filmov
tv
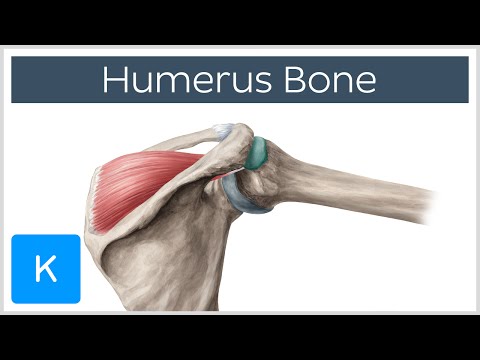
greater tubercle of the humerus

Показать описание
A bony projection of the lateral part of the proximal end of the humerus. It is situated lateral to the head of the humerus, and posterolateral to the lesser tubercle of humerus.
It provides attachment points for the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, and teres minor muscles, 3 of the 4 muscles of the rotator cuff, a muscle group that stabilizes the shoulder joint (glenoid) and elevates and rotates the arm.
(Rotator cuff)
• supraspinatus: Originates above the spine of the scapula and inserts on the greater tuberosity of the humerus.
• infraspinatus: Originates below the spine of the scapula in the infraspinatus fossa and inserts on the posterior aspect of the greater tuberosity of the humerus.
• teres minor: Originates on the lateral scapula border and inserts on the inferior aspect of the greater tuberosity of the humerus.
• subscapularis: Originates on the anterior, or front surface, of the scapula, sitting directly over the ribs, and inserts on the lesser tuberosity of the humerus.
(Proximal end of the humerus)
• head: A hemispheroidal shape, with hyaline cartilage covering its smooth articular surface. It faces in a medial, superior and posterior direction where it articulates with the glenoid fossa of the scapula.
• anatomical neck: A slight narrowing below the articular surface of the head. Here, the joint capsule of the shoulder joint is attached.
• greater tubercle: The most lateral portion of the proximal end of the humerus. From superior to inferior, the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, and teres minor attach. The deltoid covers the lateral aspect of it, resulting in the normal rounded shape of the shoulder.
• lesser tubercle: Located anterior to the anatomical neck. The subscapularis attaches here and the transverse humeral ligament also attaches on its lateral part.
• intertubercular sulcus (bicipital groove): An indentation located between the greater and lesser tubercles. The long tendon of the biceps brachii and an ascending branch of the anterior circumflex humeral artery are located within it. The pectoralis major tendon attaches on to the lateral lip (crest of greater tubercle), the teres major tendon attaches on to the medial lip, and the lattisimus dorsi tendon attaches to the posterior aspect.
• surgical neck: A place where the proximal end of the humerus joins with the long shaft. It is in close proximity to the axillary nerve and posterior circumflex humeral artery. It is a common fracture site.
It provides attachment points for the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, and teres minor muscles, 3 of the 4 muscles of the rotator cuff, a muscle group that stabilizes the shoulder joint (glenoid) and elevates and rotates the arm.
(Rotator cuff)
• supraspinatus: Originates above the spine of the scapula and inserts on the greater tuberosity of the humerus.
• infraspinatus: Originates below the spine of the scapula in the infraspinatus fossa and inserts on the posterior aspect of the greater tuberosity of the humerus.
• teres minor: Originates on the lateral scapula border and inserts on the inferior aspect of the greater tuberosity of the humerus.
• subscapularis: Originates on the anterior, or front surface, of the scapula, sitting directly over the ribs, and inserts on the lesser tuberosity of the humerus.
(Proximal end of the humerus)
• head: A hemispheroidal shape, with hyaline cartilage covering its smooth articular surface. It faces in a medial, superior and posterior direction where it articulates with the glenoid fossa of the scapula.
• anatomical neck: A slight narrowing below the articular surface of the head. Here, the joint capsule of the shoulder joint is attached.
• greater tubercle: The most lateral portion of the proximal end of the humerus. From superior to inferior, the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, and teres minor attach. The deltoid covers the lateral aspect of it, resulting in the normal rounded shape of the shoulder.
• lesser tubercle: Located anterior to the anatomical neck. The subscapularis attaches here and the transverse humeral ligament also attaches on its lateral part.
• intertubercular sulcus (bicipital groove): An indentation located between the greater and lesser tubercles. The long tendon of the biceps brachii and an ascending branch of the anterior circumflex humeral artery are located within it. The pectoralis major tendon attaches on to the lateral lip (crest of greater tubercle), the teres major tendon attaches on to the medial lip, and the lattisimus dorsi tendon attaches to the posterior aspect.
• surgical neck: A place where the proximal end of the humerus joins with the long shaft. It is in close proximity to the axillary nerve and posterior circumflex humeral artery. It is a common fracture site.
 0:03:50
0:03:50
 0:03:16
0:03:16
 0:05:28
0:05:28
 0:03:24
0:03:24
 0:02:40
0:02:40
 0:00:13
0:00:13
 0:00:39
0:00:39
 0:00:57
0:00:57
 0:00:18
0:00:18
 0:11:59
0:11:59
 0:07:10
0:07:10
 0:05:24
0:05:24
 0:11:17
0:11:17
 0:03:23
0:03:23
 0:03:28
0:03:28
 0:01:50
0:01:50
 0:00:59
0:00:59
 0:00:13
0:00:13
 0:00:35
0:00:35
 0:03:33
0:03:33
 0:04:32
0:04:32
 0:10:16
0:10:16
 0:08:05
0:08:05
 0:07:30
0:07:30