal injury attorney, Joe Lamb talks about the parts of the brain and their functions.
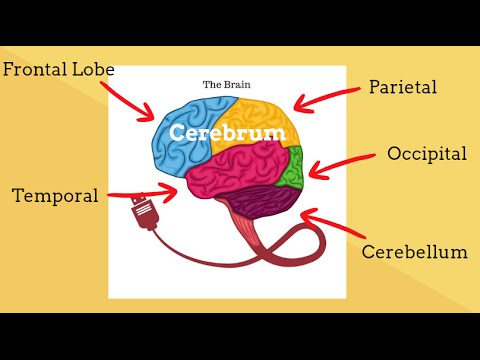
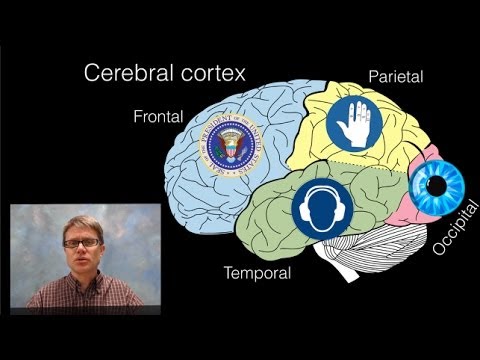
There are six main parts of the brain. Starting at the bottom, you have the brainstem. Then, up to the cerebellum, in the back, you have the occipital lobe, the parietal lobe, frontal lobe, and temporal lobe.
The Frontal Lobe
The frontal lobe is the biggest part of the brain. It is actually in both hemispheres of the brain. What that means is that it's responsible for various functions. A lot of people refer to the frontal lobe as the home of the personality, because it's what makes us human. It controls things like personality and behavioral changes. It's what helps us with fine motor movement. It's part of our judgment. It controls our emotions, problem-solving, and memories. It even controls our sense of smell. Interesting side note, there's some research out there that says that the sense of smell is in the front part of the brain in the frontal lobe, because for every other animal besides humans, it's such a critical part of how they identify their environment around them. But of course, humans, tend to rely more on sight than smell. A lot of evidence is coming out saying that smell may play a much bigger role in how we perceive our environments than we always thought. In addition, the frontal lobe is the most commonplace for brain injuries to occur, because unfortunately, it's the front of your head that is usually impacted. And the issues that can come out can cause significant emotional change and decreased motor function, as well as memory loss.
Parietal Lobe
The parietal lobe is involved with comprehension. It's responsible for integrating the other elements of the brain. For example, it integrates visual cues, language cues, reading, and sensation. It takes these inputs and it helps you navigate them. For example, if you ever tried to close your eyes and walk through a room, your parietal lobe is working overtime as it's trying to remember what's there, and associate locations within. Even if eyes are open, it's saying, "Okay, there's a table right there, there's a chair. "How do I avoid these?" All of these are parietal lobe functions. Any injuries to the parietal lobe can result in difficulty in things like paying attention.
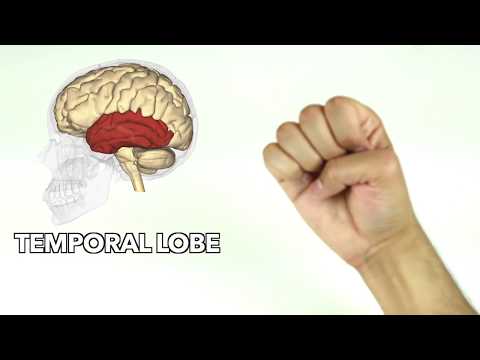
Temporal Lobe
The temporal lobe is responsible for things like multitasking. It's what lets us walk and talk at the same time. It is considered to be a processing area. The temporal lobe is located underneath the frontal lobe. The temporal lobe is responsible for long-term memory formation, processing speech, vision, smell, and sound. For example, if you've ever been in a room full of people and you're trying to make sense of just the one person talking to you and you wonder, "Why can I hear him in the room so loud?" That's what the temporal lobe is doing. Injuries to the temporal lobe can lead to trouble comprehending language and can result in obsessive behavior because it impairs what helps us filter through the noise, essentially.
Occipital Lobe
The occipital lobe is heavily associated with the eyes. But yet, it is in the back of our brain. Vision is essentially just light going through the eyes and being processed by the brain. Injuries to this area can damage our ability to see, the ability to read, and things along those lines. In severe cases, it has been shown to lead to blindness. It's the center of the brain that's translating all the images that are coming from the eyes, and turning them into something that we're able to process and comprehend.
Cerebellum
The cerebellum is located in the bottom back of the brain, just underneath the occipital and temporal lobe. It's also referred to as the little brain. It controls a lot of essential motor functions like balance and coordination. The cerebellum is what lets you stand up out of a chair or walk without falling over. This is such a critical part of our brain. Cerebellum injuries cause a loss of balance. And unfortunately for many people, this loss of balance or vertigo often never goes away. Unfortunately, when the cerebellum is injured it doesn't heal like the other parts of the brain nor do the other parts of the brain help with that loss of function
Brainstem
The brainstem connects the brain and the spinal cord. Your brainstem sends messages to the rest of your body to regulate balance, breathing, heart rate, digestion, blood circulation and other subconscious life functions. And the brainstem has some special function separate from what the spinal cord itself does. An injury to the brainstem is very traumatic and one which some people don't survive. Some other symptoms of an injury to the brainstem include breathing problems, abnormal heart rate, insensitivity to pain, and other sensations. And unfortunately, in severe cases, vegetative state or death.
There are six main parts of the brain. Starting at the bottom, you have the brainstem. Then, up to the cerebellum, in the back, you have the occipital lobe, the parietal lobe, frontal lobe, and temporal lobe.
The Frontal Lobe
The frontal lobe is the biggest part of the brain. It is actually in both hemispheres of the brain. What that means is that it's responsible for various functions. A lot of people refer to the frontal lobe as the home of the personality, because it's what makes us human. It controls things like personality and behavioral changes. It's what helps us with fine motor movement. It's part of our judgment. It controls our emotions, problem-solving, and memories. It even controls our sense of smell. Interesting side note, there's some research out there that says that the sense of smell is in the front part of the brain in the frontal lobe, because for every other animal besides humans, it's such a critical part of how they identify their environment around them. But of course, humans, tend to rely more on sight than smell. A lot of evidence is coming out saying that smell may play a much bigger role in how we perceive our environments than we always thought. In addition, the frontal lobe is the most commonplace for brain injuries to occur, because unfortunately, it's the front of your head that is usually impacted. And the issues that can come out can cause significant emotional change and decreased motor function, as well as memory loss.
Parietal Lobe
The parietal lobe is involved with comprehension. It's responsible for integrating the other elements of the brain. For example, it integrates visual cues, language cues, reading, and sensation. It takes these inputs and it helps you navigate them. For example, if you ever tried to close your eyes and walk through a room, your parietal lobe is working overtime as it's trying to remember what's there, and associate locations within. Even if eyes are open, it's saying, "Okay, there's a table right there, there's a chair. "How do I avoid these?" All of these are parietal lobe functions. Any injuries to the parietal lobe can result in difficulty in things like paying attention.
Temporal Lobe
The temporal lobe is responsible for things like multitasking. It's what lets us walk and talk at the same time. It is considered to be a processing area. The temporal lobe is located underneath the frontal lobe. The temporal lobe is responsible for long-term memory formation, processing speech, vision, smell, and sound. For example, if you've ever been in a room full of people and you're trying to make sense of just the one person talking to you and you wonder, "Why can I hear him in the room so loud?" That's what the temporal lobe is doing. Injuries to the temporal lobe can lead to trouble comprehending language and can result in obsessive behavior because it impairs what helps us filter through the noise, essentially.
Occipital Lobe
The occipital lobe is heavily associated with the eyes. But yet, it is in the back of our brain. Vision is essentially just light going through the eyes and being processed by the brain. Injuries to this area can damage our ability to see, the ability to read, and things along those lines. In severe cases, it has been shown to lead to blindness. It's the center of the brain that's translating all the images that are coming from the eyes, and turning them into something that we're able to process and comprehend.
Cerebellum
The cerebellum is located in the bottom back of the brain, just underneath the occipital and temporal lobe. It's also referred to as the little brain. It controls a lot of essential motor functions like balance and coordination. The cerebellum is what lets you stand up out of a chair or walk without falling over. This is such a critical part of our brain. Cerebellum injuries cause a loss of balance. And unfortunately for many people, this loss of balance or vertigo often never goes away. Unfortunately, when the cerebellum is injured it doesn't heal like the other parts of the brain nor do the other parts of the brain help with that loss of function
Brainstem
The brainstem connects the brain and the spinal cord. Your brainstem sends messages to the rest of your body to regulate balance, breathing, heart rate, digestion, blood circulation and other subconscious life functions. And the brainstem has some special function separate from what the spinal cord itself does. An injury to the brainstem is very traumatic and one which some people don't survive. Some other symptoms of an injury to the brainstem include breathing problems, abnormal heart rate, insensitivity to pain, and other sensations. And unfortunately, in severe cases, vegetative state or death.
Комментарии
 0:03:19
0:03:19
 0:02:09
0:02:09
 0:19:20
0:19:20
 0:05:02
0:05:02
 0:03:24
0:03:24
 0:13:56
0:13:56
 0:05:42
0:05:42
 0:04:40
0:04:40
 0:05:04
0:05:04
 0:06:48
0:06:48
 0:12:34
0:12:34
 0:11:58
0:11:58
 0:11:54
0:11:54
 0:14:36
0:14:36
 0:02:09
0:02:09
 0:18:27
0:18:27
 0:02:22
0:02:22
 0:06:50
0:06:50
 0:06:32
0:06:32
 0:03:00
0:03:00
 0:03:07
0:03:07
 0:06:20
0:06:20
 0:04:49
0:04:49
 0:27:18
0:27:18