filmov
tv
Market Structures

Показать описание
Market structures refer to the organizational characteristics of markets, which determine the behavior of firms operating within them and the outcomes for consumers and society. There are several types of market structures, each with unique features and implications:
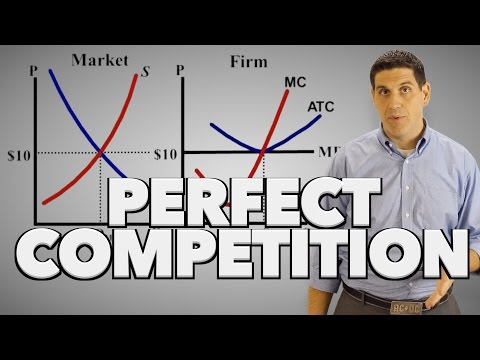
Perfect Competition: In perfect competition, there are many buyers and sellers, homogeneous products, free entry and exit, and perfect information. Firms are price takers, meaning they have no control over the price of their product, which is determined by market forces. Examples include agricultural markets and some commodity markets.
Monopoly: A monopoly exists when there is only one seller in the market, selling a unique product with no close substitutes. Monopolies have significant market power, allowing them to set prices higher than in competitive markets. Governments often regulate monopolies to prevent abuse of market power and protect consumers.
Monopolistic Competition: Monopolistic competition is characterized by many firms selling differentiated products. Each firm has some degree of market power, allowing them to set prices slightly above marginal cost. Product differentiation and non-price competition, such as advertising and branding, are common strategies in monopolistically competitive markets.
Oligopoly: An oligopoly occurs when a few large firms dominate the market, selling either homogeneous or differentiated products. These firms have significant market power and may engage in strategic behavior, such as price-fixing or collusion, to maximize profits. Oligopolistic markets often exhibit interdependence, where firms' decisions are influenced by the actions of their competitors.
Monopsony: In a monopsony, there is only one buyer in the market, facing many sellers. This situation can lead to lower prices for suppliers and reduced output compared to a competitive market. Examples include large retailers with significant purchasing power.
Understanding market structures is essential for analyzing firm behavior, market outcomes, and the effectiveness of public policies aimed at promoting competition and consumer welfare. Each market structure has its advantages and disadvantages, and policymakers must consider these factors when designing regulations and interventions to ensure efficient and equitable outcomes in markets.
Contact us on Social Media
==========================
👇👇 Subscribe For More Videos 👇👇
Peace ♥
#jceconomics #alevel #aleveleconomics #alevels #cambridge #sgparents #sgtuition #sgeconomics #juniorcollege #igcse #igcseeconomics
Perfect Competition: In perfect competition, there are many buyers and sellers, homogeneous products, free entry and exit, and perfect information. Firms are price takers, meaning they have no control over the price of their product, which is determined by market forces. Examples include agricultural markets and some commodity markets.
Monopoly: A monopoly exists when there is only one seller in the market, selling a unique product with no close substitutes. Monopolies have significant market power, allowing them to set prices higher than in competitive markets. Governments often regulate monopolies to prevent abuse of market power and protect consumers.
Monopolistic Competition: Monopolistic competition is characterized by many firms selling differentiated products. Each firm has some degree of market power, allowing them to set prices slightly above marginal cost. Product differentiation and non-price competition, such as advertising and branding, are common strategies in monopolistically competitive markets.
Oligopoly: An oligopoly occurs when a few large firms dominate the market, selling either homogeneous or differentiated products. These firms have significant market power and may engage in strategic behavior, such as price-fixing or collusion, to maximize profits. Oligopolistic markets often exhibit interdependence, where firms' decisions are influenced by the actions of their competitors.
Monopsony: In a monopsony, there is only one buyer in the market, facing many sellers. This situation can lead to lower prices for suppliers and reduced output compared to a competitive market. Examples include large retailers with significant purchasing power.
Understanding market structures is essential for analyzing firm behavior, market outcomes, and the effectiveness of public policies aimed at promoting competition and consumer welfare. Each market structure has its advantages and disadvantages, and policymakers must consider these factors when designing regulations and interventions to ensure efficient and equitable outcomes in markets.
Contact us on Social Media
==========================
👇👇 Subscribe For More Videos 👇👇
Peace ♥
#jceconomics #alevel #aleveleconomics #alevels #cambridge #sgparents #sgtuition #sgeconomics #juniorcollege #igcse #igcseeconomics
 0:01:04
0:01:04
 0:05:57
0:05:57
 0:12:42
0:12:42
 0:04:50
0:04:50
 0:27:55
0:27:55
 0:12:26
0:12:26
 0:12:55
0:12:55
 0:07:14
0:07:14
 1:40:59
1:40:59
 0:14:49
0:14:49
 0:08:25
0:08:25
 1:04:41
1:04:41
 0:11:03
0:11:03
 0:22:20
0:22:20
 0:14:05
0:14:05
 0:19:06
0:19:06
 0:40:44
0:40:44
 0:13:06
0:13:06
 0:07:43
0:07:43
 0:10:17
0:10:17
 0:29:31
0:29:31
 0:29:59
0:29:59
 0:13:44
0:13:44
 0:07:32
0:07:32