filmov
tv
Layers of Earth's 🌍Atmosphere | #shorts #sciencefacts

Показать описание
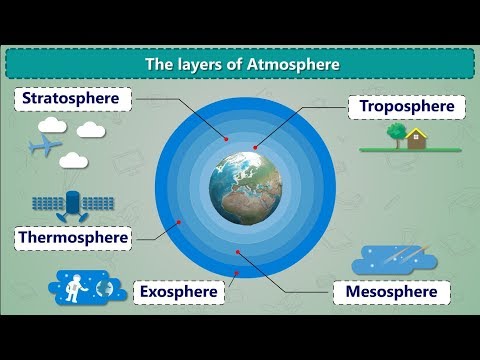
The Earth's atmosphere is composed of five distinct layers, each with its own unique characteristics. Starting from the surface and moving upwards, the layers are:
Troposphere: The troposphere is the lowest layer of the atmosphere, extending from the Earth's surface up to an average altitude of about 8 to 15 kilometers (5 to 9 miles). This layer contains the majority of the Earth's weather phenomena, such as clouds, precipitation, and convection currents. As you ascend through the troposphere, temperature generally decreases.
Stratosphere: The stratosphere lies above the troposphere and extends from about 15 kilometers (9 miles) to approximately 50 kilometers (31 miles) in altitude. The defining feature of the stratosphere is the presence of the ozone layer, which absorbs and filters out a significant amount of the Sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation. As a result, temperature increases with altitude in the stratosphere.
Mesosphere: The mesosphere is located above the stratosphere and spans from around 50 kilometers (31 miles) to about 85 kilometers (53 miles) in altitude. In this layer, the temperature decreases again as you move higher. The mesosphere is known for its extremely low temperatures, with the coldest temperatures in the Earth's atmosphere occurring near its upper boundary.
Thermosphere: The thermosphere is situated above the mesosphere and extends from approximately 85 kilometers (53 miles) to between 500 and 1,000 kilometers (311 to 621 miles) above the Earth's surface. Although the density of gas molecules is incredibly low in this layer, the thermosphere experiences extremely high temperatures due to the absorption of intense solar radiation. However, despite the high temperatures, the thermosphere would feel cold to a human observer due to the low density of particles.
Exosphere: The exosphere is the outermost layer of the Earth's atmosphere and extends beyond the thermosphere. It gradually transitions into the vacuum of space. In the exosphere, the density of gas molecules is extremely low, and they are not bound by gravity to the Earth's surface. This layer is primarily composed of hydrogen and helium atoms, which can escape into space due to their high kinetic energy.
It's important to note that these layers are not distinct boundaries but rather gradual transitions. The boundary altitudes can vary depending on factors such as latitude, season, and solar activity
#science #sciencefacts #india #shorts
Troposphere: The troposphere is the lowest layer of the atmosphere, extending from the Earth's surface up to an average altitude of about 8 to 15 kilometers (5 to 9 miles). This layer contains the majority of the Earth's weather phenomena, such as clouds, precipitation, and convection currents. As you ascend through the troposphere, temperature generally decreases.
Stratosphere: The stratosphere lies above the troposphere and extends from about 15 kilometers (9 miles) to approximately 50 kilometers (31 miles) in altitude. The defining feature of the stratosphere is the presence of the ozone layer, which absorbs and filters out a significant amount of the Sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation. As a result, temperature increases with altitude in the stratosphere.
Mesosphere: The mesosphere is located above the stratosphere and spans from around 50 kilometers (31 miles) to about 85 kilometers (53 miles) in altitude. In this layer, the temperature decreases again as you move higher. The mesosphere is known for its extremely low temperatures, with the coldest temperatures in the Earth's atmosphere occurring near its upper boundary.
Thermosphere: The thermosphere is situated above the mesosphere and extends from approximately 85 kilometers (53 miles) to between 500 and 1,000 kilometers (311 to 621 miles) above the Earth's surface. Although the density of gas molecules is incredibly low in this layer, the thermosphere experiences extremely high temperatures due to the absorption of intense solar radiation. However, despite the high temperatures, the thermosphere would feel cold to a human observer due to the low density of particles.
Exosphere: The exosphere is the outermost layer of the Earth's atmosphere and extends beyond the thermosphere. It gradually transitions into the vacuum of space. In the exosphere, the density of gas molecules is extremely low, and they are not bound by gravity to the Earth's surface. This layer is primarily composed of hydrogen and helium atoms, which can escape into space due to their high kinetic energy.
It's important to note that these layers are not distinct boundaries but rather gradual transitions. The boundary altitudes can vary depending on factors such as latitude, season, and solar activity
#science #sciencefacts #india #shorts
Комментарии
 0:03:28
0:03:28
 0:02:32
0:02:32
 0:06:17
0:06:17
 0:02:54
0:02:54
 0:03:49
0:03:49
 0:09:47
0:09:47
 0:02:37
0:02:37
 0:15:20
0:15:20
 0:00:54
0:00:54
 0:12:53
0:12:53
 0:15:53
0:15:53
 0:09:33
0:09:33
 0:06:05
0:06:05
 0:04:35
0:04:35
 0:03:59
0:03:59
 0:10:42
0:10:42
 0:00:14
0:00:14
 0:03:44
0:03:44
 0:00:37
0:00:37
 0:00:56
0:00:56
 0:00:58
0:00:58
 0:04:05
0:04:05
 0:00:07
0:00:07
 0:00:26
0:00:26