filmov
tv
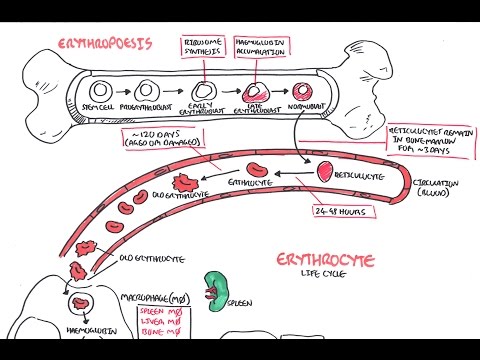
Erythropoiesis

Показать описание
Erythropoiesis
Dr Vitthal Khode MBBS, MD, (PhD), FWRA
Erythropoiesis
There are three stages of erythropoiesis
Mesoblastic,
Hepatic and
Medullary
Steps of Erythropoiesis
There are four major cell-stages or steps of erythropoiesis:
Stem cells,
Progenitor cells,
Precursor cells and
Mature cells
In general, during erythropoiesis, following cellular changes take place:
Cell size progressively reduces.
Size of nucleus and number of nucleoli decreases, chromatin material condenses and finally nucleus disappears.
Staining reaction of cytoplasm changes from deep basophilic to polychromatophillic (acidophilic plus basophilic) and finally to acidophilic type. This occurs mainly due to gradual reduction in quantity of RNA material.
Stem Cells
Pluripotent Stem Cells
Committed Stem Cell
Erythroid stem cells give rise to progenitor cells for erythroid cell lines. There are two progenitor cells: BFU-E and CFU-E
Progenitor Cells
There are two types of progenitor cells:
1) BFU-E and
2) CFU-E.
The BFU-E and CFU-E develop from a common progenitor CFU-Mg/E.
Precursor Cells
Normoblasts: Early, Intermediate and Late
Pronormoblast
Early Normoblast (Basophilic Erythroblast)
Intermediate Normoblast (Polychromatic Erythroblast)
Late Normoblast (Orthochromatic Erythroblast)
Mature Cells
Reticulocytes
Duration of Erythropoiesis
REGULATION OF ERYTHROPOIESIS
Feedback Controls
The Functional Feedback
The End-Product Feedback
Factors Controlling Erythropoiesis
The factors controlling erythropoiesis can broadly be divided into three categories:
Hormonal,
Dietary and others
Hormonal Factors
Erythropoietin
Other Factors
Intrinsic factor
Environmental Factors
Drugs and Chemicals
Effective vs. Ineffective Erythropoiesis
RETICULOCYTES
Reticulocyte Response
Reticulocytosis
Reticulocytopenia
Leuco-erythroblastic Reaction
Reticulocyte Index
Blood plasma proteins
Red blood cells
Erythropoiesis
Fate of RBC
Anemia polycythemia
Blood group 1
Blood group 2
Leucopoiesis
White blood cells
Cell mediated immunity
Humoral immunity
Applied immunity
Hemostasis
Platelet functions
Clotting factors
Blood coagulation
Anticoagulants- applied
#VKPhysiologyclasses #physiology #medical #erythropoiesis #nursing
Dr Vitthal Khode MBBS, MD, (PhD), FWRA
Erythropoiesis
There are three stages of erythropoiesis
Mesoblastic,
Hepatic and
Medullary
Steps of Erythropoiesis
There are four major cell-stages or steps of erythropoiesis:
Stem cells,
Progenitor cells,
Precursor cells and
Mature cells
In general, during erythropoiesis, following cellular changes take place:
Cell size progressively reduces.
Size of nucleus and number of nucleoli decreases, chromatin material condenses and finally nucleus disappears.
Staining reaction of cytoplasm changes from deep basophilic to polychromatophillic (acidophilic plus basophilic) and finally to acidophilic type. This occurs mainly due to gradual reduction in quantity of RNA material.
Stem Cells
Pluripotent Stem Cells
Committed Stem Cell
Erythroid stem cells give rise to progenitor cells for erythroid cell lines. There are two progenitor cells: BFU-E and CFU-E
Progenitor Cells
There are two types of progenitor cells:
1) BFU-E and
2) CFU-E.
The BFU-E and CFU-E develop from a common progenitor CFU-Mg/E.
Precursor Cells
Normoblasts: Early, Intermediate and Late
Pronormoblast
Early Normoblast (Basophilic Erythroblast)
Intermediate Normoblast (Polychromatic Erythroblast)
Late Normoblast (Orthochromatic Erythroblast)
Mature Cells
Reticulocytes
Duration of Erythropoiesis
REGULATION OF ERYTHROPOIESIS
Feedback Controls
The Functional Feedback
The End-Product Feedback
Factors Controlling Erythropoiesis
The factors controlling erythropoiesis can broadly be divided into three categories:
Hormonal,
Dietary and others
Hormonal Factors
Erythropoietin
Other Factors
Intrinsic factor
Environmental Factors
Drugs and Chemicals
Effective vs. Ineffective Erythropoiesis
RETICULOCYTES
Reticulocyte Response
Reticulocytosis
Reticulocytopenia
Leuco-erythroblastic Reaction
Reticulocyte Index
Blood plasma proteins
Red blood cells
Erythropoiesis
Fate of RBC
Anemia polycythemia
Blood group 1
Blood group 2
Leucopoiesis
White blood cells
Cell mediated immunity
Humoral immunity
Applied immunity
Hemostasis
Platelet functions
Clotting factors
Blood coagulation
Anticoagulants- applied
#VKPhysiologyclasses #physiology #medical #erythropoiesis #nursing
Комментарии
 0:04:51
0:04:51
 0:29:51
0:29:51
 0:08:58
0:08:58
 0:09:33
0:09:33
 0:06:04
0:06:04
 0:19:28
0:19:28
 0:11:07
0:11:07
 0:20:12
0:20:12
 0:17:46
0:17:46
 0:06:14
0:06:14
 0:04:06
0:04:06
 0:16:44
0:16:44
 0:17:22
0:17:22
 0:03:01
0:03:01
 0:06:26
0:06:26
 0:08:40
0:08:40
 0:04:15
0:04:15
 0:17:48
0:17:48
 0:04:45
0:04:45
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:16:18
0:16:18
 0:00:11
0:00:11
 0:22:33
0:22:33
 0:03:34
0:03:34