filmov
tv
How Synchronization Happens in Power Plants | Understanding Synchroscope & GCB Operations

Показать описание
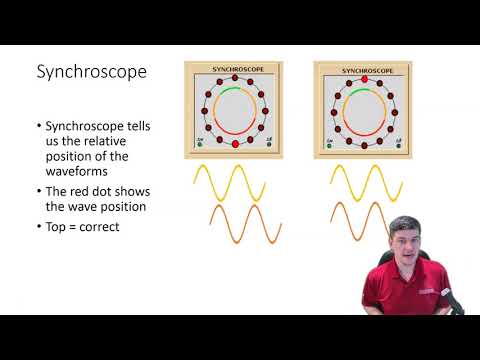
Discover the fascinating world of power plant synchronization in our latest video! Learn how electricity generated by power plants is seamlessly integrated into the grid to power homes and businesses. We delve into the critical role of the synchroscope, which visually ensures frequency alignment, and explore key synchronization parameters like voltage, frequency, phase angle, and phase sequence using relatable analogies. Understand the importance of proper synchronization to prevent equipment damage and grid disruptions. Plus, see the vital roles of the Automatic Voltage Regulator (AVR) and turbine control in maintaining voltage stability. Join us to uncover the science behind stable and reliable power delivery!
#PowerPlants #Electricity #Synchronization #Synchroscope #VoltageRegulation #GridStability #PowerSystems #AVR #EnergyEducation
Don't forget to like and share this video!
OUTLINE:
00:00:00 Introduction
00:01:08 Explaining Synchronisation
00:01:41 Why do we check parameters?
00:02:50 Checking Phase Sequence
00:03:25 Matching Voltage Profile
00:04:10 Synchronization Layout and Procedure
00:05:23 Floating Condition
00:05:52 Closing Remarks
#PowerPlants #Electricity #Synchronization #Synchroscope #VoltageRegulation #GridStability #PowerSystems #AVR #EnergyEducation
Don't forget to like and share this video!
OUTLINE:
00:00:00 Introduction
00:01:08 Explaining Synchronisation
00:01:41 Why do we check parameters?
00:02:50 Checking Phase Sequence
00:03:25 Matching Voltage Profile
00:04:10 Synchronization Layout and Procedure
00:05:23 Floating Condition
00:05:52 Closing Remarks
Комментарии
 0:03:28
0:03:28
 0:20:58
0:20:58
 0:07:57
0:07:57
 0:19:44
0:19:44
 0:10:56
0:10:56
 0:05:29
0:05:29
 0:11:14
0:11:14
 0:11:23
0:11:23
 0:00:42
0:00:42
 0:00:17
0:00:17
 0:06:21
0:06:21
 0:01:39
0:01:39
 0:00:55
0:00:55
 0:11:09
0:11:09
 0:05:29
0:05:29
 0:06:05
0:06:05
 0:05:38
0:05:38
 0:04:52
0:04:52
 0:01:39
0:01:39
 0:00:52
0:00:52
 0:10:38
0:10:38
 0:02:24
0:02:24
 0:00:57
0:00:57
 0:03:11
0:03:11