filmov
tv
Nervous system 6, Synapse

Показать описание
Nerve cells get so close, but never actually touch.There are very small gaps between individual nerve cells and between motor neurones and muscles. These gaps are called synaptic gaps. The gap is a physical space and the electrical nerve impulse is unable to jump across. The synapses are necessary to limit the propagation of an impulse around the nervous system. If all of the neurones were directly physically interconnected then any one nerve impulse would be propagated around the whole nervous system resulting in gross over- activity (this would probably result in continuous convulsions).
However, despite this need for electrical limitations, it is essential that nerve impulses can pass from one neurone to another when required. To allow this to happen the nerve fibre at one side of the synaptic gap releases a chemical called a chemical transmitter (neurotransmitter). This transmitter will then diffuse across the gap and generate a further electrical nervous impulse in the second neurone. Only the nerve fibre on one side of the synapse is able to secrete chemical transmitter. This means an impulse can travel from this first neurone to the second but not back in the other direction. The result is that synapses act as valves, only allowing one way transmission of impulses.
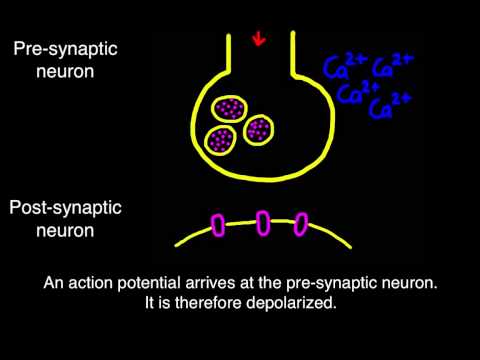
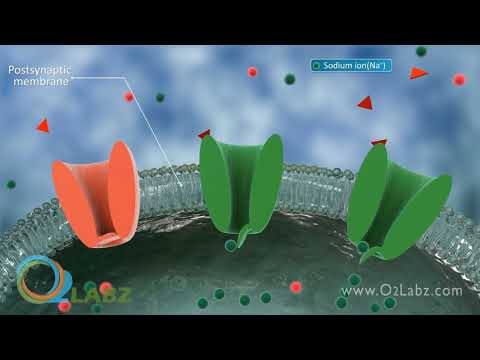
The neurone before the gap is termed the pre-synaptic neurone and the one after the gap as the post-synaptic neurone. Just before the gap, the pre-synaptic neurone widens out into a structure called the synaptic end bulb. This contains mitochondria to provide energy for the function of the synapse. The bulb also contains vesicles of chemical transmitter substances which have been previously synthesised by the neurone. When a nerve impulse arrives in the synaptic end bulb it causes some secretory vesicles to fuse with the pre-synaptic membrane releasing some chemical transmitter into the gap. After diffusing across the gap these transmitter molecules bind onto specific receptor sites on the post-synaptic membrane. Binding of transmitter into the receptor site activates the site. When enough of these receptor sites are activated by the chemical transmitter a further electrical impulse is generated in the post synaptic neurone.
If an impulse should arrive at the synapse via the post-synaptic neurone it will not be able to cross the gap and so will terminate. So, a nerve impulse is electrical when traveling along nerve fibres and chemical when traveling across a synaptic gap. A synapse may occur between two nerve fibres or between a nerve fibre and a cell body.
The connection between the synaptic end bulb of a motor neurone and a muscle is also via a synapse. Because this junction connects a nerve to a muscle it is referred to as a neuromuscular junction. As in a nerve to nerve connection, chemical transmitter is released, diffuses across the gap and binds onto specific receptor sites. When sufficient of the receptor sites are activated by the binding of transmitter, the muscle will be stimulated to contract. The surface of the muscle where the receptor sites are located is termed the motor end plate.
However, despite this need for electrical limitations, it is essential that nerve impulses can pass from one neurone to another when required. To allow this to happen the nerve fibre at one side of the synaptic gap releases a chemical called a chemical transmitter (neurotransmitter). This transmitter will then diffuse across the gap and generate a further electrical nervous impulse in the second neurone. Only the nerve fibre on one side of the synapse is able to secrete chemical transmitter. This means an impulse can travel from this first neurone to the second but not back in the other direction. The result is that synapses act as valves, only allowing one way transmission of impulses.
The neurone before the gap is termed the pre-synaptic neurone and the one after the gap as the post-synaptic neurone. Just before the gap, the pre-synaptic neurone widens out into a structure called the synaptic end bulb. This contains mitochondria to provide energy for the function of the synapse. The bulb also contains vesicles of chemical transmitter substances which have been previously synthesised by the neurone. When a nerve impulse arrives in the synaptic end bulb it causes some secretory vesicles to fuse with the pre-synaptic membrane releasing some chemical transmitter into the gap. After diffusing across the gap these transmitter molecules bind onto specific receptor sites on the post-synaptic membrane. Binding of transmitter into the receptor site activates the site. When enough of these receptor sites are activated by the chemical transmitter a further electrical impulse is generated in the post synaptic neurone.
If an impulse should arrive at the synapse via the post-synaptic neurone it will not be able to cross the gap and so will terminate. So, a nerve impulse is electrical when traveling along nerve fibres and chemical when traveling across a synaptic gap. A synapse may occur between two nerve fibres or between a nerve fibre and a cell body.
The connection between the synaptic end bulb of a motor neurone and a muscle is also via a synapse. Because this junction connects a nerve to a muscle it is referred to as a neuromuscular junction. As in a nerve to nerve connection, chemical transmitter is released, diffuses across the gap and binds onto specific receptor sites. When sufficient of the receptor sites are activated by the binding of transmitter, the muscle will be stimulated to contract. The surface of the muscle where the receptor sites are located is termed the motor end plate.
Комментарии
 0:12:16
0:12:16
 0:11:32
0:11:32
 0:04:46
0:04:46
 0:09:29
0:09:29
 0:10:57
0:10:57
 0:07:10
0:07:10
 0:10:36
0:10:36
 0:01:19
0:01:19
 0:10:29
0:10:29
 0:13:35
0:13:35
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:05:02
0:05:02
 0:11:44
0:11:44
 0:07:09
0:07:09
 0:00:48
0:00:48
 0:03:15
0:03:15
 0:05:32
0:05:32
 0:08:20
0:08:20
 0:12:04
0:12:04
 0:04:55
0:04:55
 0:13:12
0:13:12
 0:00:26
0:00:26
 0:15:45
0:15:45
 0:03:30
0:03:30