filmov
tv
Understanding Symmetrical Encryption

Показать описание
Symmetric Encryption Overview
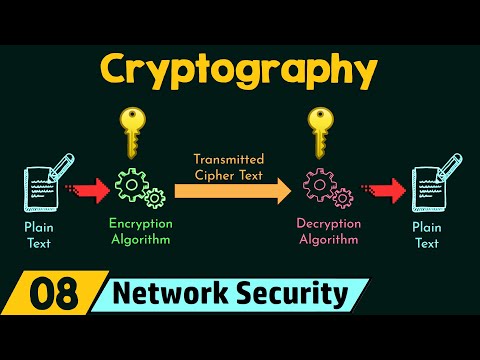
Symmetric encryption is a method of encrypting and decrypting data using a single shared secret key. Both the sender and the recipient use the same key to transform plaintext into ciphertext (encryption) and back into plaintext (decryption). This process is relatively fast and efficient, making it suitable for securing data at rest or in transit.
Key points about symmetric encryption:
Key: The security of symmetric encryption relies on keeping the secret key confidential. If the key is compromised, the encryption can be easily broken.
Algorithms: Popular symmetric encryption algorithms include AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), DES (Data Encryption Standard), and 3DES (Triple Data Encryption Standard).
Speed: Symmetric encryption is generally faster than asymmetric encryption, which is based on separate public and private keys.
Use cases: It's commonly used for encrypting data stored on disk, securing communication between devices, and protecting data within a closed system.
Challenges: Key management is a critical concern in symmetric encryption, as securely distributing and storing keys can be challenging.
Overall, symmetric encryption is an essential component of secure data protection, often used alongside asymmetric encryption for key exchange or digital signatures in various security protocols.
Symmetric encryption is a method of encrypting and decrypting data using a single shared secret key. Both the sender and the recipient use the same key to transform plaintext into ciphertext (encryption) and back into plaintext (decryption). This process is relatively fast and efficient, making it suitable for securing data at rest or in transit.
Key points about symmetric encryption:
Key: The security of symmetric encryption relies on keeping the secret key confidential. If the key is compromised, the encryption can be easily broken.
Algorithms: Popular symmetric encryption algorithms include AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), DES (Data Encryption Standard), and 3DES (Triple Data Encryption Standard).
Speed: Symmetric encryption is generally faster than asymmetric encryption, which is based on separate public and private keys.
Use cases: It's commonly used for encrypting data stored on disk, securing communication between devices, and protecting data within a closed system.
Challenges: Key management is a critical concern in symmetric encryption, as securely distributing and storing keys can be challenging.
Overall, symmetric encryption is an essential component of secure data protection, often used alongside asymmetric encryption for key exchange or digital signatures in various security protocols.
 0:04:40
0:04:40
 0:13:58
0:13:58
 0:04:18
0:04:18
 0:11:55
0:11:55
 0:01:45
0:01:45
 0:02:03
0:02:03
 0:12:33
0:12:33
 0:09:21
0:09:21
 0:06:53
0:06:53
 0:06:20
0:06:20
 0:14:14
0:14:14
 0:06:40
0:06:40
 0:02:49
0:02:49
 0:21:35
0:21:35
 0:08:15
0:08:15
 0:12:33
0:12:33
 0:13:34
0:13:34
 0:08:54
0:08:54
 0:08:40
0:08:40
 0:06:42
0:06:42
 0:04:49
0:04:49
 0:13:32
0:13:32
 0:11:11
0:11:11
 0:05:54
0:05:54