filmov
tv
Limit of lnx as x approaches Infinity (with Mean Value Theorem) | Real Analysis Exercises
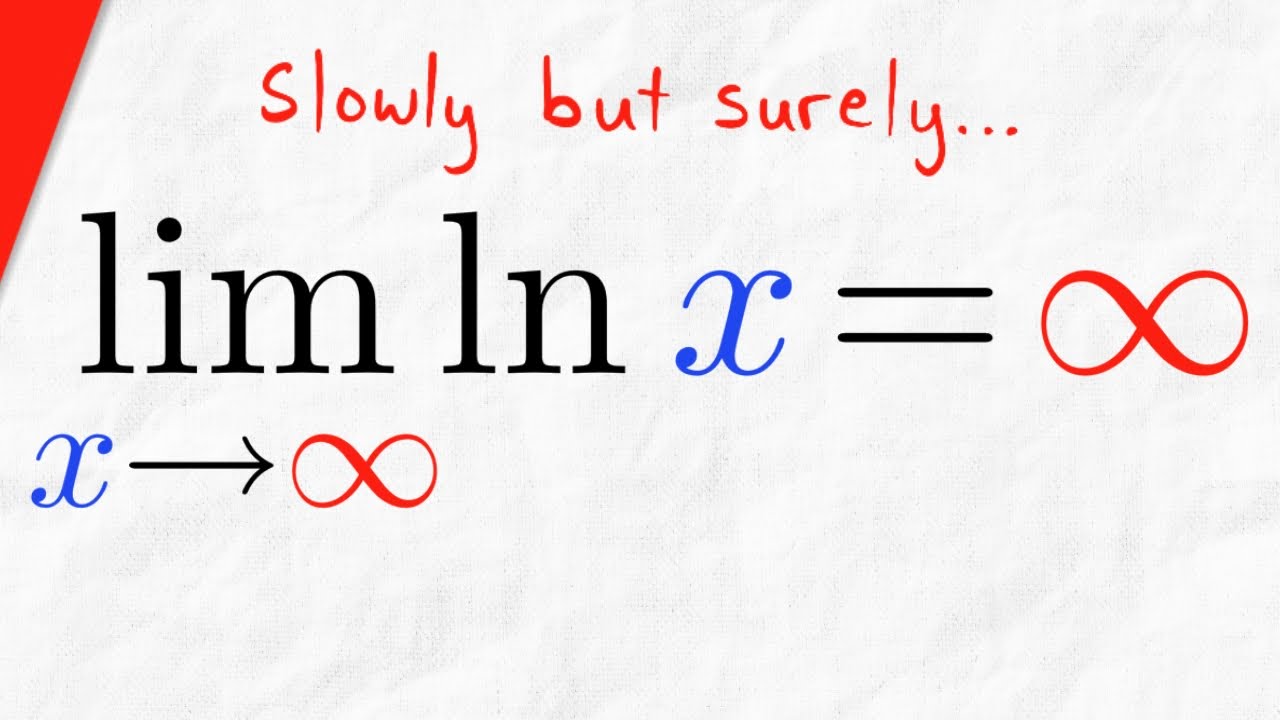
Показать описание
We prove the limit of ln(x) as x goes to infinity is infinity. To do this we use the Mean Value Theorem for definite integrals to show that ln(2) is at least 1/2, then we will take x to be greater than 2^(2M) for a fixed M greater than 0. This will quickly lead to the desired inequality, that ln x is greater than M. #RealAnalysis
Mean Value Theorem for Definite Integrals: (coming soon)
◉Textbooks I Like◉
★DONATE★
Thanks to Petar, dric, Rolf Waefler, Robert Rennie, Barbara Sharrock, Joshua Gray, Karl Kristiansen, Katy, Mohamad Nossier, and Shadow Master for their generous support on Patreon!
Follow Wrath of Math on...
Mean Value Theorem for Definite Integrals: (coming soon)
◉Textbooks I Like◉
★DONATE★
Thanks to Petar, dric, Rolf Waefler, Robert Rennie, Barbara Sharrock, Joshua Gray, Karl Kristiansen, Katy, Mohamad Nossier, and Shadow Master for their generous support on Patreon!
Follow Wrath of Math on...
Комментарии