filmov
tv
Exploring the 3D Anatomy of the Abdomen
Показать описание
### 1. **The Abdominal Wall**
The abdominal wall forms the outer boundary of the abdominal cavity and is composed of several layers, including skin, fascia, muscles, and peritoneum. These layers protect the internal organs and play a critical role in maintaining intra-abdominal pressure, which is essential for processes like respiration and defecation.
- **Skin and Superficial Fascia**: The outermost layer is the skin, which is flexible and contains nerves, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels. Beneath the skin lies the superficial fascia, a connective tissue layer that varies in thickness depending on the region and individual.
- **Muscles of the Abdominal Wall**: The muscles of the abdominal wall are arranged in layers. The primary muscles include the rectus abdominis, external oblique, internal oblique, and transversus abdominis. These muscles not only protect the underlying organs but also facilitate movement, support posture, and assist in the expulsion of contents from the gastrointestinal and urinary tracts.
- **Peritoneum**: The innermost layer of the abdominal wall is the peritoneum, a serous membrane that lines the abdominal cavity and covers most of the abdominal organs. The peritoneum is divided into the parietal peritoneum, which lines the abdominal wall, and the visceral peritoneum, which covers the organs.
### 2. **The Abdominal Cavity**
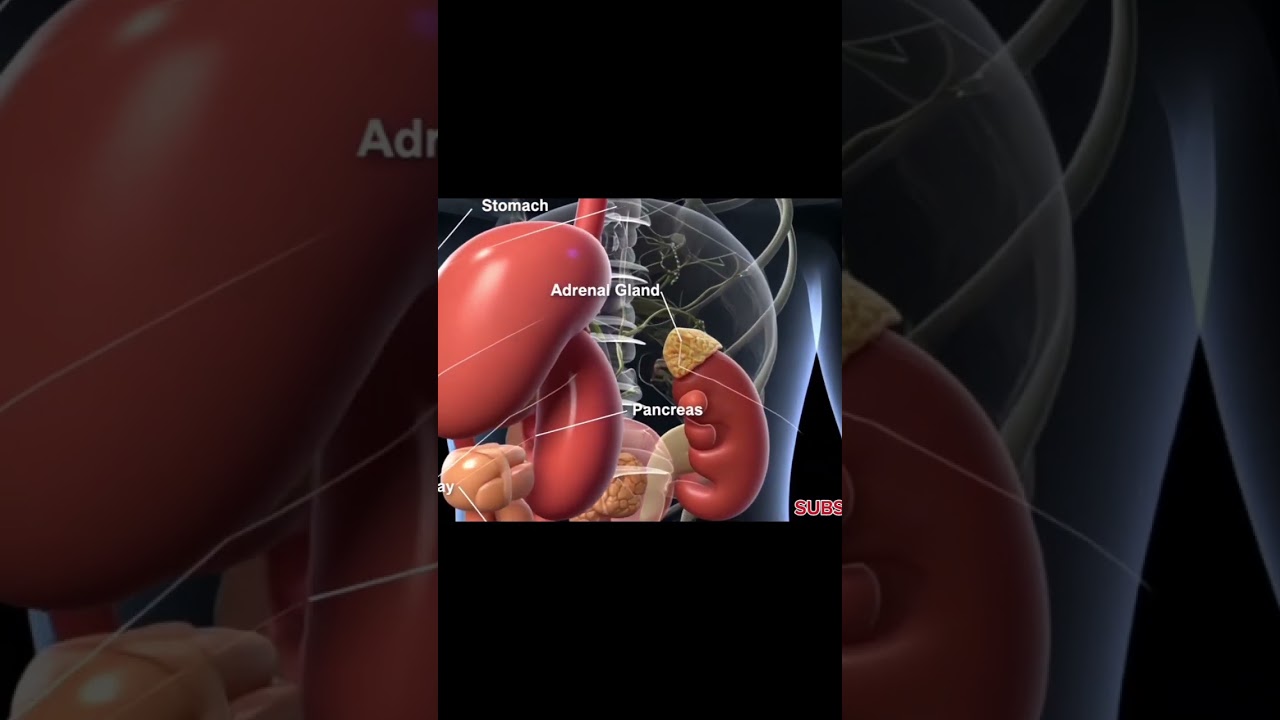
The abdominal cavity is the largest cavity in the human body, extending from the diaphragm above to the pelvic brim below. It contains the digestive organs, the spleen, kidneys, and adrenal glands. The cavity is divided into different regions and quadrants for clinical and anatomical reference.
- **Peritoneal Cavity**: The space between the parietal and visceral peritoneum is known as the peritoneal cavity. It contains a small amount of lubricating fluid that allows the organs to move smoothly against each other during digestion and other movements.
- **Retroperitoneal Space**: Some organs, such as the kidneys and pancreas, are located behind the peritoneum in an area known as the retroperitoneal space. These structures are partially covered by peritoneum and are protected by the posterior abdominal wall.
### 3. **The Digestive Organs**
The abdomen houses the majority of the digestive system, which is responsible for breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, and expelling waste. The key organs involved in digestion within the abdominal cavity include:
- **Stomach**: Located in the upper left quadrant, the stomach is a J-shaped organ that plays a central role in digestion. It receives food from the oesophagus and mixes it with gastric juices to break it down into a semi-liquid substance called chyme.
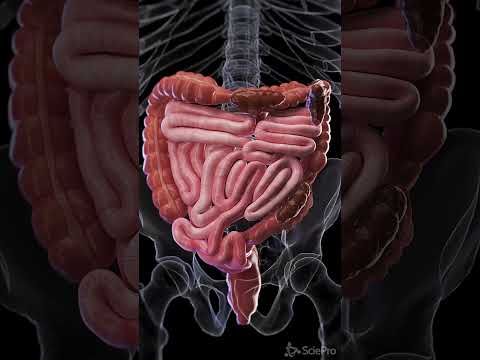
- **Small Intestine**: The small intestine is a long, coiled tube where most of the digestion and absorption of nutrients occurs. It is divided into three sections: the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. The duodenum receives chyme from the stomach, along with bile from the liver and digestive enzymes from the pancreas, to further break down food.
- **Large Intestine**: The large intestine absorbs water and electrolytes from the remaining indigestible food matter and forms solid waste (faeces). It consists of the caecum, colon, rectum, and anal canal. The colon is further divided into the ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid colon.
- **Liver**: The liver, located in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen, is the largest internal organ. It performs various vital functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and the production of bile, which aids in the digestion of fats.
- **Gallbladder**: The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ located beneath the liver. It stores and concentrates bile, releasing it into the small intestine to aid in the digestion of dietary fats.
- **Pancreas**: The pancreas lies behind the stomach and serves both endocrine and exocrine functions. It secretes digestive enzymes into the duodenum and produces hormones such as insulin and glucagon, which regulate blood sugar levels.
### 4. **The Spleen**
The abdominal wall forms the outer boundary of the abdominal cavity and is composed of several layers, including skin, fascia, muscles, and peritoneum. These layers protect the internal organs and play a critical role in maintaining intra-abdominal pressure, which is essential for processes like respiration and defecation.
- **Skin and Superficial Fascia**: The outermost layer is the skin, which is flexible and contains nerves, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels. Beneath the skin lies the superficial fascia, a connective tissue layer that varies in thickness depending on the region and individual.
- **Muscles of the Abdominal Wall**: The muscles of the abdominal wall are arranged in layers. The primary muscles include the rectus abdominis, external oblique, internal oblique, and transversus abdominis. These muscles not only protect the underlying organs but also facilitate movement, support posture, and assist in the expulsion of contents from the gastrointestinal and urinary tracts.
- **Peritoneum**: The innermost layer of the abdominal wall is the peritoneum, a serous membrane that lines the abdominal cavity and covers most of the abdominal organs. The peritoneum is divided into the parietal peritoneum, which lines the abdominal wall, and the visceral peritoneum, which covers the organs.
### 2. **The Abdominal Cavity**
The abdominal cavity is the largest cavity in the human body, extending from the diaphragm above to the pelvic brim below. It contains the digestive organs, the spleen, kidneys, and adrenal glands. The cavity is divided into different regions and quadrants for clinical and anatomical reference.
- **Peritoneal Cavity**: The space between the parietal and visceral peritoneum is known as the peritoneal cavity. It contains a small amount of lubricating fluid that allows the organs to move smoothly against each other during digestion and other movements.
- **Retroperitoneal Space**: Some organs, such as the kidneys and pancreas, are located behind the peritoneum in an area known as the retroperitoneal space. These structures are partially covered by peritoneum and are protected by the posterior abdominal wall.
### 3. **The Digestive Organs**
The abdomen houses the majority of the digestive system, which is responsible for breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, and expelling waste. The key organs involved in digestion within the abdominal cavity include:
- **Stomach**: Located in the upper left quadrant, the stomach is a J-shaped organ that plays a central role in digestion. It receives food from the oesophagus and mixes it with gastric juices to break it down into a semi-liquid substance called chyme.
- **Small Intestine**: The small intestine is a long, coiled tube where most of the digestion and absorption of nutrients occurs. It is divided into three sections: the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. The duodenum receives chyme from the stomach, along with bile from the liver and digestive enzymes from the pancreas, to further break down food.
- **Large Intestine**: The large intestine absorbs water and electrolytes from the remaining indigestible food matter and forms solid waste (faeces). It consists of the caecum, colon, rectum, and anal canal. The colon is further divided into the ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid colon.
- **Liver**: The liver, located in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen, is the largest internal organ. It performs various vital functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and the production of bile, which aids in the digestion of fats.
- **Gallbladder**: The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ located beneath the liver. It stores and concentrates bile, releasing it into the small intestine to aid in the digestion of dietary fats.
- **Pancreas**: The pancreas lies behind the stomach and serves both endocrine and exocrine functions. It secretes digestive enzymes into the duodenum and produces hormones such as insulin and glucagon, which regulate blood sugar levels.
### 4. **The Spleen**
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:00:20
0:00:20
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:00:21
0:00:21
 0:00:09
0:00:09
 0:00:19
0:00:19
 0:00:14
0:00:14
 0:01:36
0:01:36
 0:00:13
0:00:13
 0:00:13
0:00:13
 0:00:25
0:00:25
 0:01:06
0:01:06
 0:00:13
0:00:13
 0:00:24
0:00:24
 0:00:09
0:00:09
 0:02:36
0:02:36
 0:00:13
0:00:13
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:00:13
0:00:13
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:00:34
0:00:34
 0:00:15
0:00:15
 0:00:39
0:00:39
 0:00:18
0:00:18