filmov
tv
Class 7 Science - HEAT - NCERT Science - Part 2 (Last Part)

Показать описание
Chapter 4 of the NCERT Class 7 Science textbook is titled "Heat." This chapter introduces the concept of heat, its sources, transfer, and effects. Here is a summary of the key points covered in this chapter:
Introduction to Heat: Heat is a form of energy that flows from a hotter object to a colder object. It can be produced by various sources such as the sun, burning fuel, electricity, and friction.
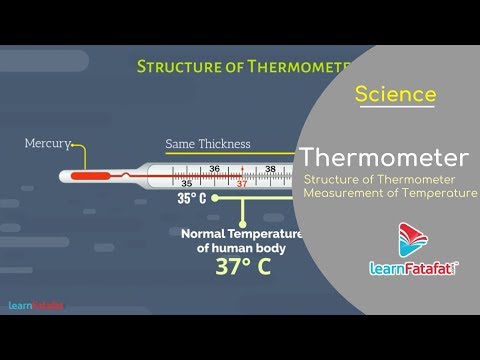
Temperature: Temperature is a measure of the hotness or coldness of an object. It is measured using a thermometer and is usually expressed in degrees Celsius (°C).
Measuring Temperature: The common scales used to measure temperature are Celsius and Fahrenheit. The Celsius scale has 0°C as the freezing point of water and 100°C as its boiling point, while the Fahrenheit scale has 32°F as the freezing point of water and 212°F as its boiling point.
Transfer of Heat: Heat can be transferred through three processes: conduction, convection, and radiation.
a. Conduction: Conduction is the transfer of heat through direct contact between particles of different temperatures. Heat transfers from the hotter object to the colder object.
b. Convection: Convection is the transfer of heat through the movement of fluids (liquids or gases). It occurs due to the difference in density of hot and cold fluids, creating a convection current.
c. Radiation: Radiation is the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves. It does not require any medium and can travel through a vacuum. The sun emits heat through radiation.
Effects of Heat: Heat has various effects on objects and substances.
a. Expansion and Contraction: When objects are heated, they expand, and when they are cooled, they contract. This property is utilized in various applications, such as the functioning of thermometers and bimetallic strips.
b. Change of State: Heat causes changes in the state of matter. Adding heat to a solid can melt it into a liquid, and adding more heat can turn the liquid into a gas. The reverse processes, such as condensation and freezing, also occur due to the removal of heat.
c. Evaporation: Evaporation is the process in which a liquid changes into a gas at its surface, even at temperatures below its boiling point. Heat is absorbed during evaporation.
d. Effects on Substances: Heat can cause chemical reactions, such as burning or decomposition. It can also change the physical properties of substances, such as color, texture, or taste.
Heat and Temperature: Heat and temperature are related but different concepts. Heat is the energy transferred from a hotter object to a colder object, while temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles of a substance.
This summary provides an overview of the key concepts covered in Chapter 4 of the NCERT Class 7 Science textbook, "Heat."
#ncert #class7 #science #heat #exam #exammotivation #exampreparation #learneverything #india #cbse #chapter #keepitsimple
Introduction to Heat: Heat is a form of energy that flows from a hotter object to a colder object. It can be produced by various sources such as the sun, burning fuel, electricity, and friction.
Temperature: Temperature is a measure of the hotness or coldness of an object. It is measured using a thermometer and is usually expressed in degrees Celsius (°C).
Measuring Temperature: The common scales used to measure temperature are Celsius and Fahrenheit. The Celsius scale has 0°C as the freezing point of water and 100°C as its boiling point, while the Fahrenheit scale has 32°F as the freezing point of water and 212°F as its boiling point.
Transfer of Heat: Heat can be transferred through three processes: conduction, convection, and radiation.
a. Conduction: Conduction is the transfer of heat through direct contact between particles of different temperatures. Heat transfers from the hotter object to the colder object.
b. Convection: Convection is the transfer of heat through the movement of fluids (liquids or gases). It occurs due to the difference in density of hot and cold fluids, creating a convection current.
c. Radiation: Radiation is the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves. It does not require any medium and can travel through a vacuum. The sun emits heat through radiation.
Effects of Heat: Heat has various effects on objects and substances.
a. Expansion and Contraction: When objects are heated, they expand, and when they are cooled, they contract. This property is utilized in various applications, such as the functioning of thermometers and bimetallic strips.
b. Change of State: Heat causes changes in the state of matter. Adding heat to a solid can melt it into a liquid, and adding more heat can turn the liquid into a gas. The reverse processes, such as condensation and freezing, also occur due to the removal of heat.
c. Evaporation: Evaporation is the process in which a liquid changes into a gas at its surface, even at temperatures below its boiling point. Heat is absorbed during evaporation.
d. Effects on Substances: Heat can cause chemical reactions, such as burning or decomposition. It can also change the physical properties of substances, such as color, texture, or taste.
Heat and Temperature: Heat and temperature are related but different concepts. Heat is the energy transferred from a hotter object to a colder object, while temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles of a substance.
This summary provides an overview of the key concepts covered in Chapter 4 of the NCERT Class 7 Science textbook, "Heat."
#ncert #class7 #science #heat #exam #exammotivation #exampreparation #learneverything #india #cbse #chapter #keepitsimple
Комментарии
 0:37:42
0:37:42
 0:08:32
0:08:32
 0:08:33
0:08:33
 0:02:53
0:02:53
 0:53:26
0:53:26
 0:03:25
0:03:25
 0:06:34
0:06:34
 0:04:15
0:04:15
 0:27:48
0:27:48
 0:49:37
0:49:37
 0:25:30
0:25:30
 0:08:19
0:08:19
 0:47:47
0:47:47
 0:08:30
0:08:30
 0:23:34
0:23:34
 0:40:25
0:40:25
 0:06:42
0:06:42
 0:02:05
0:02:05
 0:02:09
0:02:09
 0:24:17
0:24:17
 0:51:12
0:51:12
 0:08:38
0:08:38
 0:37:44
0:37:44
 0:45:46
0:45:46