filmov
tv
3 Minutes SIADH Causes Symptoms Treatment Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone USMLE NCLEX

Показать описание
ADH Antidiuretic Hormone is produced in the hypothalamus and stored and released by the Posterior Pituitary
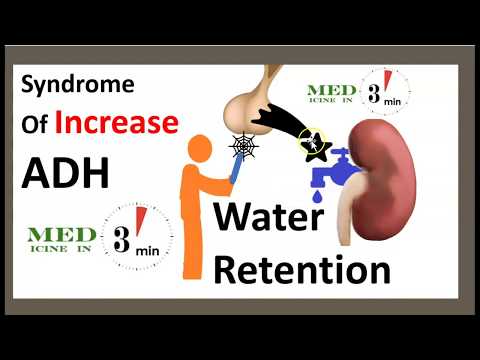
SIADH is characterized by excessive release of (ADH) either from the Posterior Pituitary or an abnormal non-pituitary source. Unsuppressed ADH causes an unrelenting increase in solute-free water being returned by the tubules of the kidney to the Venous Circulation.
The syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone (SIADH) is manifested by excessive and uncontrollable secretion of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) by the posterior pituitary gland.
It may also be caused by non-pituitary abnormalities. In this case, the hormone DHA leads to an increase in the amount of solute of free water that is returned by the tubules of the kidney into the venous system.
The causes of SIADH are multiples:
1) Disorders of the Central Nervous System, which directly stimulate the hypothalamus that controls the secretion of ADH secretion.
2) A variety of cancers which synthesize and secrete ectopically ADH hormone, particularly certain lung cancers
3) Some drugs interfere by directly stimulating the hypothalamus;
4) There are a number of hereditary mutations;
5) Certain cases may appear as episodic form.
Physiopathology:
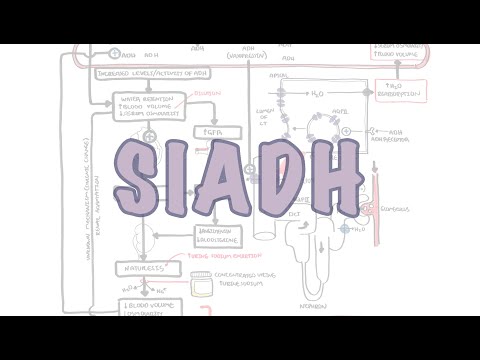
ADH is first synthesized by the hypothalamus, which stores it before it is shed through the portal system in the posterior pituitary gland.
The osmoreceptors of hypothalamic allow the regulation of the synthesis of ADH:
These receptors are active by plasma hypertonicity. Thus the Adh is released in the general circulation
The kidney interferes by increasing the return of free water into the circulation. This eliminates hypertonicity.
On the other hand, increased secretion of ADH hormone leads to an increase in the absorption of water by the kidneys causing a low osmolarity accompanied by a hyponatremia
At the same time, the intracellular volume increases, which causes particularly neurological damage to the brain, which can wait for convulsions and even coma and death.
Several therapies are proposed:
The restriction of fluid intake is the rule
It is also necessary to cure the underlying causes
In the case of cerebral edema, we give solute hypertonic dependent on the rate of natremia
Some drugs act on the kidneys to increase the fluid excretion
Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH) - SIADH (causes, treatment) in 3 minutes
Комментарии
 0:04:56
0:04:56
 0:16:10
0:16:10
 0:03:47
0:03:47
 0:05:22
0:05:22
 0:03:51
0:03:51
 0:16:39
0:16:39
 0:04:20
0:04:20
 0:11:50
0:11:50
 0:10:14
0:10:14
 0:05:53
0:05:53
 0:08:28
0:08:28
 0:09:02
0:09:02
![SIADH 3 [Treatment/Warning]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/fJ6nbXfpcI8/hqdefault.jpg) 0:18:04
0:18:04
 0:07:33
0:07:33
 0:08:26
0:08:26
 0:14:58
0:14:58
 0:05:00
0:05:00
 0:02:15
0:02:15
 0:33:05
0:33:05
 0:12:39
0:12:39
 0:09:51
0:09:51
 0:04:23
0:04:23
 0:01:09
0:01:09
 0:10:24
0:10:24