filmov
tv
Medullary thyroid carcinoma or Cancer ; Definition, Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment
Показать описание
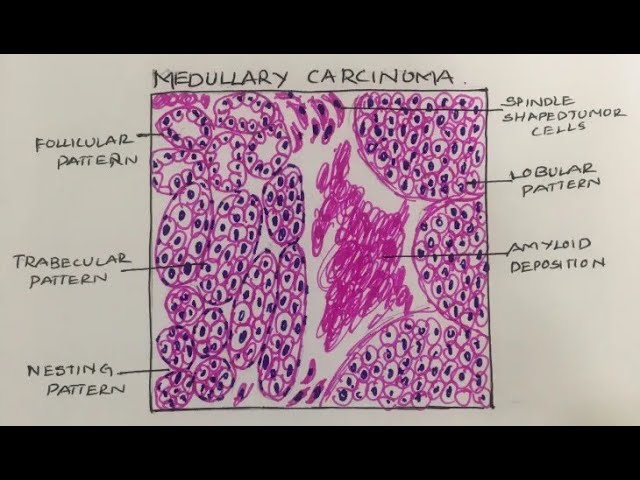
Medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) is a rare type of thyroid cancer that originates from the parafollicular C cells of the thyroid gland. These cells produce the hormone calcitonin1. Here are some key points about MTC:
Characteristics
Type: MTC is a form of thyroid carcinoma that arises from the parafollicular cells (C cells).
Incidence: MTC accounts for about 1-2% of all thyroid cancers.
Causes
Genetic Factors: Approximately 25% of MTC cases are hereditary and linked to Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia type 2 (MEN 2). The rest are sporadic with no known cause1.
Genetic Mutation: The RET proto-oncogene mutation is responsible for hereditary MTC.
Symptoms
Common Symptoms: Diarrhea, flushing episodes, and a thyroid nodule.
Advanced Symptoms: Enlarged cervical lymph nodes, liver, lung, and bone metastasis.
Diagnosis
Imaging: Ultrasound, CT scans, and MRI are used to detect and evaluate MTC1.
Blood Tests: Elevated levels of calcitonin and carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) can indicate MTC.
Treatment
Surgery: The primary treatment is surgical removal of the thyroid gland (thyroidectomy).
Genetic Testing: For hereditary cases, genetic testing for the RET proto-oncogene can help identify at-risk family members.
Additional Treatments: Radiation therapy and targeted therapies may be used for advanced cases1.
Prognosis
Survival Rate: The prognosis varies depending on the stage at diagnosis and whether the cancer is sporadic or hereditary
#Medullarythyroidcarcinoma
Characteristics
Type: MTC is a form of thyroid carcinoma that arises from the parafollicular cells (C cells).
Incidence: MTC accounts for about 1-2% of all thyroid cancers.
Causes
Genetic Factors: Approximately 25% of MTC cases are hereditary and linked to Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia type 2 (MEN 2). The rest are sporadic with no known cause1.
Genetic Mutation: The RET proto-oncogene mutation is responsible for hereditary MTC.
Symptoms
Common Symptoms: Diarrhea, flushing episodes, and a thyroid nodule.
Advanced Symptoms: Enlarged cervical lymph nodes, liver, lung, and bone metastasis.
Diagnosis
Imaging: Ultrasound, CT scans, and MRI are used to detect and evaluate MTC1.
Blood Tests: Elevated levels of calcitonin and carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) can indicate MTC.
Treatment
Surgery: The primary treatment is surgical removal of the thyroid gland (thyroidectomy).
Genetic Testing: For hereditary cases, genetic testing for the RET proto-oncogene can help identify at-risk family members.
Additional Treatments: Radiation therapy and targeted therapies may be used for advanced cases1.
Prognosis
Survival Rate: The prognosis varies depending on the stage at diagnosis and whether the cancer is sporadic or hereditary
#Medullarythyroidcarcinoma
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:00:43
0:00:43
 0:08:05
0:08:05
 0:02:03
0:02:03
 0:22:42
0:22:42
 0:12:16
0:12:16
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:13:38
0:13:38
 0:01:56
0:01:56
 0:03:49
0:03:49
 0:56:11
0:56:11
 0:02:46
0:02:46
 0:18:13
0:18:13
 0:05:26
0:05:26
 0:09:32
0:09:32
 0:15:13
0:15:13
 0:02:00
0:02:00
 0:07:21
0:07:21
 0:06:53
0:06:53
 0:07:06
0:07:06
 1:06:10
1:06:10
 0:05:17
0:05:17
 0:01:47
0:01:47
 0:00:32
0:00:32