filmov
tv
Cse lecture boolean functions syntax

Показать описание
okay, let's dive into the world of boolean functions in c/c++ (cse context usually implies c-style or c++), covering syntax, common use cases, and best practices. we'll provide extensive examples to solidify your understanding.
**what are boolean functions?**
at their core, boolean functions are functions that **return a boolean value**, which is either `true` or `false`. these functions are fundamental in programming for decision-making, logic control, and validation. they allow you to encapsulate and reuse complex logical expressions, making your code more readable and maintainable.
**boolean data type (c++)**
c++ natively provides a boolean data type, `bool`. its values are `true` and `false`.
**boolean data type (c - using `stdbool.h`)**
c doesn't have a built-in `bool` type in its earliest versions. however, the `stdbool.h` header was introduced in c99 to address this. including `stdbool.h` defines `bool` as a macro equivalent to `_bool`, and it defines `true` as `1` and `false` as `0`. for all practical purposes, you can then use `bool`, `true`, and `false` as if they were built into the language.
**basic syntax**
the general structure of a boolean function looks like this:
**c++:**
**c (with `stdbool.h`):**
**explanation:**
* **`bool`**: this is the *return type* of the function. it specifies that the function *must* return a `bool` value.
* **`functionname`**: the name you give to your function. choose a descriptive name that indicates what the function does.
* **`(parameter1type parameter1name, ...)`**: this is the *parameter list*. it defines the inputs that the function takes. each parameter has a *type* (e.g., `int`, `float`, `char`, `bool`, or custom types) and a *name*. a function can have zero or more parameters.
* **`{ ... }`**: the function body. this contains the code that is executed when the function is called.
* **`return true;` / `return false;`**: the `return` statement is *essential*. it specifies the boo ...
#BooleanFunctions #CSLecture #Syntax
boolean functions
syntax
CSE lecture
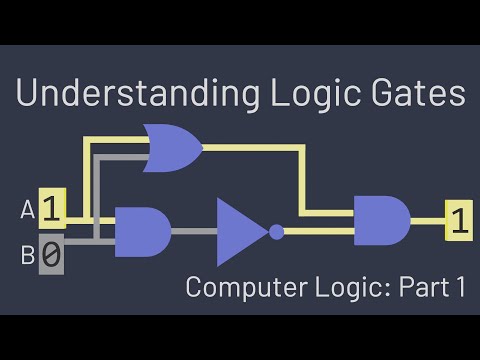
logic gates
truth tables
digital logic
combinational circuits
binary operations
logical expressions
Karnaugh maps
minimization techniques
circuit design
programming logic
discrete mathematics
Boolean algebra
**what are boolean functions?**
at their core, boolean functions are functions that **return a boolean value**, which is either `true` or `false`. these functions are fundamental in programming for decision-making, logic control, and validation. they allow you to encapsulate and reuse complex logical expressions, making your code more readable and maintainable.
**boolean data type (c++)**
c++ natively provides a boolean data type, `bool`. its values are `true` and `false`.
**boolean data type (c - using `stdbool.h`)**
c doesn't have a built-in `bool` type in its earliest versions. however, the `stdbool.h` header was introduced in c99 to address this. including `stdbool.h` defines `bool` as a macro equivalent to `_bool`, and it defines `true` as `1` and `false` as `0`. for all practical purposes, you can then use `bool`, `true`, and `false` as if they were built into the language.
**basic syntax**
the general structure of a boolean function looks like this:
**c++:**
**c (with `stdbool.h`):**
**explanation:**
* **`bool`**: this is the *return type* of the function. it specifies that the function *must* return a `bool` value.
* **`functionname`**: the name you give to your function. choose a descriptive name that indicates what the function does.
* **`(parameter1type parameter1name, ...)`**: this is the *parameter list*. it defines the inputs that the function takes. each parameter has a *type* (e.g., `int`, `float`, `char`, `bool`, or custom types) and a *name*. a function can have zero or more parameters.
* **`{ ... }`**: the function body. this contains the code that is executed when the function is called.
* **`return true;` / `return false;`**: the `return` statement is *essential*. it specifies the boo ...
#BooleanFunctions #CSLecture #Syntax
boolean functions
syntax
CSE lecture
logic gates
truth tables
digital logic
combinational circuits
binary operations
logical expressions
Karnaugh maps
minimization techniques
circuit design
programming logic
discrete mathematics
Boolean algebra
 0:07:04
0:07:04
 0:07:25
0:07:25
 0:06:24
0:06:24
 0:07:20
0:07:20
 0:07:28
0:07:28
 0:01:32
0:01:32
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:05:29
0:05:29
 0:05:49
0:05:49
 0:00:05
0:00:05
 0:00:17
0:00:17
 0:05:29
0:05:29
 0:08:24
0:08:24
 0:10:32
0:10:32
 0:27:44
0:27:44
 0:00:59
0:00:59
 0:07:40
0:07:40
 0:07:33
0:07:33
![[CSE 116] Lecture](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/pi0lDBSVz1U/hqdefault.jpg) 0:47:38
0:47:38
 0:00:20
0:00:20
 0:10:01
0:10:01
 0:07:13
0:07:13
![[CSE 116] Lecture](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/gymSbqigbLo/hqdefault.jpg) 1:12:58
1:12:58
 0:00:05
0:00:05