filmov
tv
Receptor Tyrosine Kinase | RTK Signalling

Показать описание
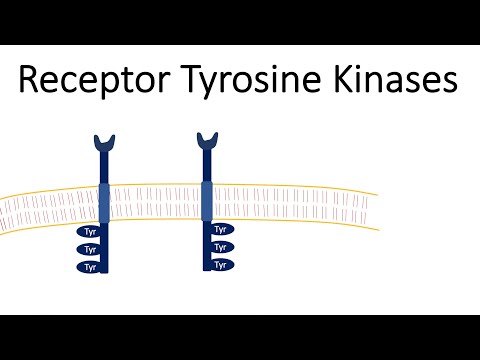
Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) are the high-affinity cell surface receptors for many polypeptide growth factors, cytokines, and hormones. Of the 90 unique tyrosine kinase genes identified in the human genome, 59 encode receptor tyrosine kinase proteins.
Most RTKs are single subunit receptors but some exist as multimeric complexes, e.g., the insulin receptor that forms disulfide linked dimers in the presence of hormone (insulin); moreover, ligand binding to the extracellular domain induces formation of receptor dimers.[6] Each monomer has a single hydrophobic transmembrane-spanning domain composed of 25 to 38 amino acids, an extracellular N terminal region, and an intracellular C terminal region.
In biochemistry, a kinase is a type of enzyme that transfers phosphate groups (see below) from high-energy donor molecules, such as ATP (see below) to specific target molecules (substrates); the process is termed phosphorylation. The opposite, an enzyme that removes phosphate groups from targets, is known as a phosphatase. Kinase enzymes that specifically phosphorylate tyrosine amino acids are termed tyrosine kinases.
Through diverse means, extracellular ligand binding will typically cause or stabilize receptor dimerization. This allows a tyrosine in the cytoplasmic portion of each receptor monomer to be trans-phosphorylated by its partner receptor, propagating a signal through the plasma membrane.[8] The phosphorylation of specific tyrosine residues within the activated receptor creates binding sites for Src homology 2 (SH2) domain- and phosphotyrosine binding (PTB) domain-containing proteins.Specific proteins containing these domains include Src and phospholipase Cγ. Phosphorylation and activation of these two proteins on receptor binding lead to the initiation of signal transduction pathways. Other proteins that interact with the activated receptor act as adaptor proteins and have no intrinsic enzymatic activity of their own.
Most RTKs are single subunit receptors but some exist as multimeric complexes, e.g., the insulin receptor that forms disulfide linked dimers in the presence of hormone (insulin); moreover, ligand binding to the extracellular domain induces formation of receptor dimers.[6] Each monomer has a single hydrophobic transmembrane-spanning domain composed of 25 to 38 amino acids, an extracellular N terminal region, and an intracellular C terminal region.
In biochemistry, a kinase is a type of enzyme that transfers phosphate groups (see below) from high-energy donor molecules, such as ATP (see below) to specific target molecules (substrates); the process is termed phosphorylation. The opposite, an enzyme that removes phosphate groups from targets, is known as a phosphatase. Kinase enzymes that specifically phosphorylate tyrosine amino acids are termed tyrosine kinases.
Through diverse means, extracellular ligand binding will typically cause or stabilize receptor dimerization. This allows a tyrosine in the cytoplasmic portion of each receptor monomer to be trans-phosphorylated by its partner receptor, propagating a signal through the plasma membrane.[8] The phosphorylation of specific tyrosine residues within the activated receptor creates binding sites for Src homology 2 (SH2) domain- and phosphotyrosine binding (PTB) domain-containing proteins.Specific proteins containing these domains include Src and phospholipase Cγ. Phosphorylation and activation of these two proteins on receptor binding lead to the initiation of signal transduction pathways. Other proteins that interact with the activated receptor act as adaptor proteins and have no intrinsic enzymatic activity of their own.
Комментарии
 0:04:14
0:04:14
 0:04:24
0:04:24
 0:04:39
0:04:39
 0:04:51
0:04:51
 0:13:47
0:13:47
 0:07:26
0:07:26
 0:07:56
0:07:56
 0:08:51
0:08:51
 0:07:34
0:07:34
 0:18:40
0:18:40
 0:04:05
0:04:05
 0:09:41
0:09:41
 0:17:26
0:17:26
 0:11:05
0:11:05
 0:02:34
0:02:34
 0:06:45
0:06:45
 0:00:51
0:00:51
 0:06:48
0:06:48
 0:04:36
0:04:36
 0:04:26
0:04:26
 0:03:50
0:03:50
 0:13:17
0:13:17
 0:03:54
0:03:54
 0:04:28
0:04:28