filmov
tv
What is LDAP and Active Directory ? How LDAP works and what is the structure of LDAP/AD?

Показать описание
#ldap #ldapauth
What is LDAP and Active Directory ? How LDAP works and what is the structure of LDAP/AD?
In this video, I have discussed regarding LDAP, Active Directory, LDAP vs Active Directory, Structure of LDAP, How LDAP works, LDAP Authentication.
GitHub:
LDAP in Java:
LDAP Updated:
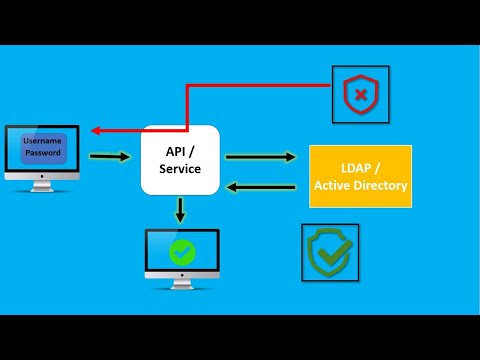
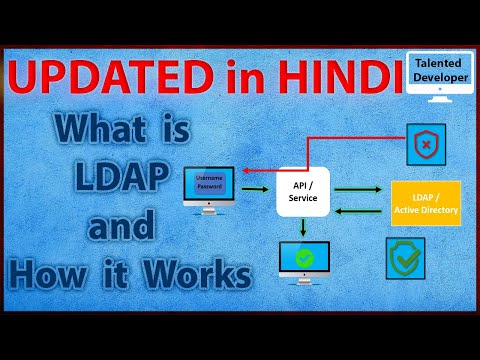
What is LDAP?
LDAP, the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol, is a mature, flexible, and well supported standards-based mechanism for interacting with directory servers. It’s often used for authentication and storing information about users, groups, and applications, but an LDAP directory server is a fairly general-purpose data store and can be used in a wide variety of applications
How Does LDAP work?
In short, LDAP specifies a method of directory storage that allows for adding, deleting, and modifying records, and it enables the search of those records to facilitate both authentication and authorization of users to resources.
LDAP’s three main functions are:
Update: This includes adding, deleting, or modifying directory information.
Query: This includes searching and comparing directory information.
Authenticate: The main authentication functions include binding and unbinding; a third function, abandon, can be used to stop a server from completing an operation
LDAP Directory Information Tree
LDAP organizes information in a hierarchical tree structure, referred to as a directory information tree (DIT). The LDAP DIT can vary based on the software or directory service you use; however, LDAP directories generally follow this tree structure, where entries without subordinates (users, for example) are leaves, and the root is the overarching entity that encompasses all the information within the directory.
LDAP Authentication and Authorization
The LDAP protocol both authenticates and authorizes users to their resources. The protocol authenticates users with a bind operation that allows the user to communicate with an LDAP directory, then authorizes the authenticated user to the resources they need if their input login information matches what’s listed for them in the database.
1.What Is LDAP Authentication ?
LDAP authentication relies on a client/server bind operation, which allows the LDAP-ready client, referred to as the directory user agent (DUA), and the directory server, referred to as the directory system agent (DSA), to communicate within a secure, encrypted session.
When authenticating against an LDAP server in an attempt to gain access to the database, the user is prompted to provide their username and password.
If the values the user inputs into the client matches what is found in the LDAP database, the user is granted access by the LDAP server to whatever the IT resource may be.
2. What Is LDAP Authorization ?
Once a user is successfully authenticated, they need to be authorized to the resource(s) requested. While different LDAP instances may structure and encode this slightly differently, this is essentially accomplished by assigning permissions with groups and roles in the directory.
What is LDAP and Active Directory ? How LDAP works and what is the structure of LDAP/AD?
In this video, I have discussed regarding LDAP, Active Directory, LDAP vs Active Directory, Structure of LDAP, How LDAP works, LDAP Authentication.
GitHub:
LDAP in Java:
LDAP Updated:
What is LDAP?
LDAP, the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol, is a mature, flexible, and well supported standards-based mechanism for interacting with directory servers. It’s often used for authentication and storing information about users, groups, and applications, but an LDAP directory server is a fairly general-purpose data store and can be used in a wide variety of applications
How Does LDAP work?
In short, LDAP specifies a method of directory storage that allows for adding, deleting, and modifying records, and it enables the search of those records to facilitate both authentication and authorization of users to resources.
LDAP’s three main functions are:
Update: This includes adding, deleting, or modifying directory information.
Query: This includes searching and comparing directory information.
Authenticate: The main authentication functions include binding and unbinding; a third function, abandon, can be used to stop a server from completing an operation
LDAP Directory Information Tree
LDAP organizes information in a hierarchical tree structure, referred to as a directory information tree (DIT). The LDAP DIT can vary based on the software or directory service you use; however, LDAP directories generally follow this tree structure, where entries without subordinates (users, for example) are leaves, and the root is the overarching entity that encompasses all the information within the directory.
LDAP Authentication and Authorization
The LDAP protocol both authenticates and authorizes users to their resources. The protocol authenticates users with a bind operation that allows the user to communicate with an LDAP directory, then authorizes the authenticated user to the resources they need if their input login information matches what’s listed for them in the database.
1.What Is LDAP Authentication ?
LDAP authentication relies on a client/server bind operation, which allows the LDAP-ready client, referred to as the directory user agent (DUA), and the directory server, referred to as the directory system agent (DSA), to communicate within a secure, encrypted session.
When authenticating against an LDAP server in an attempt to gain access to the database, the user is prompted to provide their username and password.
If the values the user inputs into the client matches what is found in the LDAP database, the user is granted access by the LDAP server to whatever the IT resource may be.
2. What Is LDAP Authorization ?
Once a user is successfully authenticated, they need to be authorized to the resource(s) requested. While different LDAP instances may structure and encode this slightly differently, this is essentially accomplished by assigning permissions with groups and roles in the directory.
Комментарии
 0:01:51
0:01:51
 0:14:19
0:14:19
 0:11:17
0:11:17
 0:03:46
0:03:46
 0:07:33
0:07:33
 0:03:49
0:03:49
 0:03:27
0:03:27
 0:09:07
0:09:07
 0:03:46
0:03:46
 0:08:04
0:08:04
 0:00:40
0:00:40
 0:03:23
0:03:23
 0:15:25
0:15:25
 0:09:37
0:09:37
 0:15:09
0:15:09
 0:16:01
0:16:01
 0:03:03
0:03:03
 0:07:25
0:07:25
 0:05:45
0:05:45
 0:01:10
0:01:10
 0:03:04
0:03:04
 0:11:12
0:11:12
 0:03:48
0:03:48
 0:02:32
0:02:32