filmov
tv
Special Relativity: Length Contraction

Показать описание
In this video, I use the equation for time dilation that I derived in that video to derive the equation for length contraction. There is also a more qualitative explanation for why moving objects experience length contraction.
Special Relativity Part 3: Length Contraction
Length Contraction and Time Dilation | Special Relativity Ch. 5
Length contraction: the real explanation
Is Length Contraction Real? The Genuine answer (Special Relativity)
Length Contraction is NOT an Illusion!
Length Contraction | Physics with Professor Matt Anderson | M29-01
Time Dilation and Length Contraction | Special Relativity
Length Contraction (Special Theory of Relativity)
EINSTEIN'S SPECIAL RELATIVITY | The Basics in a Minute
Special Relativity: Crash Course Physics #42
Length Contraction and Special Relativity
Time Dilation - Einstein's Theory Of Relativity Explained!
Special Theory Of Relativity: Length Contraction
How Are Time Dilatation and Length Contraction Connected
Physics: Deriving the formula for length contraction (Special relativity)
I wish I was taught Einstein's Special Relativity this way!
Length contraction class 12 | 12th class physics | consequence of special theory of relativity
I Never Understood Why Space Shrinks as You Approach Light Speed... Until Now
Special Relativity
5 / How lengths get shorter in special relativity
Time Dilation & Theory Of Relativity Simplified
Who is measuring proper time and proper length?
25.2 Time Dilation and Length Contraction | Relativity | General Physics
How Superposition Causes Length Contraction -- And Explains the Principle of Relativity
Комментарии
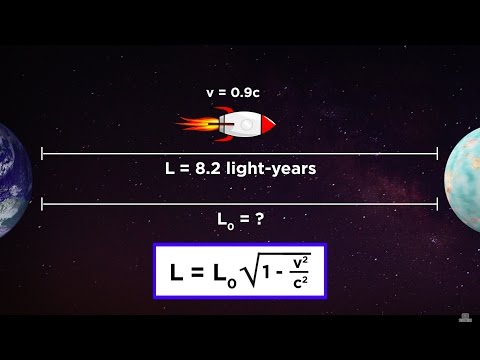 0:06:02
0:06:02
 0:07:17
0:07:17
 0:11:23
0:11:23
 0:06:46
0:06:46
 0:10:19
0:10:19
 0:04:32
0:04:32
 0:10:03
0:10:03
 0:19:54
0:19:54
 0:00:45
0:00:45
 0:08:59
0:08:59
 0:06:45
0:06:45
 0:08:06
0:08:06
 0:00:51
0:00:51
 0:05:40
0:05:40
 0:09:58
0:09:58
 0:21:42
0:21:42
 0:11:48
0:11:48
 0:18:57
0:18:57
 0:12:59
0:12:59
 0:05:02
0:05:02
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:05:34
0:05:34
 0:28:48
0:28:48
 0:23:08
0:23:08