filmov
tv
Statistics and probability - Variance Covariance and Correlation Coefficient of random variables

Показать описание
Statistics and probability: Variance, Covariance and Correlation Coefficient of random variables
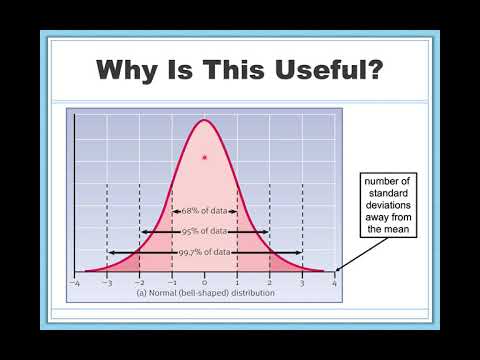
In addition to the mean or average of statistical distribution for a random variable, we also need to characterize the variability in the distribution in statistics.
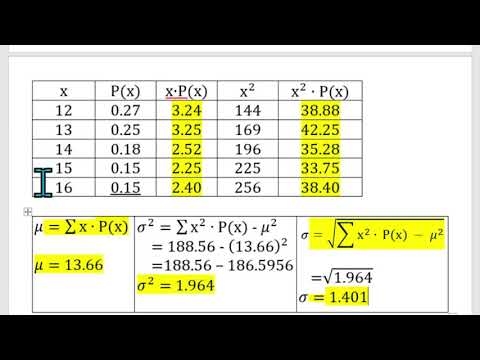
The most important measure of variability of a random variable X is obtained by applying function . The quantity is referred to as the variance of the random variable X or the variance of the probability distribution of X and is denoted by Var(X) .
The covariance between two random variables is a measure of the nature of the association between the two. If large values of X often result in large values of Y or small values of X result in small values of Y , positive X−μX will often result in positive Y −μY and negative X−μX will often result in negative Y −μY . Thus, the product (X −μX )(Y −μY ) will tend to be positive. On the other hand, if large X values often result in small Y values, the product (X−μX )(Y −μY ) will tend to be negative. The sign of the covariance indicates whether the relationship between two dependent random variables is positive or negative. When X and Y are statistically independent, it can be shown that the covariance is zero- The converse, however, is not generally true. Two variables may have zero covariance and still not be statistically independent. Note that the covariance only describes the linear relationship between two random variables. Therefore, if a covariance between X and Y is zero, X and Y may have a nonlinear relationship, which means that they are not necessarily independent.
#Statistics
#probability
#variance
#random
#variable
#distribution
#covariance
#discrete
#correlationcoefficient
#continuous
#statistics32
In addition to the mean or average of statistical distribution for a random variable, we also need to characterize the variability in the distribution in statistics.
The most important measure of variability of a random variable X is obtained by applying function . The quantity is referred to as the variance of the random variable X or the variance of the probability distribution of X and is denoted by Var(X) .
The covariance between two random variables is a measure of the nature of the association between the two. If large values of X often result in large values of Y or small values of X result in small values of Y , positive X−μX will often result in positive Y −μY and negative X−μX will often result in negative Y −μY . Thus, the product (X −μX )(Y −μY ) will tend to be positive. On the other hand, if large X values often result in small Y values, the product (X−μX )(Y −μY ) will tend to be negative. The sign of the covariance indicates whether the relationship between two dependent random variables is positive or negative. When X and Y are statistically independent, it can be shown that the covariance is zero- The converse, however, is not generally true. Two variables may have zero covariance and still not be statistically independent. Note that the covariance only describes the linear relationship between two random variables. Therefore, if a covariance between X and Y is zero, X and Y may have a nonlinear relationship, which means that they are not necessarily independent.
#Statistics
#probability
#variance
#random
#variable
#distribution
#covariance
#discrete
#correlationcoefficient
#continuous
#statistics32
 0:06:26
0:06:26
 0:10:24
0:10:24
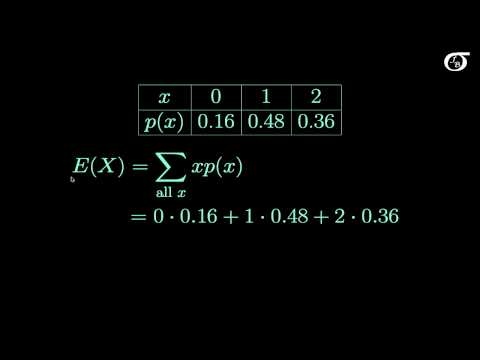 0:07:57
0:07:57
 0:07:33
0:07:33
 0:17:04
0:17:04
 0:09:57
0:09:57
 0:12:34
0:12:34
 0:10:21
0:10:21
 0:58:30
0:58:30
 0:10:38
0:10:38
 0:09:30
0:09:30
 0:27:58
0:27:58
 0:11:20
0:11:20
 0:14:44
0:14:44
 0:32:13
0:32:13
 0:02:48
0:02:48
 0:10:47
0:10:47
 0:11:44
0:11:44
 0:14:32
0:14:32
 0:05:38
0:05:38
 0:08:26
0:08:26
 0:08:20
0:08:20
 0:06:19
0:06:19
 0:05:50
0:05:50