filmov
tv
Simple Interest and Maturity Value by Exact and ordinary interest, Partial payments CH10

Показать описание
Calculation of Simple Interest and Maturity Value
1. Calculate simple interest and maturity values for months and years.
2. Calculate simple interest and maturity value by (a) exact interest and (b) ordinary interest.
Finding Unknown in Simple Interest Formula
1. Using the interest formula, calculate the unknown when the other two (principal, rate, or time) are given.
U.S. Rule - Making Partial Note Payments before Due Date
1. List the steps to complete the U.S. Rule.
2. Complete the proper interest credits under U.S. Rule.
Compound Interest: Compound interest is the interest calculated on the initial principal and any accumulated interest from previous periods. It results in the amount of interest earned increasing over time, as the interest earned in previous periods is added to the principal.
Table Lookup: Table lookup is a method of finding the value of a function or equation using pre-calculated values in a table, rather than by performing calculations.
Present Value: The present value is the current value of a future stream of payments, discounted by a specified interest rate. It represents the amount that would need to be invested today in order to generate future payments.
APY stands for Annual Percentage Yield, which is the annual rate of return on an investment, including the effect of compounding.
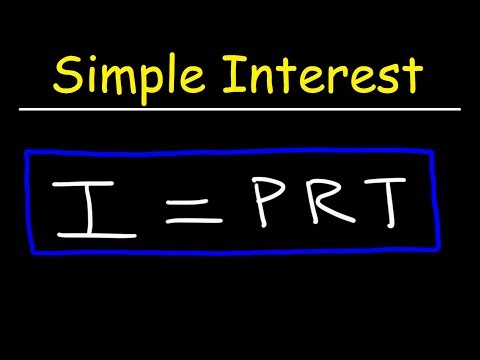
Simple Interest: Simple interest is the interest calculated only on the initial principal, without taking into account any accumulated interest from previous periods.
Exact Interest: Exact interest is the interest calculated based on the exact number of days between the start and end dates of the investment period, using the actual number of days in each month.
Ordinary Interest: Ordinary interest is the interest calculated based on the assumption that each month has 30 days, regardless of the actual number of days in the month.
Maturity Value: The maturity value is the final value of an investment, including the principal and any interest earned, at the end of the investment period.
Partial Payments: Partial payments are payments made on a debt or investment that are less than the full amount due, but are still applied to the outstanding balance.
#Principal_Interest
#amount_of_loan
#Cost_of_borrowing
#face_value
#money
#Simple_Interest
#Simple_Interest_Formula
#Exact_Interest
#Ordinary_Interest
#Banker’s_Rule
#MV
#U.S._Rule_Making_Partial_Note
#Payments_before_Due_Date
#Maturity_Value
#CompoundInterest
#TableLookup
#PresentValue
#APY
#AnnualPercentageYield
#AOU #Arab_Open_University #FBS #BUS101 #BUS102 #Business_Studies #business_school
#الفائدة_الرئيسية
#مقدا_القرض
# تكلفة_الاقتراض
#قيمة_الوجه
#مال
# الفائدة_البسيطة
# قانون_الفائدة_البسيطة
# الفائدة_التامة
# الفائدة_العادية
# قاعدة_المصرفي
#السداد_قبل_وقت_الاستحقاق
#قيمة_الاستحقاق
#الفائدة_المركبة
#القيمة_الجدولية
#القيمة_الحالية
#نسبة_العائد_السنوي
1. Calculate simple interest and maturity values for months and years.
2. Calculate simple interest and maturity value by (a) exact interest and (b) ordinary interest.
Finding Unknown in Simple Interest Formula
1. Using the interest formula, calculate the unknown when the other two (principal, rate, or time) are given.
U.S. Rule - Making Partial Note Payments before Due Date
1. List the steps to complete the U.S. Rule.
2. Complete the proper interest credits under U.S. Rule.
Compound Interest: Compound interest is the interest calculated on the initial principal and any accumulated interest from previous periods. It results in the amount of interest earned increasing over time, as the interest earned in previous periods is added to the principal.
Table Lookup: Table lookup is a method of finding the value of a function or equation using pre-calculated values in a table, rather than by performing calculations.
Present Value: The present value is the current value of a future stream of payments, discounted by a specified interest rate. It represents the amount that would need to be invested today in order to generate future payments.
APY stands for Annual Percentage Yield, which is the annual rate of return on an investment, including the effect of compounding.
Simple Interest: Simple interest is the interest calculated only on the initial principal, without taking into account any accumulated interest from previous periods.
Exact Interest: Exact interest is the interest calculated based on the exact number of days between the start and end dates of the investment period, using the actual number of days in each month.
Ordinary Interest: Ordinary interest is the interest calculated based on the assumption that each month has 30 days, regardless of the actual number of days in the month.
Maturity Value: The maturity value is the final value of an investment, including the principal and any interest earned, at the end of the investment period.
Partial Payments: Partial payments are payments made on a debt or investment that are less than the full amount due, but are still applied to the outstanding balance.
#Principal_Interest
#amount_of_loan
#Cost_of_borrowing
#face_value
#money
#Simple_Interest
#Simple_Interest_Formula
#Exact_Interest
#Ordinary_Interest
#Banker’s_Rule
#MV
#U.S._Rule_Making_Partial_Note
#Payments_before_Due_Date
#Maturity_Value
#CompoundInterest
#TableLookup
#PresentValue
#APY
#AnnualPercentageYield
#AOU #Arab_Open_University #FBS #BUS101 #BUS102 #Business_Studies #business_school
#الفائدة_الرئيسية
#مقدا_القرض
# تكلفة_الاقتراض
#قيمة_الوجه
#مال
# الفائدة_البسيطة
# قانون_الفائدة_البسيطة
# الفائدة_التامة
# الفائدة_العادية
# قاعدة_المصرفي
#السداد_قبل_وقت_الاستحقاق
#قيمة_الاستحقاق
#الفائدة_المركبة
#القيمة_الجدولية
#القيمة_الحالية
#نسبة_العائد_السنوي
 0:02:12
0:02:12
 0:06:35
0:06:35
 0:11:02
0:11:02
 0:02:02
0:02:02
 0:13:20
0:13:20
 0:17:00
0:17:00
 0:16:58
0:16:58
 0:09:41
0:09:41
 0:44:17
0:44:17
 0:07:50
0:07:50
 0:19:47
0:19:47
 0:04:13
0:04:13
 0:10:23
0:10:23
 0:07:59
0:07:59
 0:17:58
0:17:58
 0:02:27
0:02:27
 0:26:21
0:26:21
 0:09:54
0:09:54
 0:01:19
0:01:19
 0:14:03
0:14:03
 0:06:41
0:06:41
 0:18:58
0:18:58
 0:02:09
0:02:09
 0:11:35
0:11:35