filmov
tv
Data Visualization and Network Visualization | Introduction

Показать описание
#datavisualization #networkvisualization #socialmedia #graphics #socialmedia #analysis
Hello and welcome to this introduction to data visualization and network visualization.
00:10
What is data visualization.
00:14
Data visualization is the practice of representing data in a visual format such as charts, graphs, and maps to help people to understand and analyze complex information.
00:27
By representing data visually, we can quickly identify patterns, trends, and relationships that might be difficult to spot in a table of numbers or text.
00:41
What is network visualization.
00:44
Network visualization, on the other hand, is a type of data visualization that focuses on displaying relationships and connections between different entities.
00:56
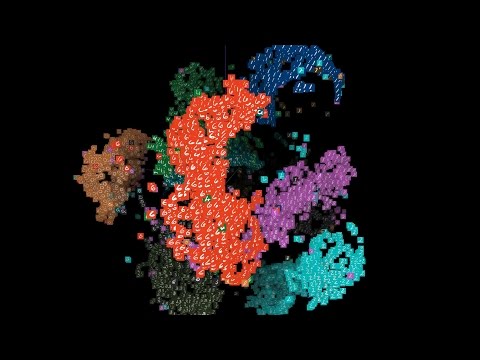
In the network visualization, nodes represent the entities and edges represent the connections between them.
01:05
By visualizing networks, we can gain insights into the structure, dynamics, and behavior of complex systems such as social networks, transportation systems, and biological networks.
01:22
Applications of data visualization and network visualization.
01:27
Both data visualization and network visualization are important tools for a wide range of applications, including business, science, education and journalism.
01:42
They can help us communicate ideas and findings more effectively, discover new insights and patterns, and make a better decision based on data.
01:56
Best practices in data visualization.
02:01
Simplifying the design using clear labels and providing context to help the viewer understand the data's relevance and impact.
02:10
Misleading visualizations should be avoided.
02:14
The audience should be considered an interactivity can be incorporated to increase engagement.
02:21
Finally, it's important to continuously test and refine the visualization to meet the needs of the audience.
02:32
Best practices in network visualization.
02:36
Choosing an appropriate layout that represent the network structure effectively, using colors and sizes to highlight important nodes and edges, simplifying the design to reduce visual clutter and providing context to help the viewer to understand the network's relevance and significance.
02:58
The audience should be considered when selecting the appropriate visualization method, and it's important to test and refine the network visualization to ensure that it is effectively communicating the intended message.
03:16
Next, we are going to evaluate some different types of network visualization.
03:24
Node-link diagrams.
03:26
These are the most common and well-known types of network visualization.
03:31
In Nord link diagrams, nodes are represented as circles or other shapes, and edges are represented as lines connecting the nodes.
03:42
Node link diagrams are good for showing the overall structure and connections of a network, but can become cluttered and hard to read when dealing with large and complex networks.
03:56
Matrix visualizations.
03:59
In matrix visualizations, the network is represented as a matrix or grid, where the rows and columns represent nodes and the cells represent the edges between them.
04:12
Matrix visualizations are useful for showing their strength and directionality of connections between nodes but can be limited in their ability to convey more nuanced information about the network structure.
04:29
Arc diagrams. Arc diagrams are a type of network visualization that use arcs to represent the edges between nodes.
04:39
Arc diagrams are useful for showing the relationships between nodes in a clear and easy to read way, but can be limited in their ability to convey information about the relative position and clustering of nodes.
04:56
Tree Maps.
04:58
Tree maps are type of network visualization that use nested rectangles to represent the nodes in hierarchical network.
05:07
Tree maps are useful for showing the overall structure of a network and the relationships between different levels of hierarchy, but can be less effective in solving the precise connections between the individual nodes.
05:25
Force directed layouts. Force directed layouts are a type of network visualization that simulate physical forces to position the nodes and edges in a way that minimizes overlap and maximizes the clarity of the network structure.
05:42
Forced directed layouts can be effective for showing the overall structure and connections of a network, but can be computationally intensive and sensitive to the initial positioning of the nodes.
05:58
Choosing the best visualization.
06:02
Overall, the choice of network visualization type will depend on the specific goals of the visualization and the size, the complexity of the network, and the type of data being represented.
06:16
Each type of visualization has its own strengths and weaknesses, and the best visualization for a given situation will depend on the specific context and requirements of the project.
06:32
Thank you for your time and your attention.
Hello and welcome to this introduction to data visualization and network visualization.
00:10
What is data visualization.
00:14
Data visualization is the practice of representing data in a visual format such as charts, graphs, and maps to help people to understand and analyze complex information.
00:27
By representing data visually, we can quickly identify patterns, trends, and relationships that might be difficult to spot in a table of numbers or text.
00:41
What is network visualization.
00:44
Network visualization, on the other hand, is a type of data visualization that focuses on displaying relationships and connections between different entities.
00:56
In the network visualization, nodes represent the entities and edges represent the connections between them.
01:05
By visualizing networks, we can gain insights into the structure, dynamics, and behavior of complex systems such as social networks, transportation systems, and biological networks.
01:22
Applications of data visualization and network visualization.
01:27
Both data visualization and network visualization are important tools for a wide range of applications, including business, science, education and journalism.
01:42
They can help us communicate ideas and findings more effectively, discover new insights and patterns, and make a better decision based on data.
01:56
Best practices in data visualization.
02:01
Simplifying the design using clear labels and providing context to help the viewer understand the data's relevance and impact.
02:10
Misleading visualizations should be avoided.
02:14
The audience should be considered an interactivity can be incorporated to increase engagement.
02:21
Finally, it's important to continuously test and refine the visualization to meet the needs of the audience.
02:32
Best practices in network visualization.
02:36
Choosing an appropriate layout that represent the network structure effectively, using colors and sizes to highlight important nodes and edges, simplifying the design to reduce visual clutter and providing context to help the viewer to understand the network's relevance and significance.
02:58
The audience should be considered when selecting the appropriate visualization method, and it's important to test and refine the network visualization to ensure that it is effectively communicating the intended message.
03:16
Next, we are going to evaluate some different types of network visualization.
03:24
Node-link diagrams.
03:26
These are the most common and well-known types of network visualization.
03:31
In Nord link diagrams, nodes are represented as circles or other shapes, and edges are represented as lines connecting the nodes.
03:42
Node link diagrams are good for showing the overall structure and connections of a network, but can become cluttered and hard to read when dealing with large and complex networks.
03:56
Matrix visualizations.
03:59
In matrix visualizations, the network is represented as a matrix or grid, where the rows and columns represent nodes and the cells represent the edges between them.
04:12
Matrix visualizations are useful for showing their strength and directionality of connections between nodes but can be limited in their ability to convey more nuanced information about the network structure.
04:29
Arc diagrams. Arc diagrams are a type of network visualization that use arcs to represent the edges between nodes.
04:39
Arc diagrams are useful for showing the relationships between nodes in a clear and easy to read way, but can be limited in their ability to convey information about the relative position and clustering of nodes.
04:56
Tree Maps.
04:58
Tree maps are type of network visualization that use nested rectangles to represent the nodes in hierarchical network.
05:07
Tree maps are useful for showing the overall structure of a network and the relationships between different levels of hierarchy, but can be less effective in solving the precise connections between the individual nodes.
05:25
Force directed layouts. Force directed layouts are a type of network visualization that simulate physical forces to position the nodes and edges in a way that minimizes overlap and maximizes the clarity of the network structure.
05:42
Forced directed layouts can be effective for showing the overall structure and connections of a network, but can be computationally intensive and sensitive to the initial positioning of the nodes.
05:58
Choosing the best visualization.
06:02
Overall, the choice of network visualization type will depend on the specific goals of the visualization and the size, the complexity of the network, and the type of data being represented.
06:16
Each type of visualization has its own strengths and weaknesses, and the best visualization for a given situation will depend on the specific context and requirements of the project.
06:32
Thank you for your time and your attention.
Комментарии
 0:08:33
0:08:33
 0:00:18
0:00:18
 0:00:18
0:00:18
 0:03:50
0:03:50
 0:03:14
0:03:14
 0:02:20
0:02:20
 0:18:51
0:18:51
 0:00:45
0:00:45
 1:42:31
1:42:31
 0:20:15
0:20:15
 0:01:07
0:01:07
 0:00:45
0:00:45
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:00:12
0:00:12
 0:01:25
0:01:25
 0:20:18
0:20:18
 0:00:35
0:00:35
 0:03:17
0:03:17
 0:27:09
0:27:09
 0:08:04
0:08:04
 0:15:03
0:15:03
 0:19:51
0:19:51
 0:03:49
0:03:49
 0:00:24
0:00:24