filmov
tv
IVF What Are Test Tube Babies? || In vitro fertilisation

Показать описание
IVF What Are Test Tube Babies? || In vitro fertilisation
IVF" and "Test tube baby" redirect here. For other uses, see IVF (disambiguation) and Test tube baby (disambiguation).
In vitro fertilization
Intervention
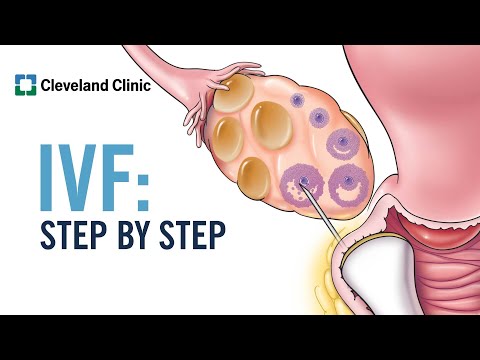
Illustrated schematic of IVF with
single-sperm injection (ICSI )
Synonyms IVF
ICD-10-PCS 8E0ZXY1
MeSH D005307
[edit on Wikidata]
In vitro fertilisation (or fertilization; IVF) is a process of fertilisation where an egg is combined with sperm outside the body, in vitro ("in glass"). The process involves monitoring and stimulating a woman's ovulatory process, removing an ovum or ova (egg or eggs) from the woman's ovaries and letting sperm fertilise them in a liquid in a laboratory. The fertilised egg (zygote) is cultured for 2–6 days in a growth medium, an embryo culture, and is then transferred to the same or another woman's uterus, with the intention of establishing a successful pregnancy.
IVF is a type of assisted reproductive technology used for infertility treatment and gestational surrogacy, in which a fertilized egg is implanted into a surrogate's uterus, and the resulting child is genetically unrelated to the surrogate. Some countries banned or otherwise regulate the availability of IVF treatment, giving rise to fertility tourism. Restrictions on availability of IVF include costs and age to carry a healthy pregnancy to term. IVF is mostly attempted if less invasive or expensive options have failed or are unlikely to work.
The first successful birth of a child after IVF treatment, Louise Brown, occurred in 1978. Louise Brown was born as a result of natural cycle IVF where no stimulation was made. Robert G. Edwards was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2010, the physiologist who co-developed the treatment together with Patrick Steptoe; Steptoe was not eligible for consideration as the Nobel Prize is not awarded posthumously.[1] With egg donation and IVF, women who are past their reproductive years or have reached menopause can still become pregnant. Adriana Iliescu held the record as the oldest woman to give birth using IVF and donated egg, when she gave birth in 2004 at the age of 66, a record passed in 2006. After the IVF treatment many couples are able to get pregnant without any fertility treatments.[2] In 2012 it was estimated that five million children had been born worldwide using IVF and other assisted reproduction techniques.[3]
my channel top entertainment universal news
astrologic,trending and so many types of news. so friends subscribe my channel and give me suggestions to improve my
channel work.
subscribe my entertainment channel
top entertainment universal news
subscribe my recipee channel
Delicious breakfast to dinner Recipes
subscribe my health channel
subscribe my rangoli mehandi and art channel
my facebook link
my twitter link
Category
Entertainment
Licence
Standard YouTube Licence
subscribe my channel
IVF" and "Test tube baby" redirect here. For other uses, see IVF (disambiguation) and Test tube baby (disambiguation).
In vitro fertilization
Intervention
Illustrated schematic of IVF with
single-sperm injection (ICSI )
Synonyms IVF
ICD-10-PCS 8E0ZXY1
MeSH D005307
[edit on Wikidata]
In vitro fertilisation (or fertilization; IVF) is a process of fertilisation where an egg is combined with sperm outside the body, in vitro ("in glass"). The process involves monitoring and stimulating a woman's ovulatory process, removing an ovum or ova (egg or eggs) from the woman's ovaries and letting sperm fertilise them in a liquid in a laboratory. The fertilised egg (zygote) is cultured for 2–6 days in a growth medium, an embryo culture, and is then transferred to the same or another woman's uterus, with the intention of establishing a successful pregnancy.
IVF is a type of assisted reproductive technology used for infertility treatment and gestational surrogacy, in which a fertilized egg is implanted into a surrogate's uterus, and the resulting child is genetically unrelated to the surrogate. Some countries banned or otherwise regulate the availability of IVF treatment, giving rise to fertility tourism. Restrictions on availability of IVF include costs and age to carry a healthy pregnancy to term. IVF is mostly attempted if less invasive or expensive options have failed or are unlikely to work.
The first successful birth of a child after IVF treatment, Louise Brown, occurred in 1978. Louise Brown was born as a result of natural cycle IVF where no stimulation was made. Robert G. Edwards was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2010, the physiologist who co-developed the treatment together with Patrick Steptoe; Steptoe was not eligible for consideration as the Nobel Prize is not awarded posthumously.[1] With egg donation and IVF, women who are past their reproductive years or have reached menopause can still become pregnant. Adriana Iliescu held the record as the oldest woman to give birth using IVF and donated egg, when she gave birth in 2004 at the age of 66, a record passed in 2006. After the IVF treatment many couples are able to get pregnant without any fertility treatments.[2] In 2012 it was estimated that five million children had been born worldwide using IVF and other assisted reproduction techniques.[3]
my channel top entertainment universal news
astrologic,trending and so many types of news. so friends subscribe my channel and give me suggestions to improve my
channel work.
subscribe my entertainment channel
top entertainment universal news
subscribe my recipee channel
Delicious breakfast to dinner Recipes
subscribe my health channel
subscribe my rangoli mehandi and art channel
my facebook link
my twitter link
Category
Entertainment
Licence
Standard YouTube Licence
subscribe my channel
 0:04:34
0:04:34
 0:00:52
0:00:52
 0:01:15
0:01:15
 0:01:40
0:01:40
 0:00:23
0:00:23
 0:00:36
0:00:36
 0:00:18
0:00:18
 0:03:09
0:03:09
 0:02:19
0:02:19
 0:01:39
0:01:39
 0:05:12
0:05:12
 0:00:42
0:00:42
 0:00:12
0:00:12
 0:00:37
0:00:37
 0:02:32
0:02:32
 0:00:15
0:00:15
 0:00:54
0:00:54
 0:04:04
0:04:04
 0:00:36
0:00:36
 0:00:58
0:00:58
 0:00:19
0:00:19
 0:00:38
0:00:38
 0:00:37
0:00:37
 0:00:44
0:00:44