filmov
tv
Routing Information Protocol (RIP) | MCQ-63

Показать описание
#cisco #ccna #rip #shorts
Question-63: A RIP route, after being marked as invalid, is advertised to all other routers as unreachable.
A. True
B. False
Correct Answer: ABCD
*Routing Information Protocol*
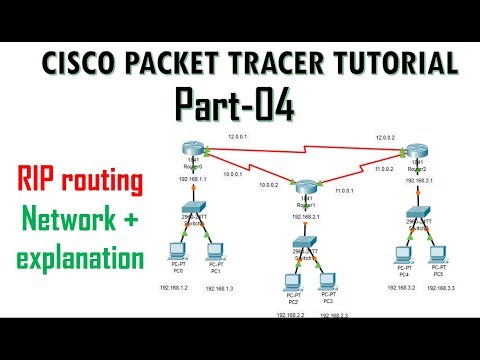
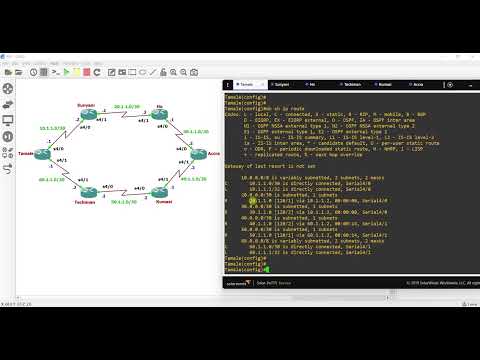
Routing Information Protocol (RIP) is a distance-vector routing protocol used in computer networks to dynamically exchange routing information among routers. RIP is a simple protocol that allows routers to determine the best path for forwarding packets to their destinations within an IP-based network.
Here are some key features of the Routing Information Protocol:
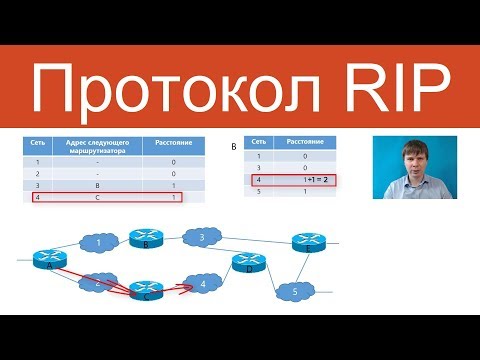
1. Distance-Vector Protocol: RIP is based on the distance-vector algorithm, where routers exchange routing tables periodically with their neighboring routers. Each router calculates the distance to reach a destination network based on the number of hops (routers) between them.
2. Hop Count: RIP uses hop count as a metric to determine the best path. The hop count represents the number of routers that a packet must traverse to reach its destination. RIP allows a maximum hop count of 15, and any route with a hop count higher than that is considered unreachable.
3. Periodic Updates: RIP routers exchange routing information with their neighboring routers at regular intervals. By default, this update occurs every 30 seconds, but it can be configured. Routers send their entire routing table to their neighbors during these updates.
4. Split Horizon: RIP incorporates a technique called "split horizon" to prevent routing loops. With split horizon, a router does not advertise a route back to the router from which it learned the route. This helps avoid loops caused by inconsistent routing information.
5. Triggered Updates: In addition to periodic updates, RIP also supports triggered updates. A triggered update occurs when there is a change in the network topology, such as a link failure or a newly discovered route. These updates are sent immediately to inform neighboring routers about the change.
6. Limited Network Size: RIP is suitable for small to medium-sized networks due to its limitations. The maximum hop count of 15 restricts the network diameter, and the periodic updates can cause significant overhead in large networks.
RIP has two versions: RIP version 1 (RIPv1) and RIP version 2 (RIPv2). RIPv2 is an enhanced version that supports features like route authentication, variable-length subnet masks (VLSM), and support for classless inter-domain routing (CIDR).
However, it's worth noting that RIP is considered an older routing protocol and is less commonly used in modern networks. Other routing protocols like OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) and BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) are more widely deployed in larger and more complex networks.
*Social Media*
Like, Share, Comment, Follow and Subscribe
#networkinghubone
Question-63: A RIP route, after being marked as invalid, is advertised to all other routers as unreachable.
A. True
B. False
Correct Answer: ABCD
*Routing Information Protocol*
Routing Information Protocol (RIP) is a distance-vector routing protocol used in computer networks to dynamically exchange routing information among routers. RIP is a simple protocol that allows routers to determine the best path for forwarding packets to their destinations within an IP-based network.
Here are some key features of the Routing Information Protocol:
1. Distance-Vector Protocol: RIP is based on the distance-vector algorithm, where routers exchange routing tables periodically with their neighboring routers. Each router calculates the distance to reach a destination network based on the number of hops (routers) between them.
2. Hop Count: RIP uses hop count as a metric to determine the best path. The hop count represents the number of routers that a packet must traverse to reach its destination. RIP allows a maximum hop count of 15, and any route with a hop count higher than that is considered unreachable.
3. Periodic Updates: RIP routers exchange routing information with their neighboring routers at regular intervals. By default, this update occurs every 30 seconds, but it can be configured. Routers send their entire routing table to their neighbors during these updates.
4. Split Horizon: RIP incorporates a technique called "split horizon" to prevent routing loops. With split horizon, a router does not advertise a route back to the router from which it learned the route. This helps avoid loops caused by inconsistent routing information.
5. Triggered Updates: In addition to periodic updates, RIP also supports triggered updates. A triggered update occurs when there is a change in the network topology, such as a link failure or a newly discovered route. These updates are sent immediately to inform neighboring routers about the change.
6. Limited Network Size: RIP is suitable for small to medium-sized networks due to its limitations. The maximum hop count of 15 restricts the network diameter, and the periodic updates can cause significant overhead in large networks.
RIP has two versions: RIP version 1 (RIPv1) and RIP version 2 (RIPv2). RIPv2 is an enhanced version that supports features like route authentication, variable-length subnet masks (VLSM), and support for classless inter-domain routing (CIDR).
However, it's worth noting that RIP is considered an older routing protocol and is less commonly used in modern networks. Other routing protocols like OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) and BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) are more widely deployed in larger and more complex networks.
*Social Media*
Like, Share, Comment, Follow and Subscribe
#networkinghubone
 0:07:13
0:07:13
 0:05:34
0:05:34
 0:08:49
0:08:49
 0:10:09
0:10:09
 0:06:19
0:06:19
 0:02:53
0:02:53
 0:15:07
0:15:07
 0:05:13
0:05:13
 0:43:42
0:43:42
 0:24:52
0:24:52
 0:13:45
0:13:45
 0:21:28
0:21:28
 0:06:57
0:06:57
 0:20:32
0:20:32
 0:06:52
0:06:52
 0:12:36
0:12:36
 0:18:47
0:18:47
 0:30:16
0:30:16
 0:27:48
0:27:48
 0:05:44
0:05:44
 0:04:09
0:04:09
 0:11:14
0:11:14
 0:07:19
0:07:19
 0:10:08
0:10:08