filmov
tv
What are the Conditions for Formation of Covalent Bond? Chemical Bonding & Molecular Structures
Показать описание
Lewis and Langmuir developed a theory of bonding, according to them every atom tends to complete its octet and if that cannot be achieved by electron transfer it does so by electron sharing. This approach considers the bond to be basically covalent in nature.
A covalent bond is formed when the following conditions are satisfied:
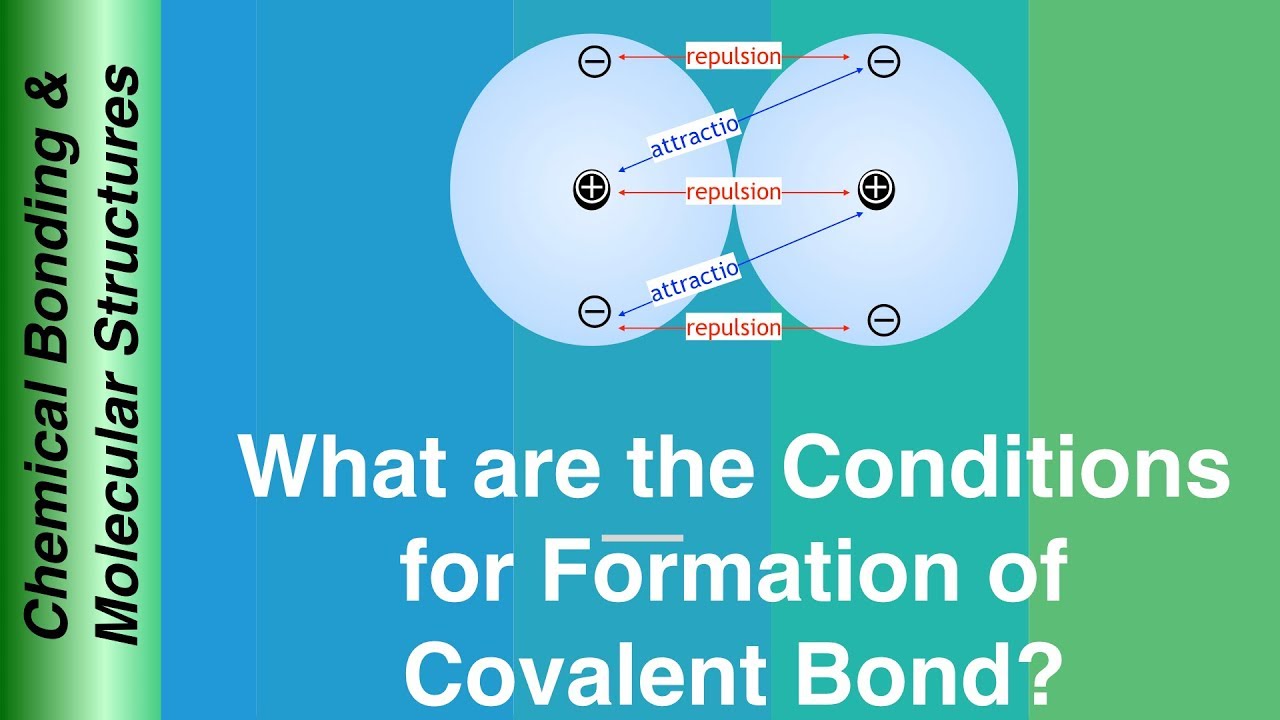
(1) A covalent bond will be formed when it is impossible to form ionic bond to be formed: Anionic bond is formed by electron transfer from one atom to another. This happens when the electron in one atom is at a higher energy level than in other atom. If the energy of the electron in both the atoms are similar, they can only combine to form a bond by sharing electrons.
(2) Two electrons are required to form a bond: A covalent bond is produced by two atoms contributing one electron each towards bond formation.
(3) There must be overlap of atomic orbitals: For a bond to be formed there must be an overlap of the atomic orbitals of the two atoms. In order to overlap, the atomic orbitals should occupy the same region in space.
(4) There must be a maximum of eight electrons in the valence shell for the majority of molecules. This is the octet rule suggested by G.N. Lewis. Thus the total number of shared pairs (bonds) and unshared pairs (lone pairs) must be equal to four. In ammonia molecule, for example, there are three shared pairs (bonds) and one lone pair, viz.,
(5) Elements with available d-orbitals can have expanded valence shell (beyond an octet). Elements from the third period onwards have 'd' orbitals available for bonding. They can utilise these d orbitals along with s and p orbitals for bonding. Hence they can have more than eight electrons in the valence shell, i.e., an expanded valence shell. For example, in SF6 the sulphur atom has 6 bonds means twelve electrons in its valence shell.
(6) Bonds will be formed in such a way that repulsion between electrons is minimised: Electrons which form bonds and other electrons not involved in bond formation adjust themselves by reorientation so that the repulsion between electrons is minimised .
(7) The resultant molecule after bond formation will have the lowest overall energy: A molecule will be more stable than its constituent atoms only if it possesses lower energy. Hence, number of bonds that will be formed and their strength would be determined only by the consideration of maximum stability of the molecule.
A covalent bond is formed when the following conditions are satisfied:
(1) A covalent bond will be formed when it is impossible to form ionic bond to be formed: Anionic bond is formed by electron transfer from one atom to another. This happens when the electron in one atom is at a higher energy level than in other atom. If the energy of the electron in both the atoms are similar, they can only combine to form a bond by sharing electrons.
(2) Two electrons are required to form a bond: A covalent bond is produced by two atoms contributing one electron each towards bond formation.
(3) There must be overlap of atomic orbitals: For a bond to be formed there must be an overlap of the atomic orbitals of the two atoms. In order to overlap, the atomic orbitals should occupy the same region in space.
(4) There must be a maximum of eight electrons in the valence shell for the majority of molecules. This is the octet rule suggested by G.N. Lewis. Thus the total number of shared pairs (bonds) and unshared pairs (lone pairs) must be equal to four. In ammonia molecule, for example, there are three shared pairs (bonds) and one lone pair, viz.,
(5) Elements with available d-orbitals can have expanded valence shell (beyond an octet). Elements from the third period onwards have 'd' orbitals available for bonding. They can utilise these d orbitals along with s and p orbitals for bonding. Hence they can have more than eight electrons in the valence shell, i.e., an expanded valence shell. For example, in SF6 the sulphur atom has 6 bonds means twelve electrons in its valence shell.
(6) Bonds will be formed in such a way that repulsion between electrons is minimised: Electrons which form bonds and other electrons not involved in bond formation adjust themselves by reorientation so that the repulsion between electrons is minimised .
(7) The resultant molecule after bond formation will have the lowest overall energy: A molecule will be more stable than its constituent atoms only if it possesses lower energy. Hence, number of bonds that will be formed and their strength would be determined only by the consideration of maximum stability of the molecule.
Комментарии
 0:07:18
0:07:18
 0:07:36
0:07:36
 0:00:33
0:00:33
 0:02:38
0:02:38
 0:00:51
0:00:51
 0:04:55
0:04:55
 0:01:20
0:01:20
 0:02:08
0:02:08
 1:03:55
1:03:55
 0:00:40
0:00:40
 0:10:29
0:10:29
 0:00:36
0:00:36
 0:01:36
0:01:36
 0:00:50
0:00:50
 0:01:14
0:01:14
 0:02:50
0:02:50
 0:00:36
0:00:36
 0:00:30
0:00:30
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:00:20
0:00:20
 0:07:14
0:07:14
 0:04:54
0:04:54
 0:04:02
0:04:02
 0:25:31
0:25:31