filmov
tv
Mercantilism and Why It Matters for AP US History

Показать описание
This expert video- written by Warren Hierl- breaks down the impact of Mercantilism.
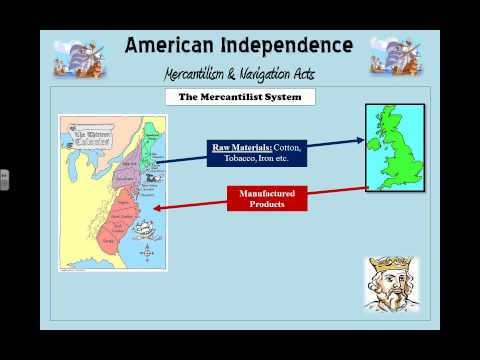
Mercantilism is the economic idea that a country’s wealth is measured by the amount of gold it owns. The goal of mercantilist economic policy is to export more goods than you import, so that you bring more money into the country than you send out to other nations.
The goal of mercantilist economic policy is to export more goods than you import, so that you bring more money into the country than you send out to other nations.
Mercantilism dominated economic thoughts of Europe from the end of the fifteenth century until the end of the eighteenth century. Under it, national governments significantly increased their role in economic matters and colonies existed for the good of the mother country. While the mercantilist philosophy initially benefitted both the mother country and her colonies, over time the colonies suffered from economic exploitation. In the British North American colonies, the impact of salutary neglect (the inability of Great Britain to enforce mercantilist measures) created a sense of economic freedom in the colonies. When Great Britain attempted to end salutary neglect, the colonies rebelled. However, that did not mean that elements of mercantilism were subsequently pursued by the United States. Even today, debate over protective tariffs (America First policies or economic nationalism) stimulate debate concerning consumer prices (increased by protective tariffs) and job opportunities for American workers that advocates of America First policies tout as a positive benefit of protectionism.
Mercantilism is the economic idea that a country’s wealth is measured by the amount of gold it owns. The goal of mercantilist economic policy is to export more goods than you import, so that you bring more money into the country than you send out to other nations.
The goal of mercantilist economic policy is to export more goods than you import, so that you bring more money into the country than you send out to other nations.
Mercantilism dominated economic thoughts of Europe from the end of the fifteenth century until the end of the eighteenth century. Under it, national governments significantly increased their role in economic matters and colonies existed for the good of the mother country. While the mercantilist philosophy initially benefitted both the mother country and her colonies, over time the colonies suffered from economic exploitation. In the British North American colonies, the impact of salutary neglect (the inability of Great Britain to enforce mercantilist measures) created a sense of economic freedom in the colonies. When Great Britain attempted to end salutary neglect, the colonies rebelled. However, that did not mean that elements of mercantilism were subsequently pursued by the United States. Even today, debate over protective tariffs (America First policies or economic nationalism) stimulate debate concerning consumer prices (increased by protective tariffs) and job opportunities for American workers that advocates of America First policies tout as a positive benefit of protectionism.
Комментарии
 0:14:06
0:14:06
 0:04:47
0:04:47
 0:28:05
0:28:05
 0:04:56
0:04:56
 0:05:12
0:05:12
 0:13:49
0:13:49
 0:04:59
0:04:59
 0:13:01
0:13:01
 0:14:10
0:14:10
 0:05:36
0:05:36
 0:04:17
0:04:17
 0:07:28
0:07:28
 0:00:40
0:00:40
 0:08:28
0:08:28
 0:04:13
0:04:13
 0:14:51
0:14:51
 0:04:59
0:04:59
 0:06:42
0:06:42
 0:03:24
0:03:24
 0:27:18
0:27:18
 0:06:14
0:06:14
 0:06:39
0:06:39
 0:05:14
0:05:14
 0:07:02
0:07:02